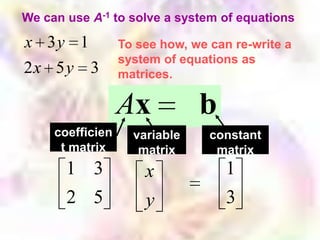
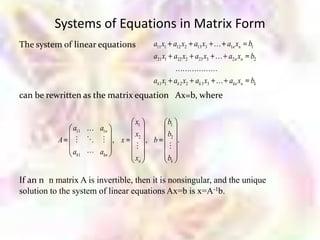
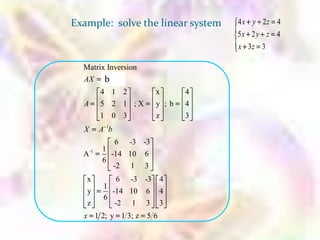
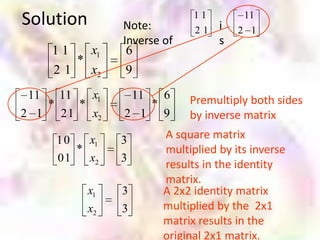
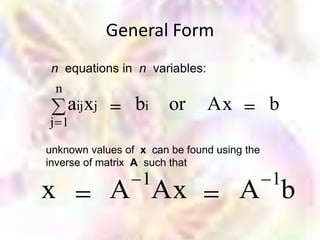
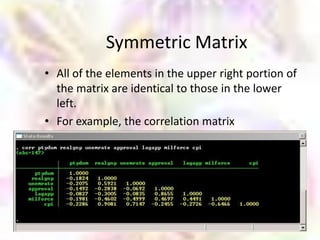
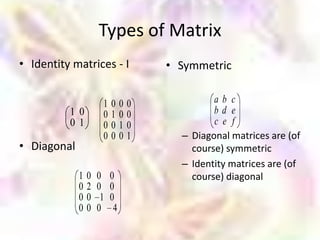
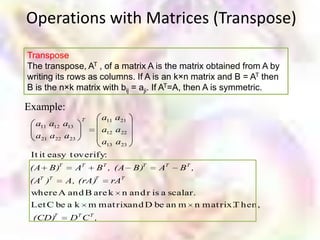
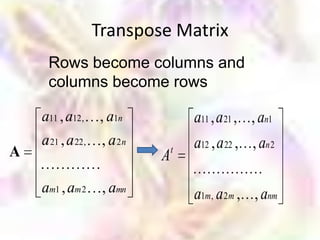
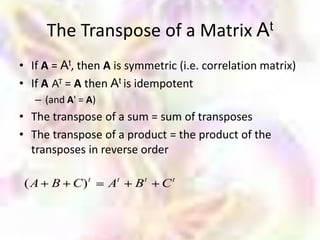
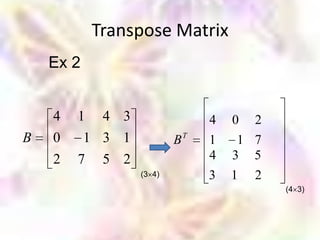
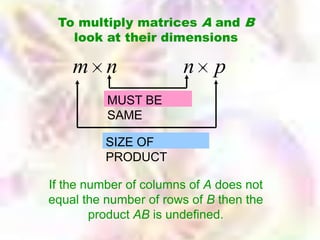
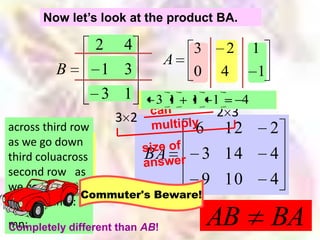
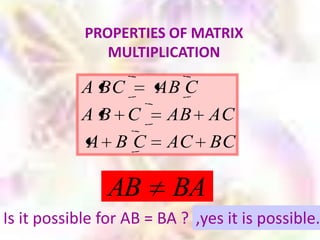
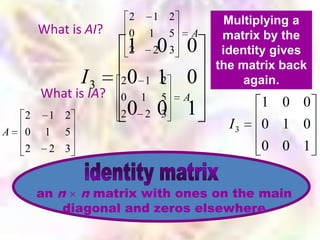
Matrix algebra allows expressing large numbers of calculations on ordered sets of numbers. A matrix is an array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. Common matrix operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and transposition. Matrix multiplication requires the number of columns in the first matrix to equal the number of rows in the second matrix. Special matrices include identity, diagonal, symmetric, null, and square matrices.






![Definitions - scalar
• scalar - a number
– denoted with regular type as is scalar algebra
– [1] or [a]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-7-320.jpg)

![Row Vector
[1 x n] matrix
A a1 a2 , , an aj](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-9-320.jpg)
![Column Vector
[m x 1] matrix
a1
a2
A ai
am](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-10-320.jpg)


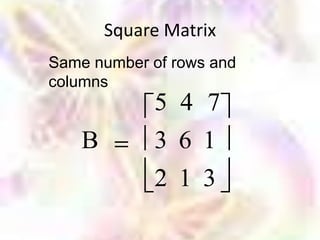






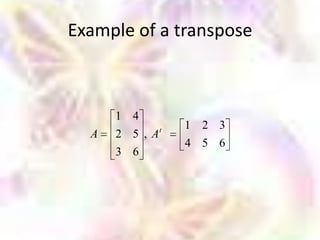
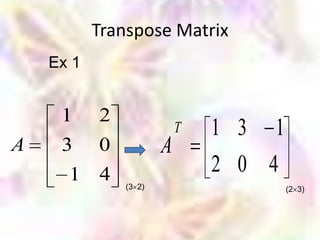

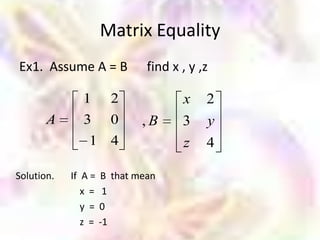



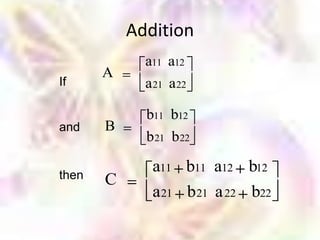








![Matrix Multiplication
Matrices A and B have these dimensions:
[r x c] and [s x d]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-49-320.jpg)
![Matrix Multiplication
Matrices A and B can be multiplied if:
[r x c] and [s x d]
c=s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-50-320.jpg)
![Matrix Multiplication
The resulting matrix will have the dimensions:
[r x c] and [s x d]
rxd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-51-320.jpg)
![Computation: A x B = C
a11 a12
A [2 x 2]
a 21 a 22
b11 b12 b13
B [2 x 3]
b 21 b 22 b 23
a11b11 a12b21 a11b12 a12b22 a11b13 a12b23
C
a 21b11 a 22b21 a 21b12 a 22b22 a 21b13 a 22b23
[2 x 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-52-320.jpg)
![Computation: A x B = C
2 3
111
A 11 and B
1 0 2
1 0
[3 x 2] [2 x 3]
A and B can be multiplied
2 *1 3 *1 5 2 *1 3 * 0 2 2 *1 3 * 2 8 528
C 1*1 1*1 2 1*1 1* 0 1 1*1 1* 2 3 213
1*1 0 *1 1 1*1 0 * 0 1 1*1 0 * 2 1 111
[3 x 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-53-320.jpg)
![Computation: A x B = C
2 3
111
A 11 and B
1 0 2
1 0
[3 x 2] [2 x 3]
Result is 3 x 3
2 *1 3 *1 5 2 *1 3 * 0 2 2 *1 3 * 2 8 528
C 1*1 1*1 2 1*1 1* 0 1 1*1 1* 2 3 213
1*1 0 *1 1 1*1 0 * 0 1 1*1 0 * 2 1 111
[3 x 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-54-320.jpg)





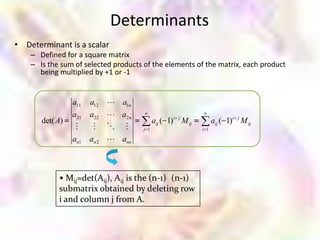
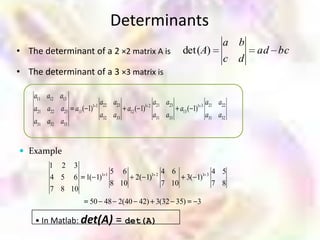
















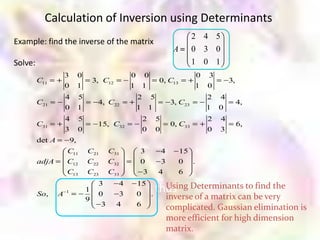
![Calculation of Inversion using Gaussian Elimination
Elementary row operations:
o Interchange two rows of a matrix
o Change a row by adding to it a multiple of
another row
o Multiply each element in a row by the same
nonzero number
• To calculate the inverse of matrix A, we apply the elementary row
operations on the augmented matrix [A I] and reduce this matrix to the
form of [I B]
• The right half of this augmented matrix B is the inverse of A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-84-320.jpg)
![Calculation of inversion using Gaussian elimination
a11 , , a1n a11 , , a1n 1 0 0
a21 , , a2 n a21 , , a2 n 0 1 0
A [A I]
an1 , , ann
an1 , , ann 0 0 1
I is the identity matrix, and use Gaussian elimination to
obtain a matrix of the form 1 0 0 b11 b12 b1n
0 1 0 b21 b22 b2 n
0 0 1 bn1 bn 2 bnn
The matrix b11 b12 b1n
b21 b22 b2 n
B
is then the matrix inverse of A
bn1 bn 2 bnn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-85-320.jpg)
![Example
1 1 1
1 1 1 |1 0 0
A 12 2 3 [A| I] 12 2 3 | 0 1 0
3 4 1 3 4 1 |0 0 1
(ii)+(-12) (i), (iii)+(-3) (i), (iii)+(ii)
3 1
(1/10) 1 0 0 | 0.4
1 1 1 | 1 0 0 35 7
2 3
0 10 15 | 12 1 0 0 1 0 | 0.6
35 7
0 0 3.5 | 4.2 0.1 1 1 2
0 0 1 | 1.2
35 7
3 1
The matrix 0.4
35 7 is then the matrix inverse of A
2 3
0.6
35 7
1 2
1.2
35 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrix-111114041118-phpapp02/85/Matrix-86-320.jpg)