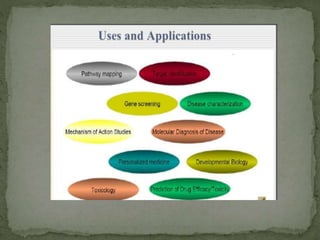
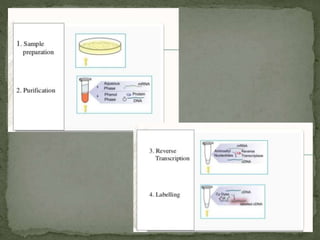
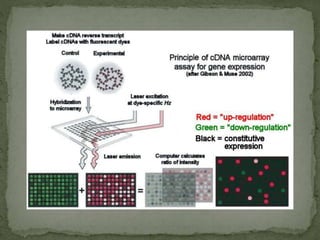
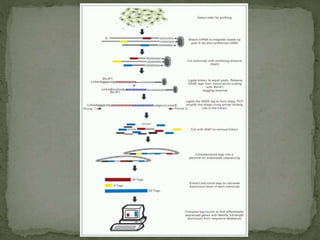
Gene expression can be analyzed using techniques like microarrays and SAGE. A microarray uses DNA probes attached to a solid surface to detect gene sequences via hybridization. SAGE involves isolating mRNA, ligating linkers, and sequencing short tag sequences to profile overall gene expression patterns in a quantitative way. Microarrays and SAGE are useful for applications like gene discovery, disease diagnosis, and analyzing differences in gene expression between cell types.