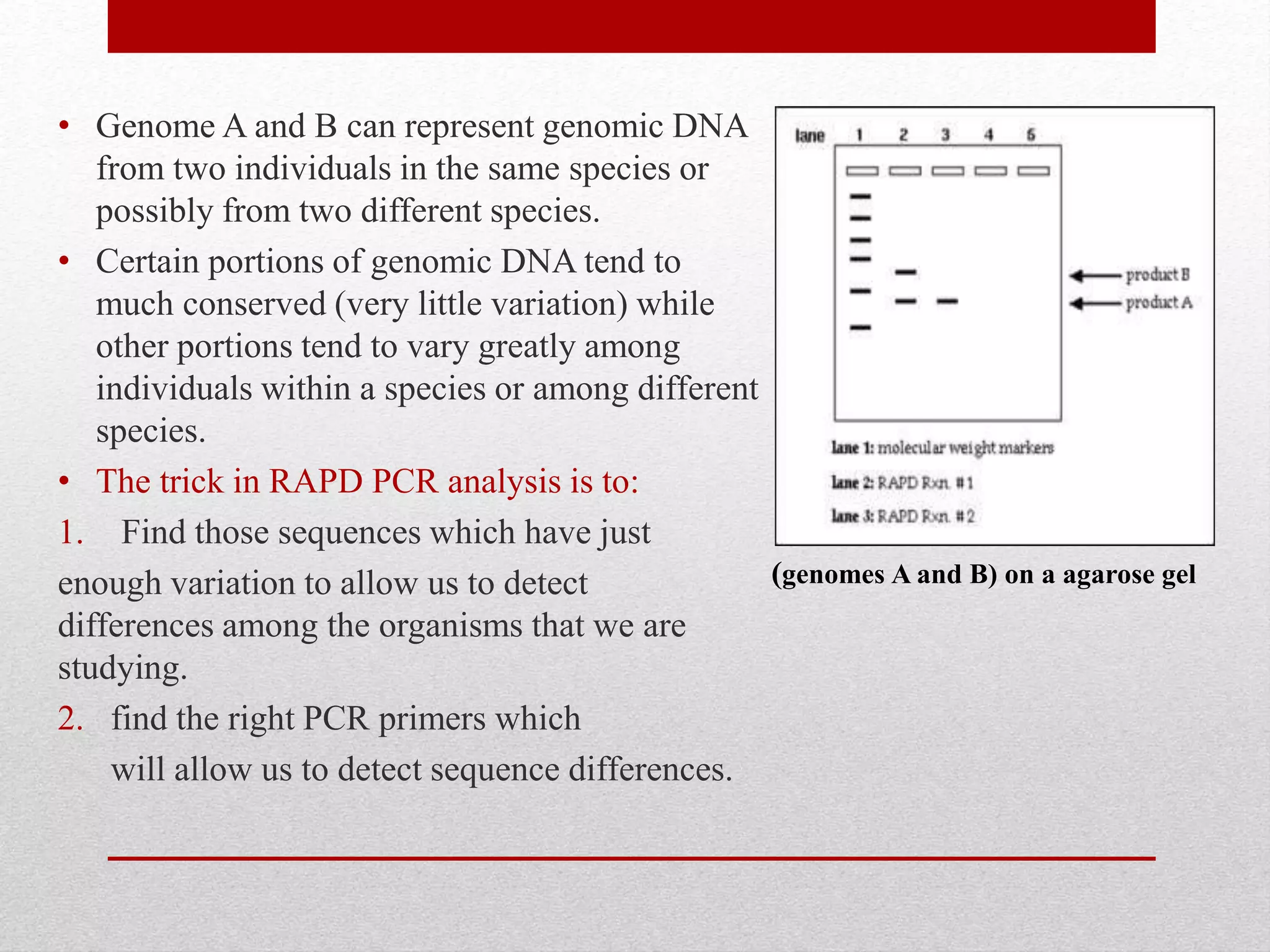
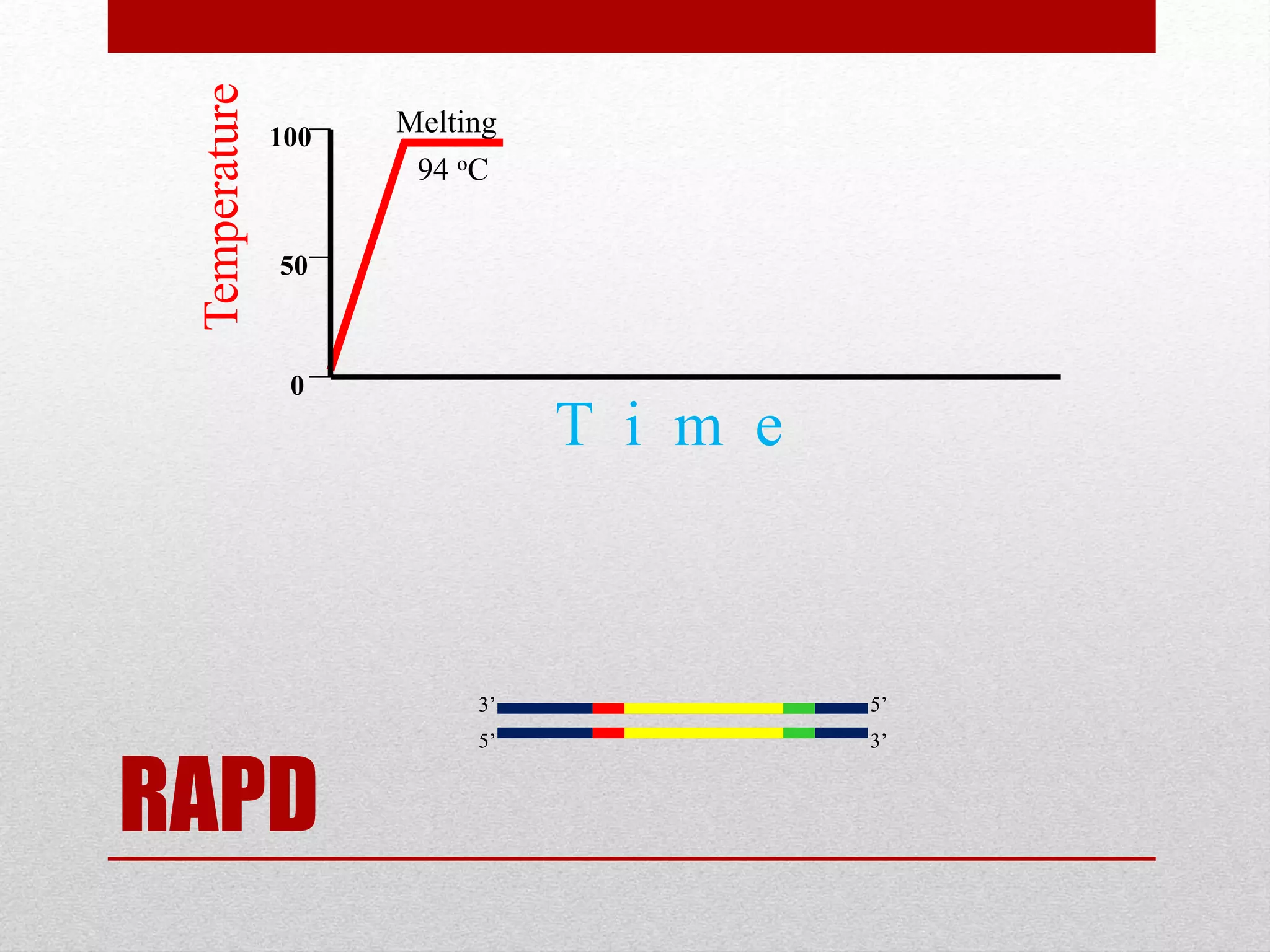
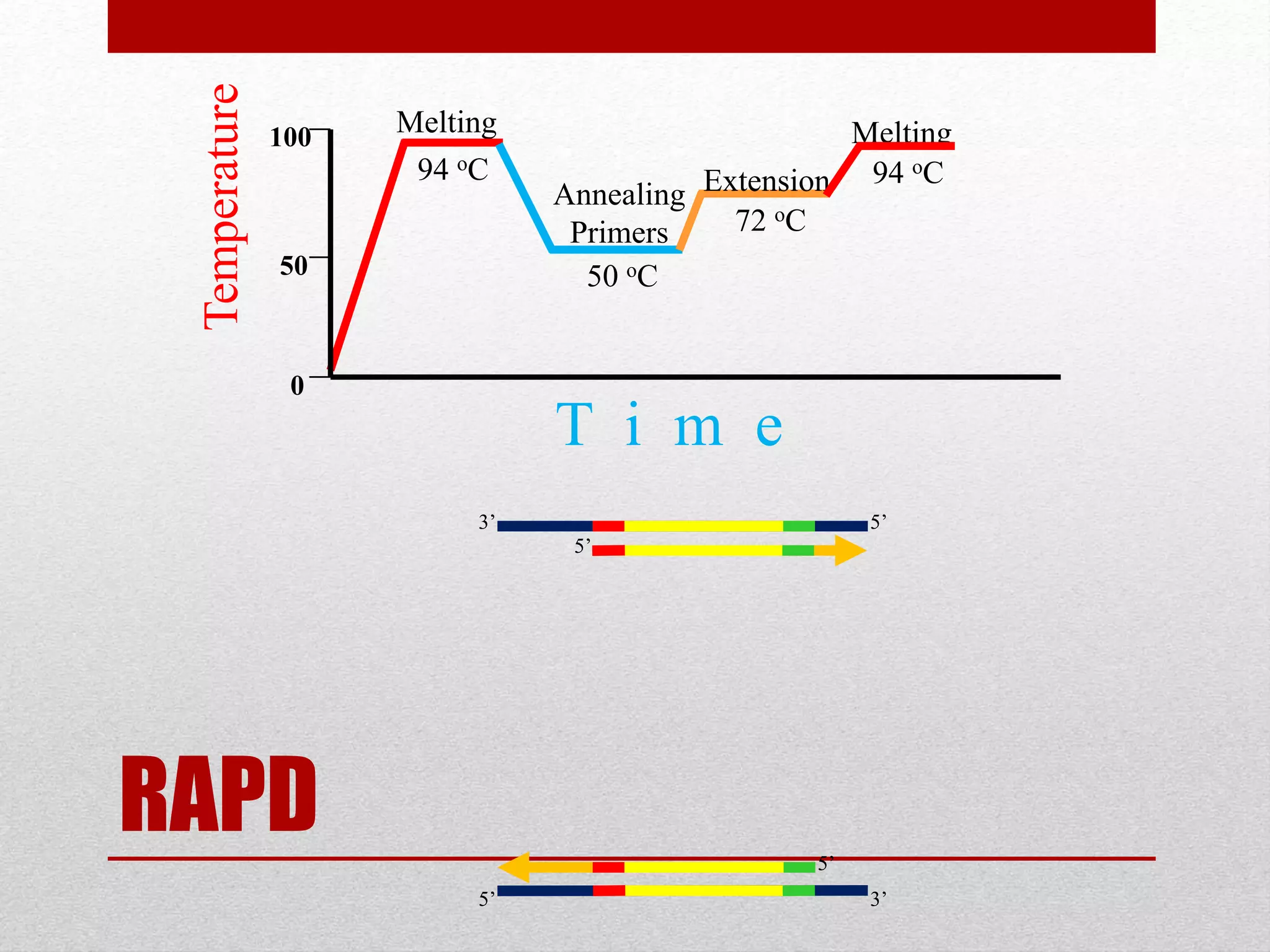
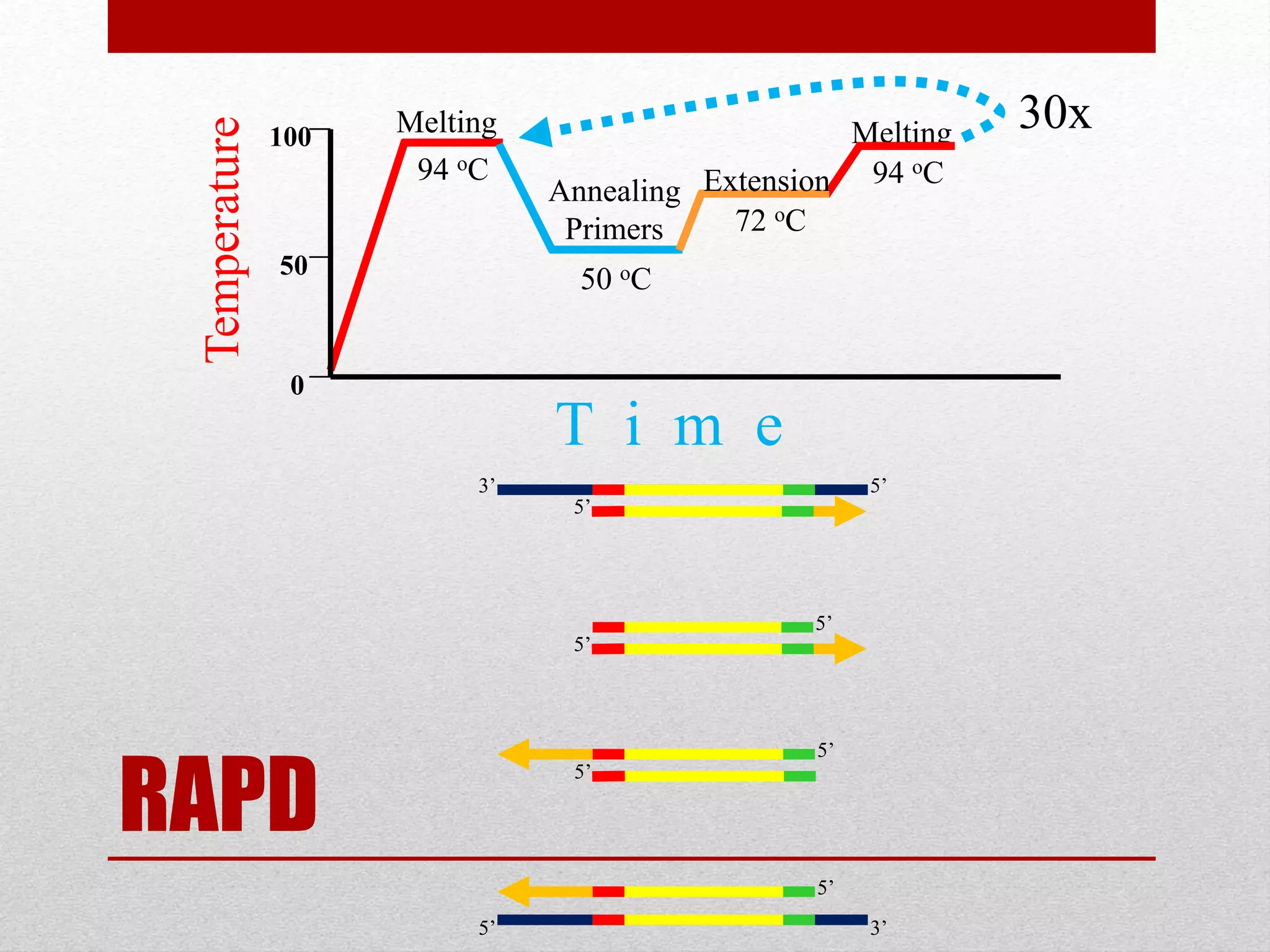
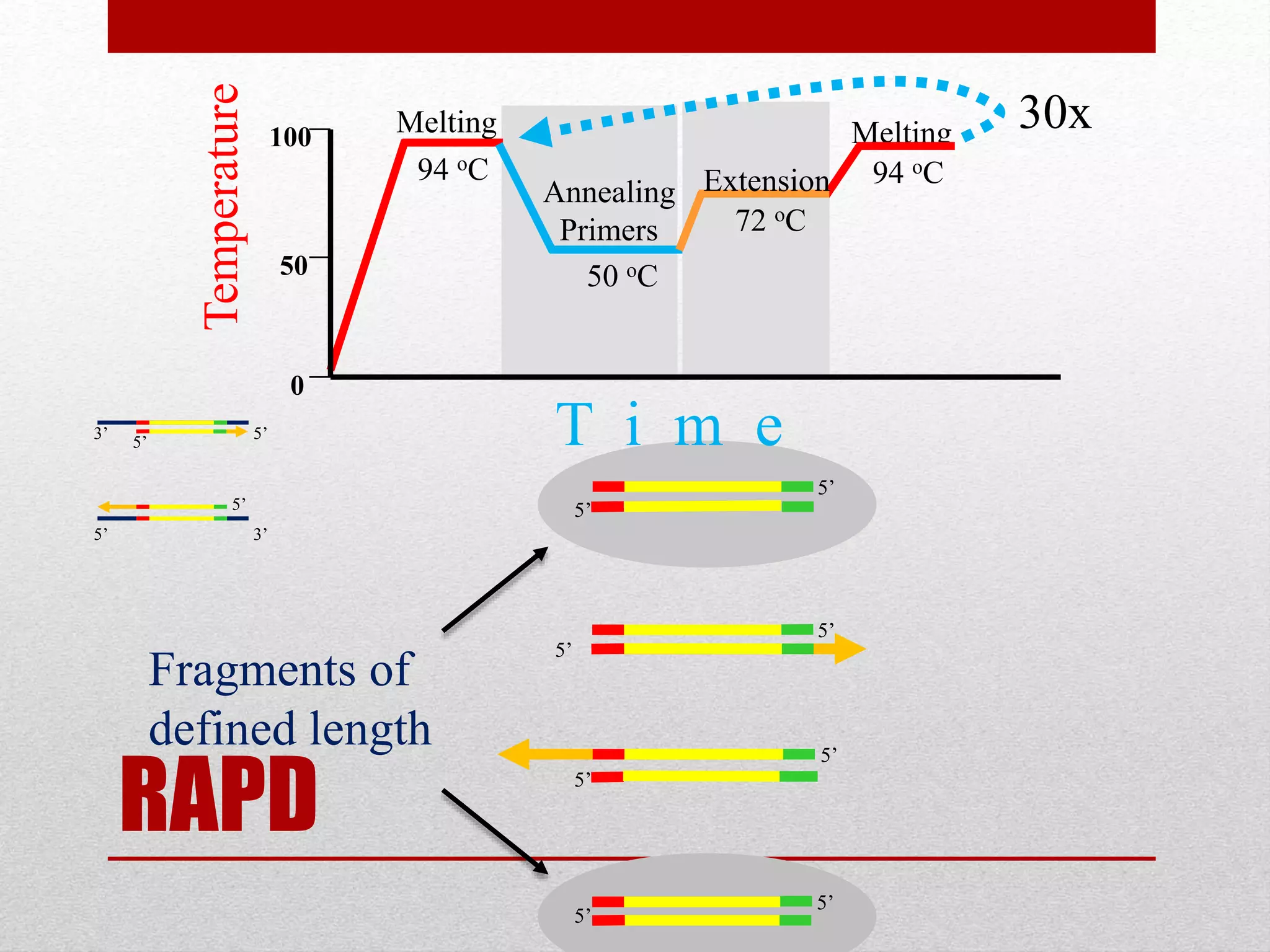
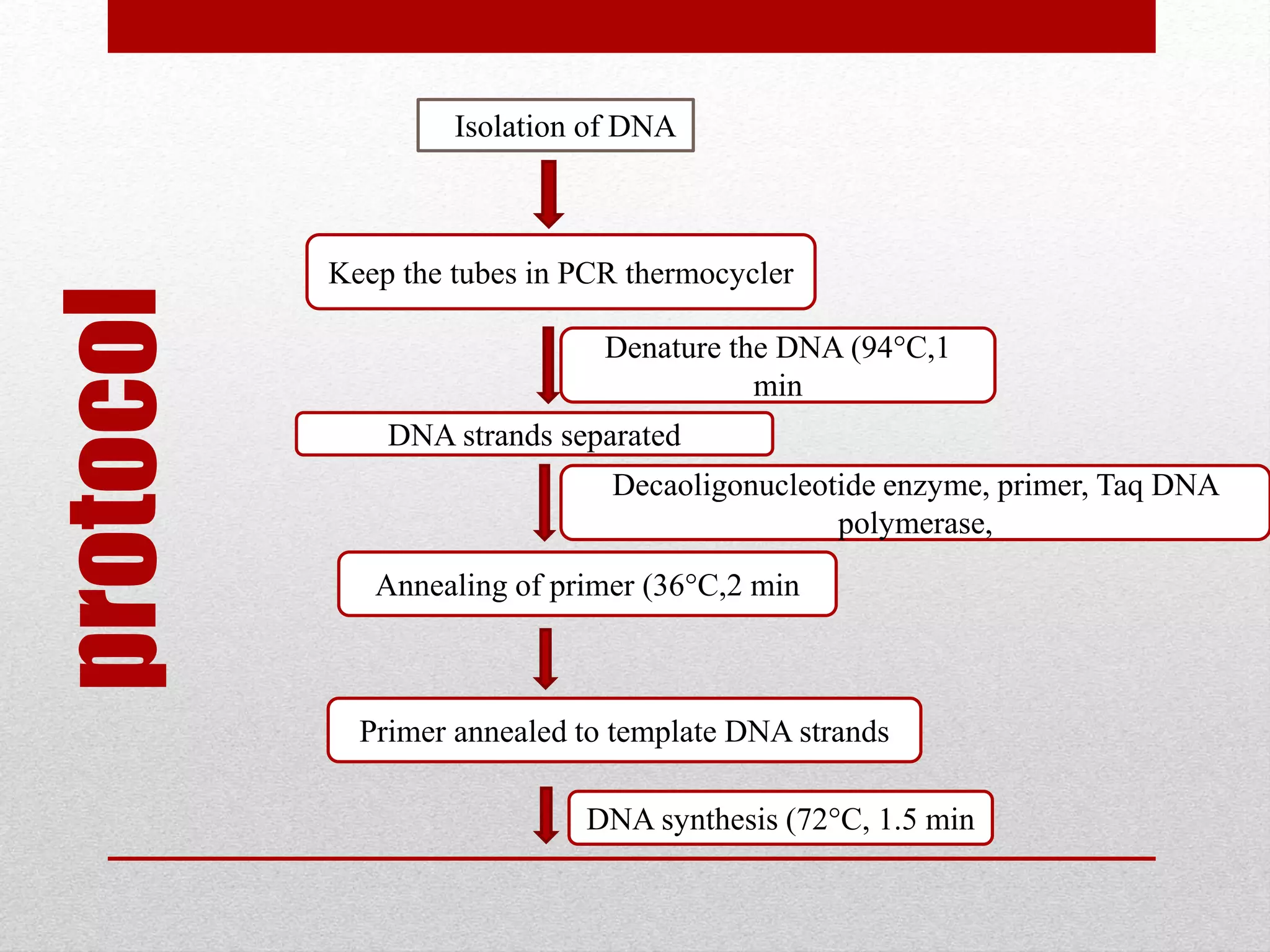
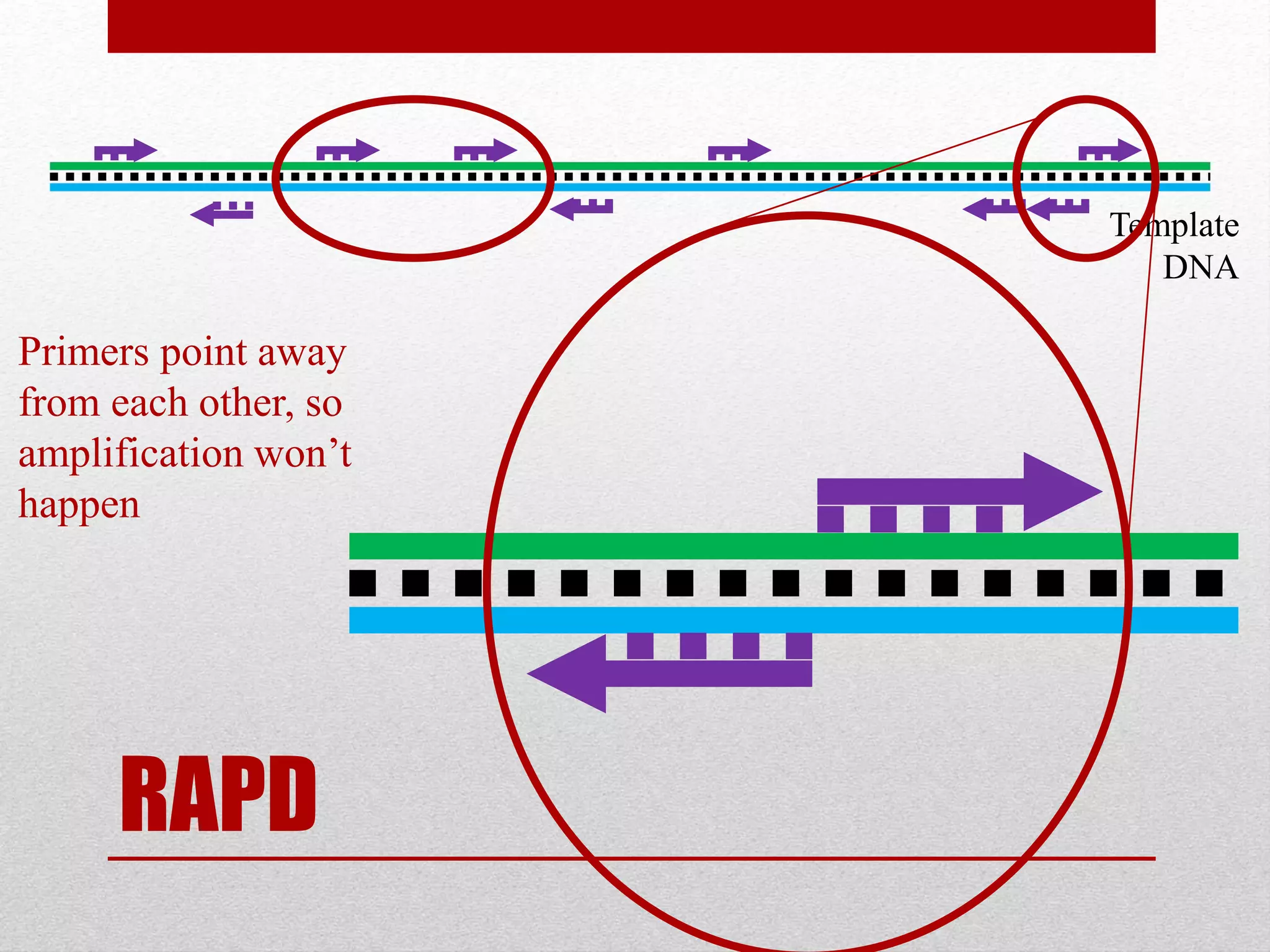
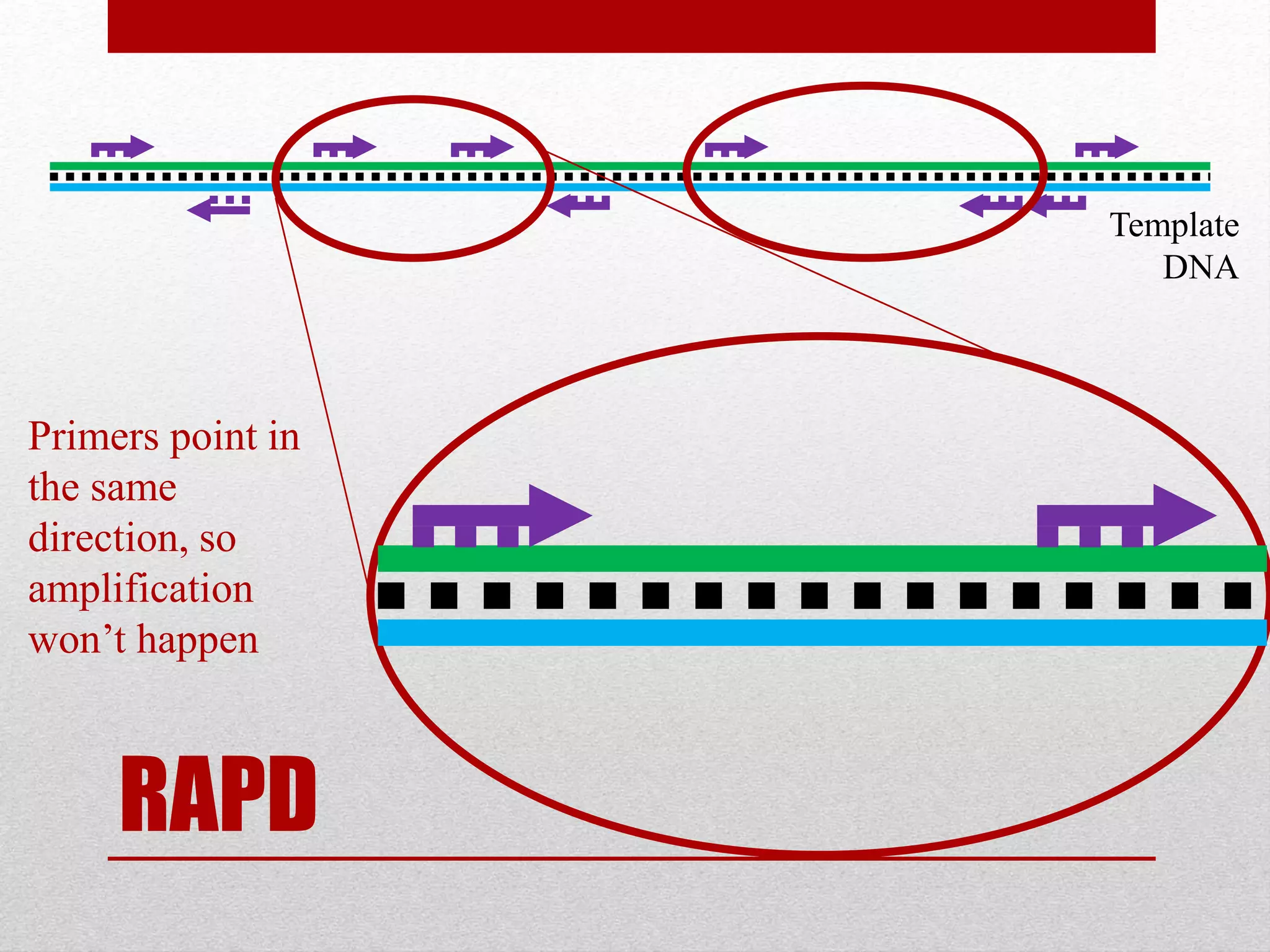
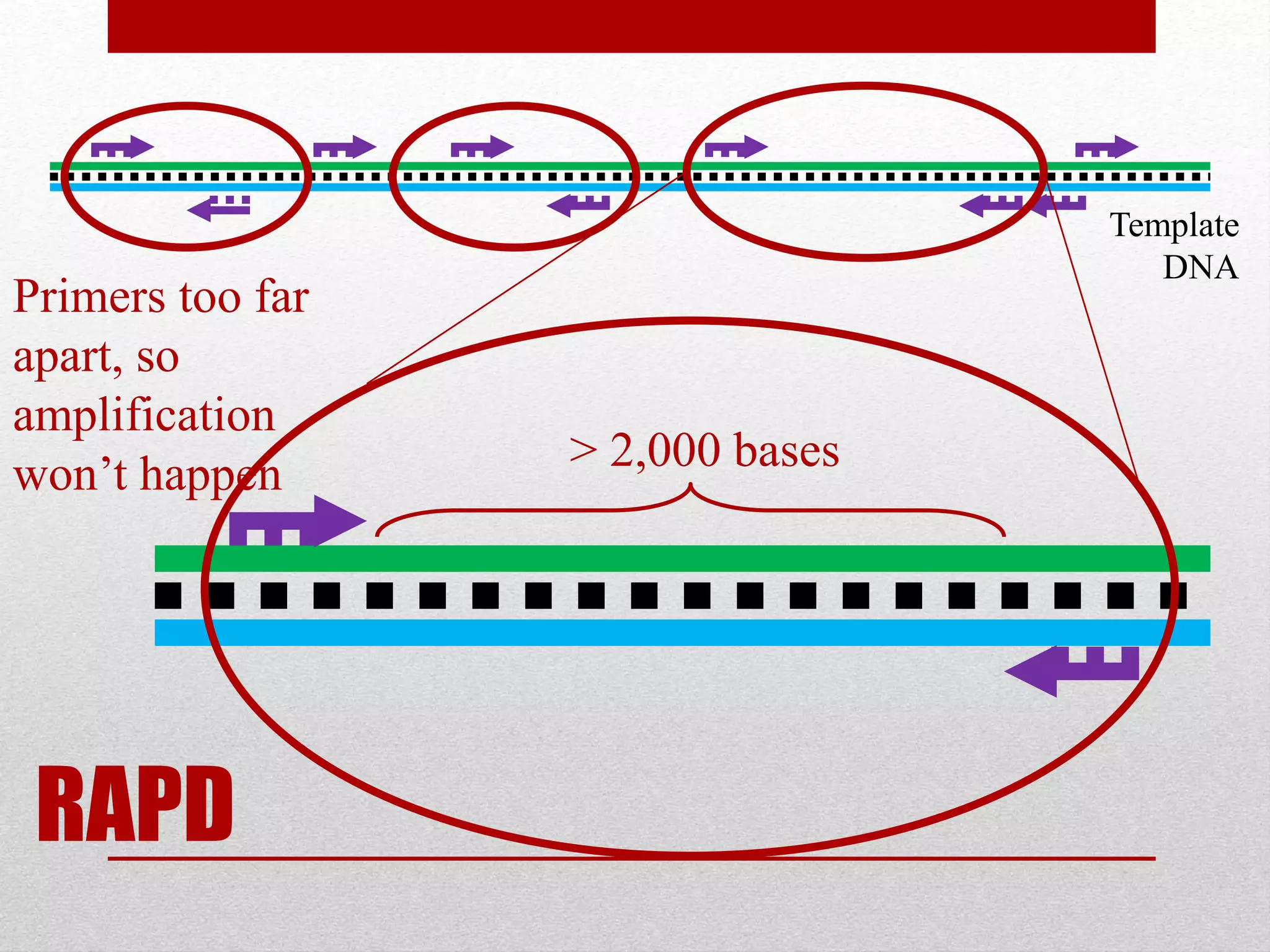
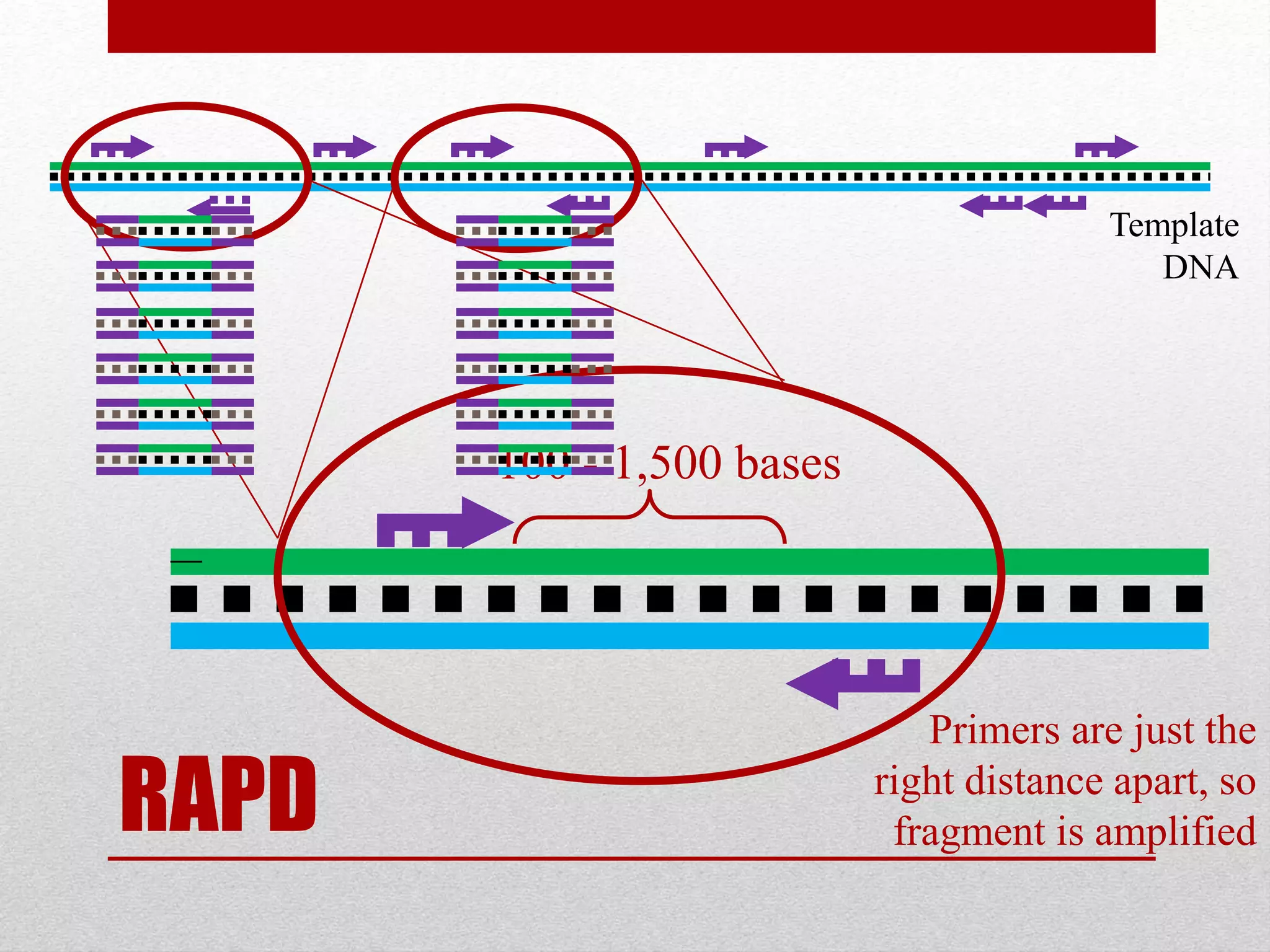
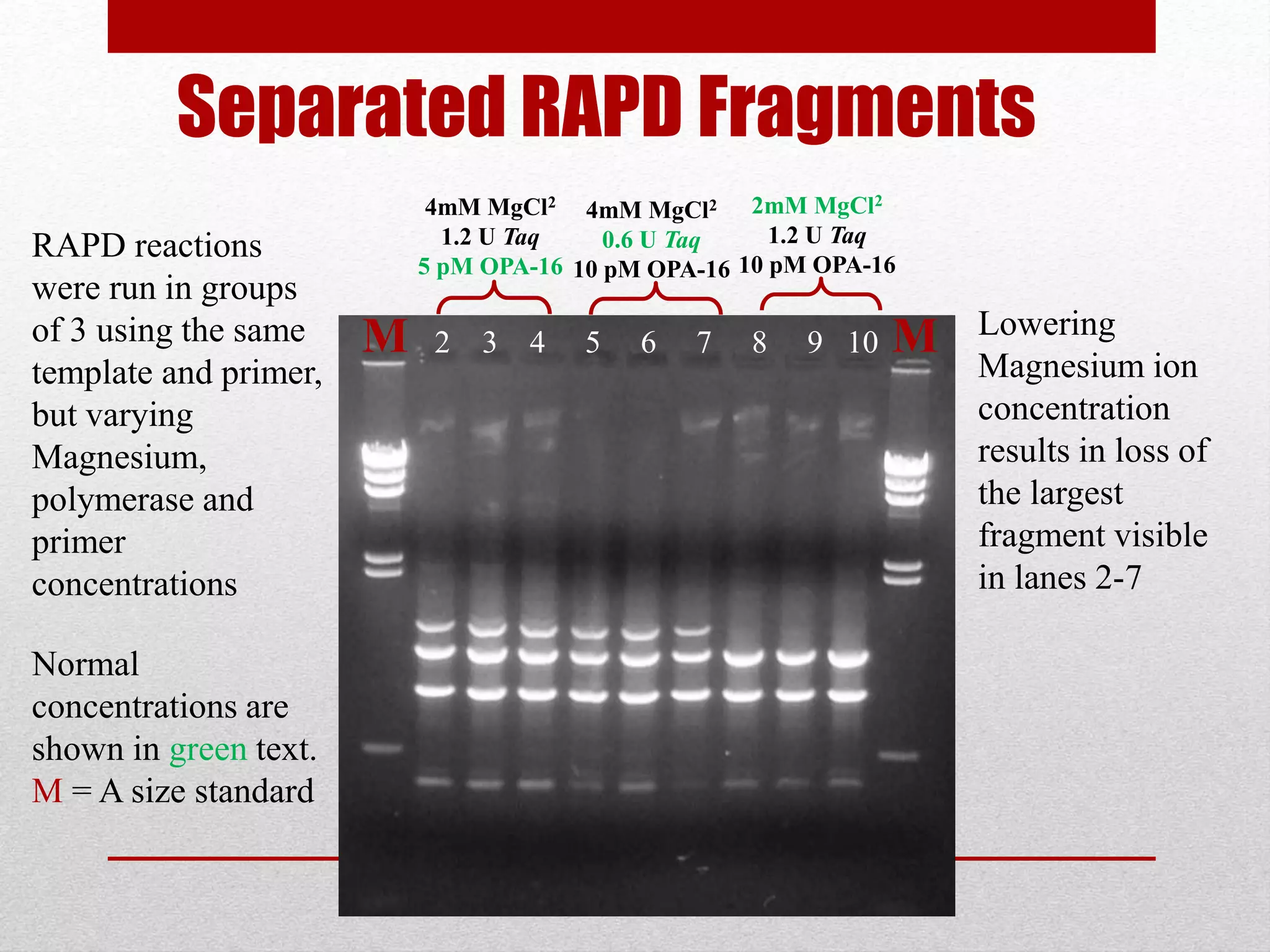
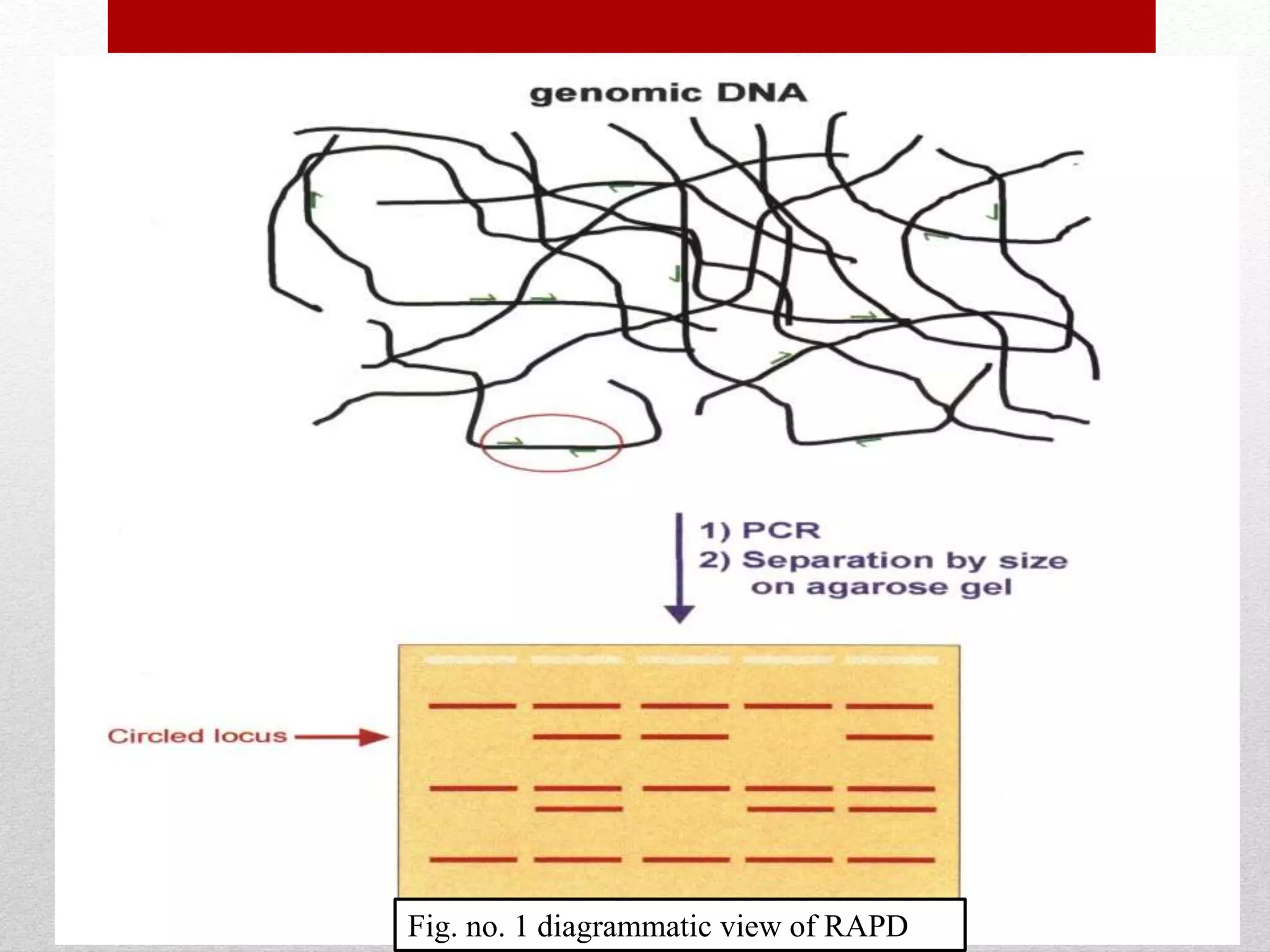
The document discusses RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA) as a technique for amplifying random DNA segments using short primers, allowing for genetic analysis without prior knowledge of DNA sequences. It outlines the procedure, advantages, and disadvantages of RAPD along with its applications in genetic diversity, genome mapping, and breeding. Additionally, it concludes that despite reproducibility issues, RAPD remains a valuable method due to its efficiency and low cost.