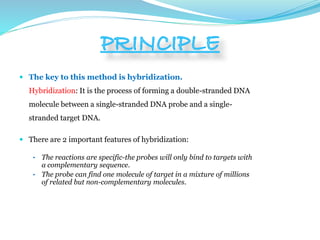
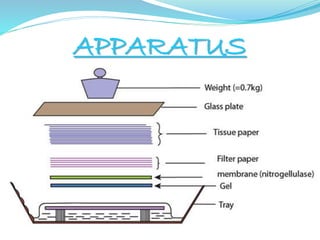
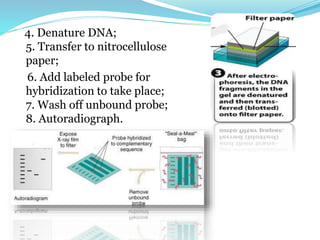
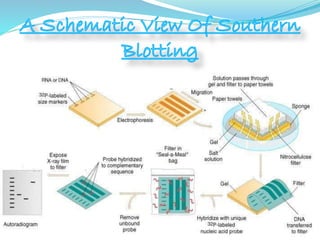
Southern blotting is a technique used to detect specific DNA sequences in a DNA sample. It involves extracting DNA from cells, cutting the DNA into fragments using restriction enzymes, separating the fragments via gel electrophoresis, transferring the DNA fragments to a membrane, and using a labeled probe to detect fragments that are complementary to the probe through hybridization. Southern blotting is useful for identifying mutations, DNA fingerprinting, and detecting DNA in applications like prenatal screening and forensics. While effective for detecting specific DNA sequences, it is a complex, time-consuming, and labor-intensive technique.