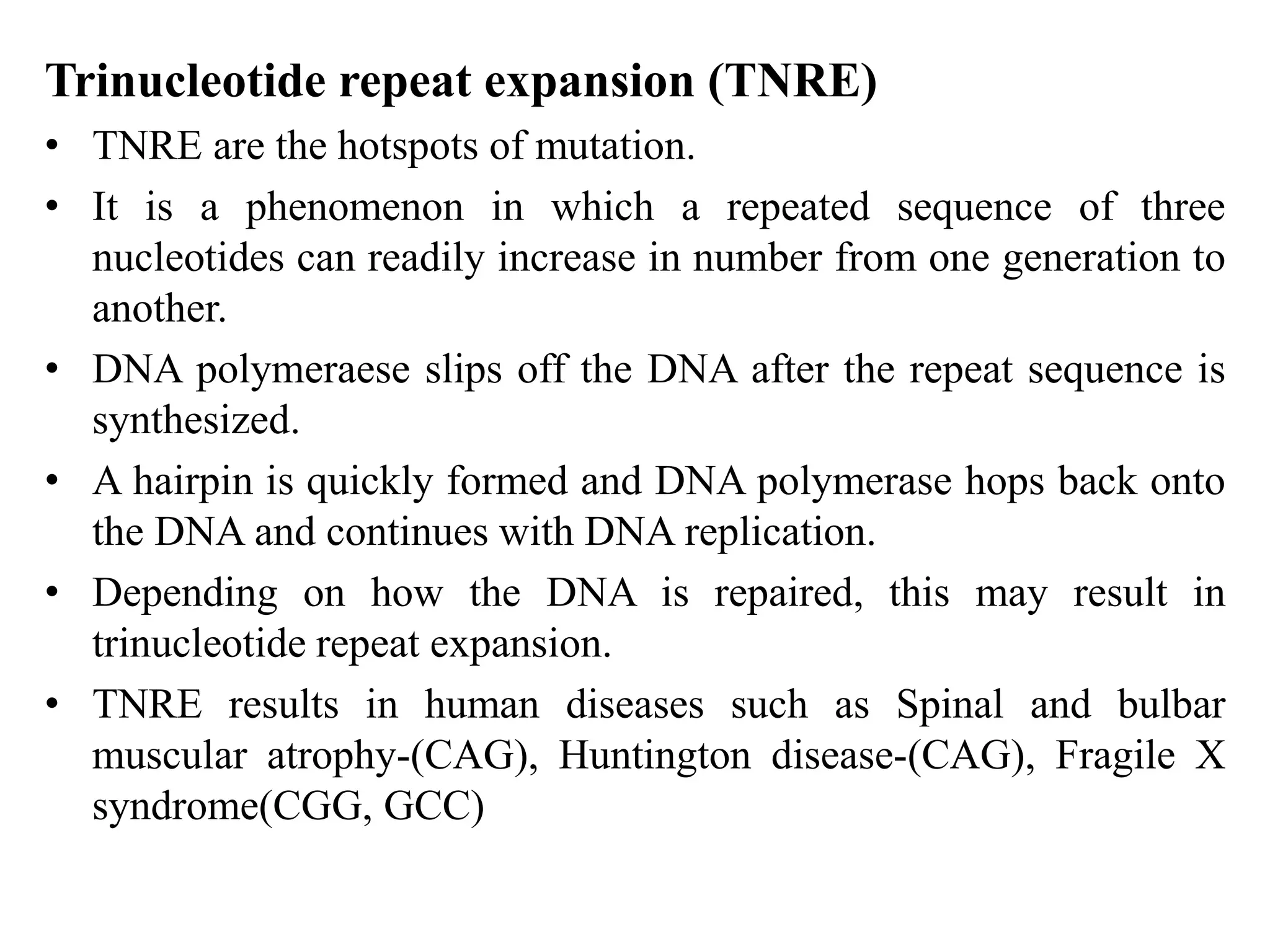
Spontaneous mutations occur naturally without an apparent cause, primarily arising from errors in DNA replication, spontaneous lesions, and transposable genetic elements. These mutations can lead to various human diseases and result from mechanisms such as tautomeric shifts, insertion and deletion of nucleotides, and oxidative damage. The document discusses the underlying processes that contribute to mutations, including specific examples and their implications in genetics.