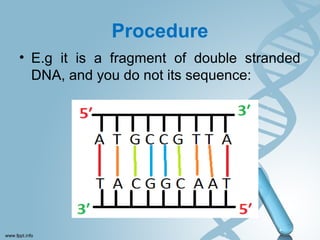
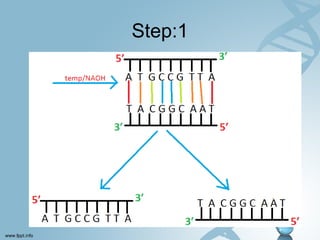
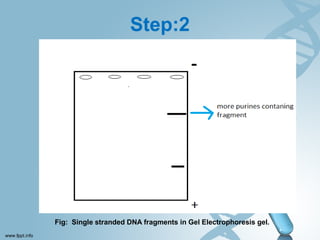
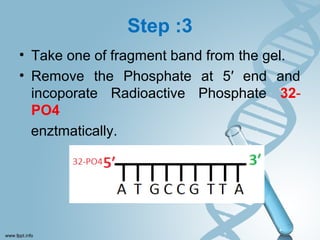
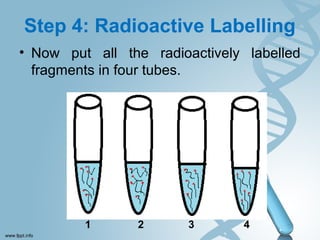
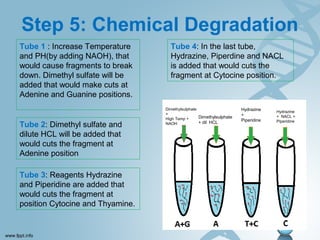
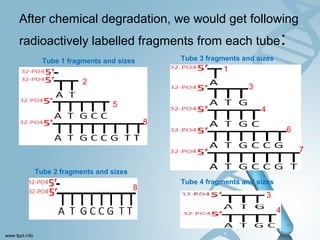
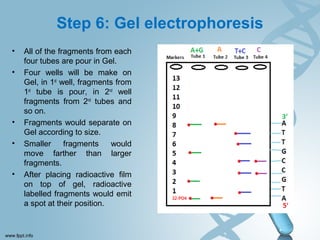
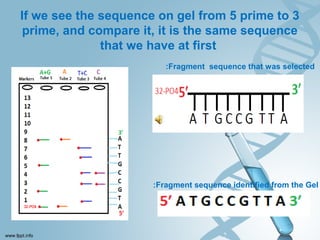
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing uses chemicals to cut DNA fragments at specific bases, allowing the sequence to be determined. It involves separating DNA strands, radioactively labeling one, then breaking it up in four reactions that specifically cleave at adenine, cytosine, guanine, or thymine. The labeled fragments are run on a gel and their sizes reveal the sequence. Though it directly sequences DNA without cloning, it uses toxic chemicals and radioactivity, has a short read length, and is technically complex.