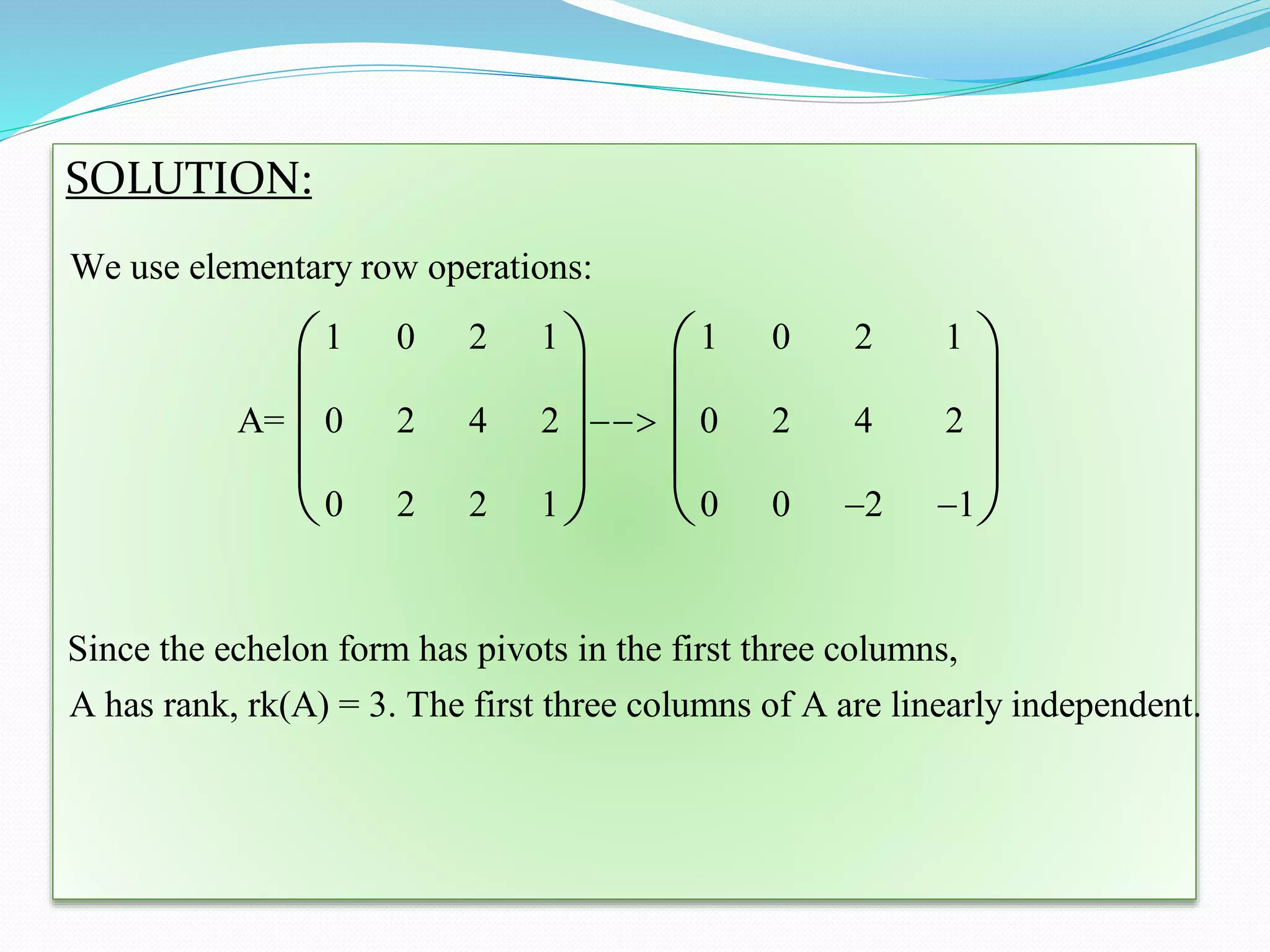
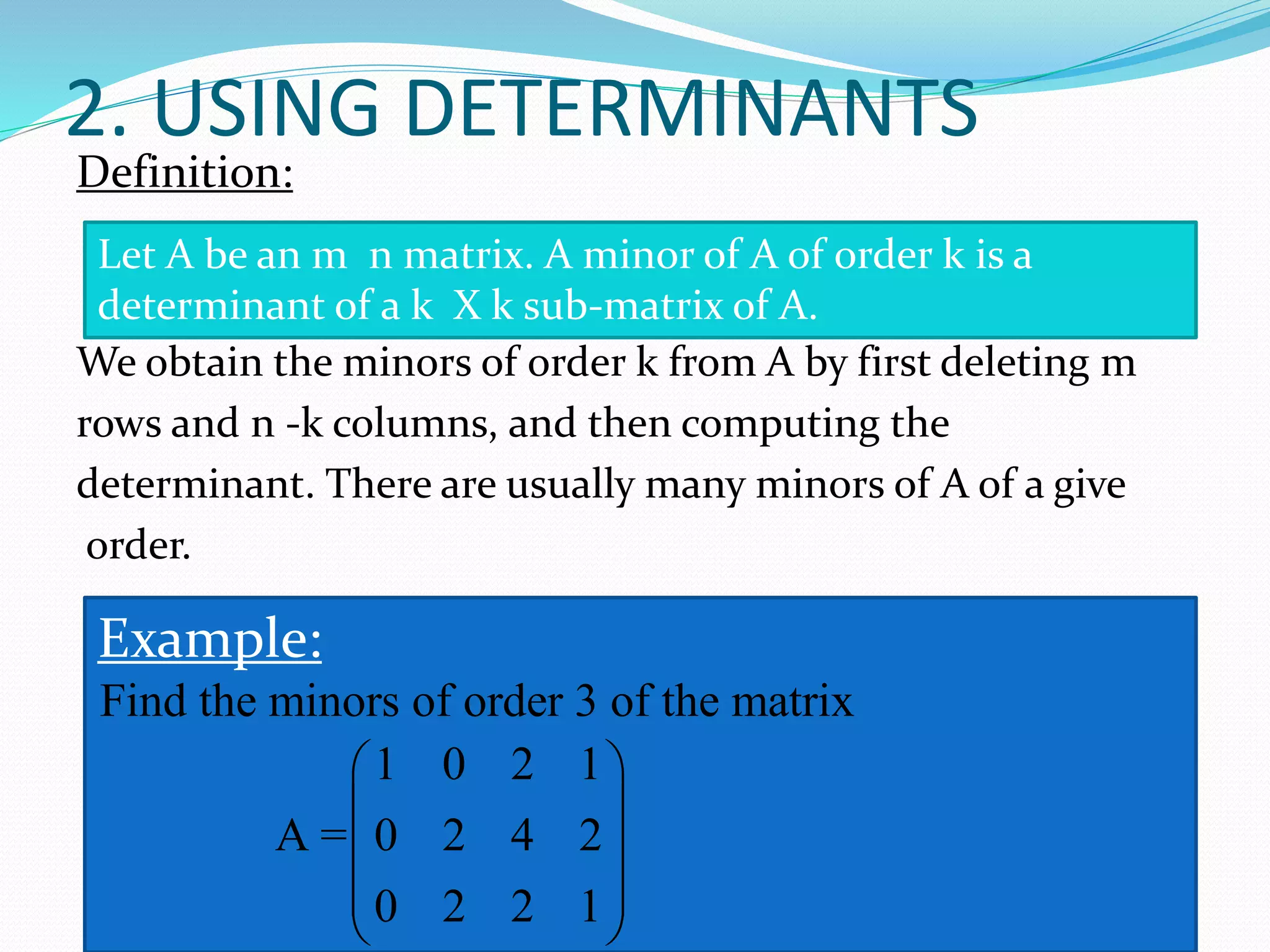
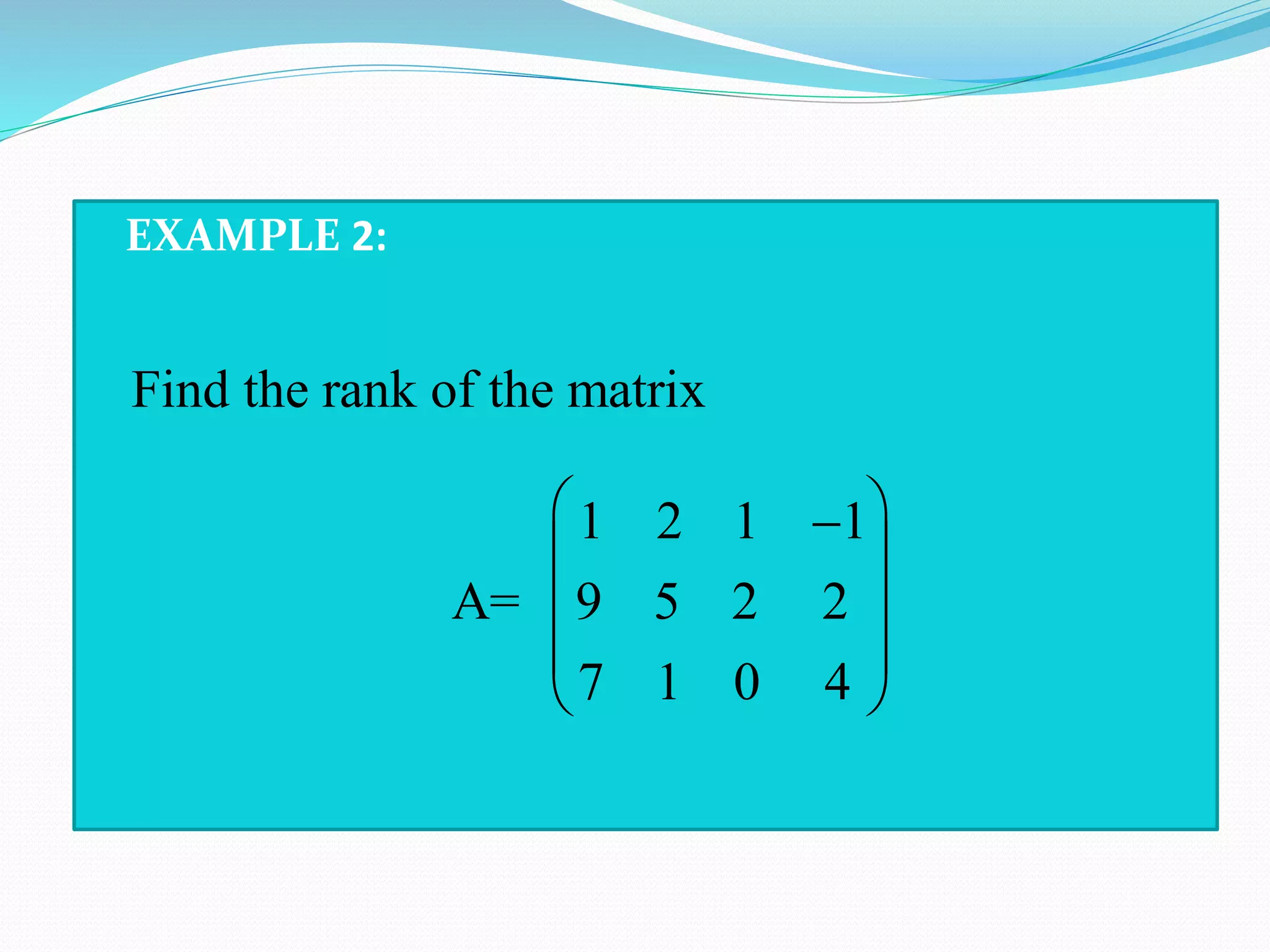
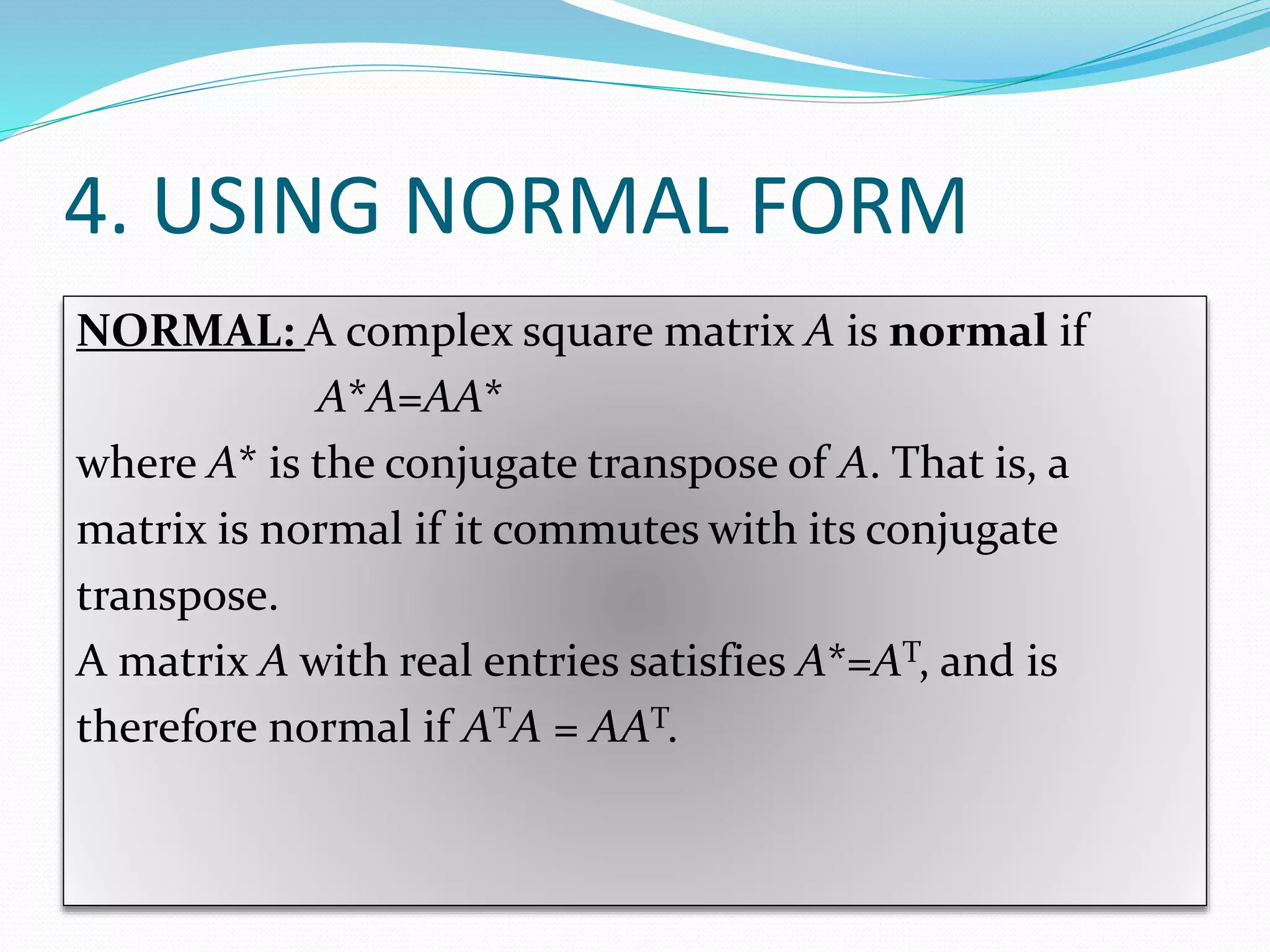
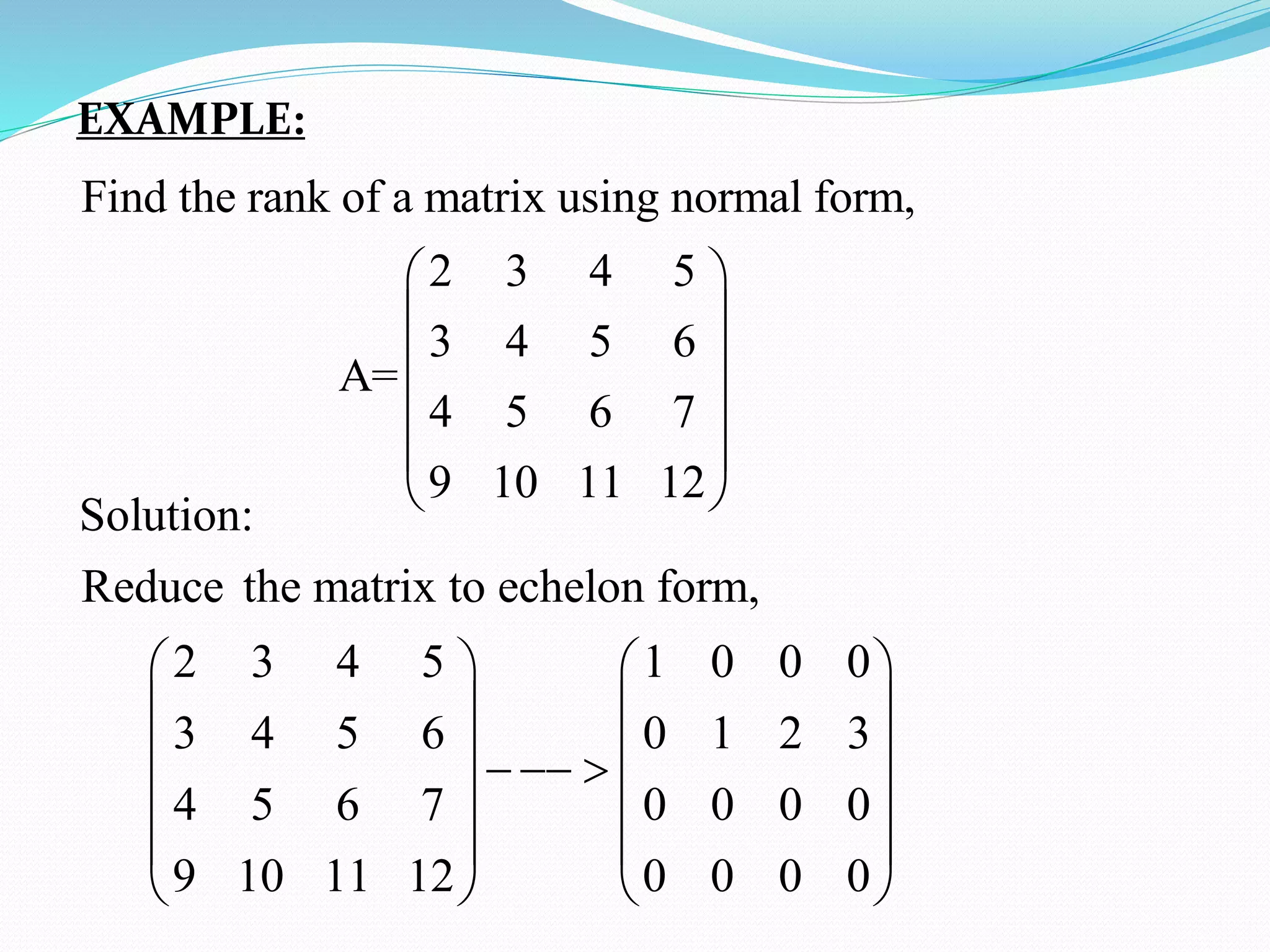
The document discusses various methods to compute the rank of a matrix:
1) Using Gauss elimination, where the rank is the number of pivot columns in the echelon form of the matrix.
2) Using determinants of sub-matrices (minors), where the rank is the largest order of a non-zero minor.
3) Transforming the matrix to normal form using row and column operations, where the rank is the number of non-zero rows of the resulting identity matrix.
Worked examples are provided to illustrate computing the rank of matrices using these different methods.