This document defines and provides examples of different types of matrices:
- Matrices are arrangements of elements in rows and columns represented by symbols.
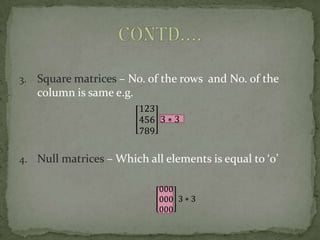
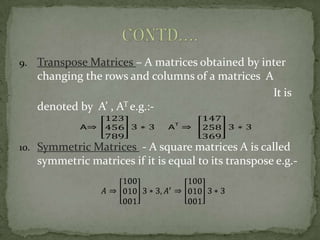
- Types include row matrices, column matrices, square matrices, null matrices, identity matrices, diagonal matrices, scalar matrices, triangular matrices, transpose matrices, symmetric matrices, skew matrices, equal matrices, and algebraic matrices.
- Algebraic matrix operations include addition, subtraction, and multiplication where the matrices must be of the same order.


![1. Row matrices – A matrices which has only one row
called row matrices e.g.-
[123]1*3
2. Column matrices – A matrices which has only one
column is called column matrices e.g. –](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-130323092558-phpapp02/85/presentation-on-matrix-3-320.jpg)