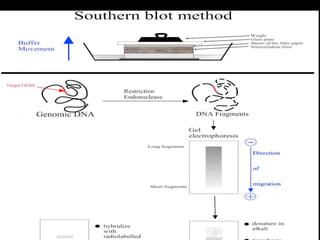
The document discusses various techniques for DNA hybridization including Southern, Northern, Western, dot, and colony hybridization. Southern hybridization involves immobilizing DNA on a membrane, adding a labeled probe, and detecting hybridization to identify DNA sequences. Factors like stringency affect specificity. Northern hybridization identifies RNA using DNA probes. Western blotting identifies proteins using antibodies or lectins as probes. Dot and colony blotting modify Southern and Northern techniques to detect DNA or RNA from multiple samples immobilized on membranes.