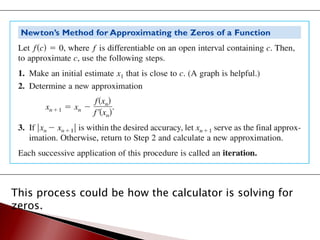
This document summarizes Newton's method, an iterative process for finding approximations of the zeroes of a function. It works by using tangent lines to get better approximations with each iteration. The method starts with an initial guess x1 and calculates successive approximations x2, x3, etc. by finding the x-intercept of the tangent line at the previous point. If the approximations converge to a limit, Newton's method has found a zero of the function. The document provides examples of functions where Newton's method does and does not converge.

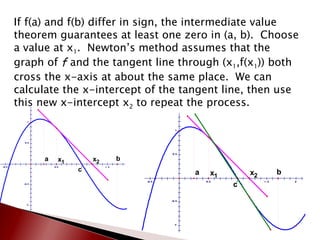
![This method, named Newton’s Method, uses tangent lines to approximate the value of the x-intercepts of a function. Consider a function that is continuous on interval [a, b]. If the graph crosses the x-axis somewhere between a and b, or in other words, if f(a) and f(b) are different signs, then a tangent line crosses the x-axis at about the same location as the actual x-intercept of f .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calc3-8-111215011806-phpapp02/85/Calc-3-8-2-320.jpg)