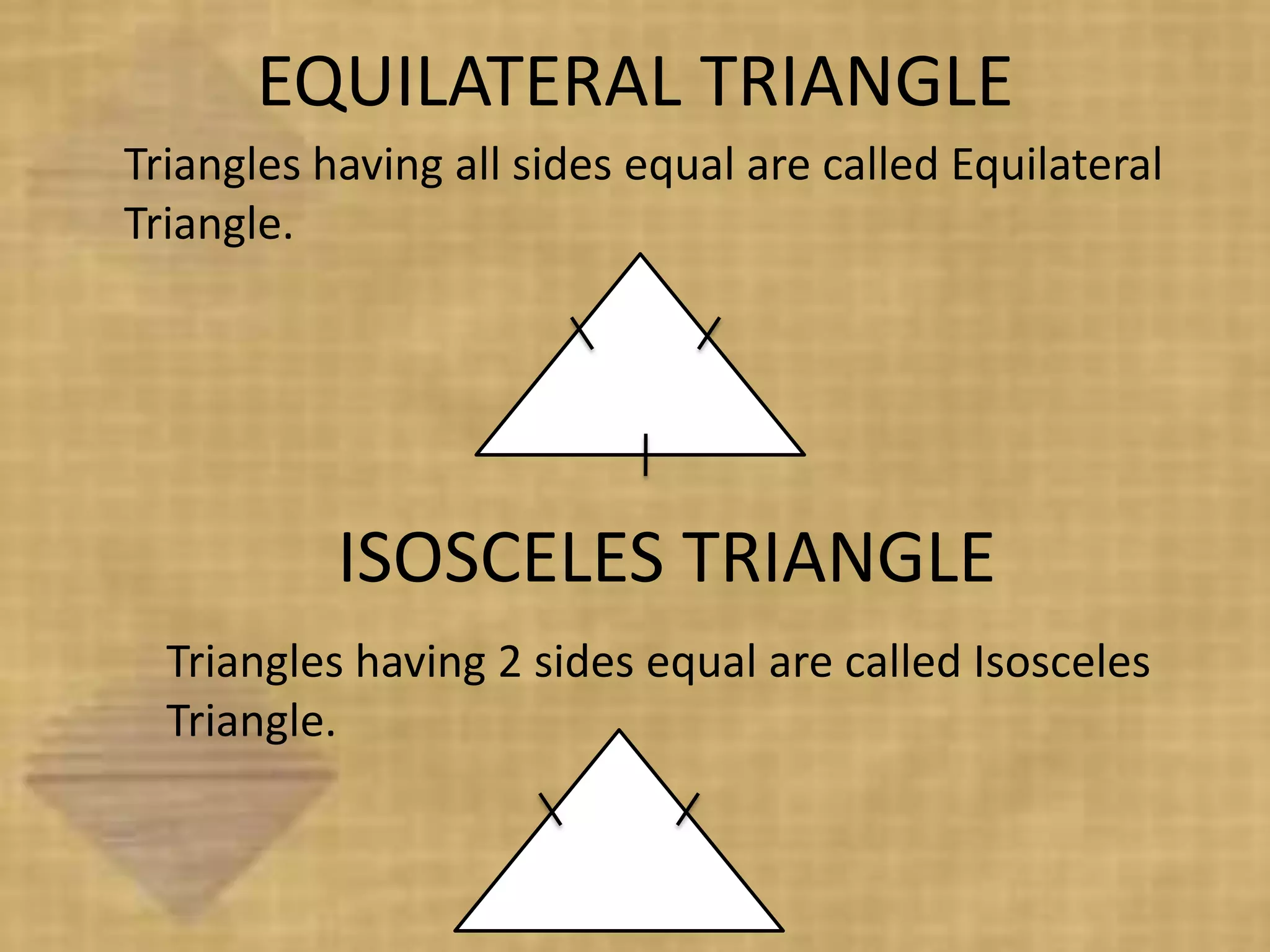
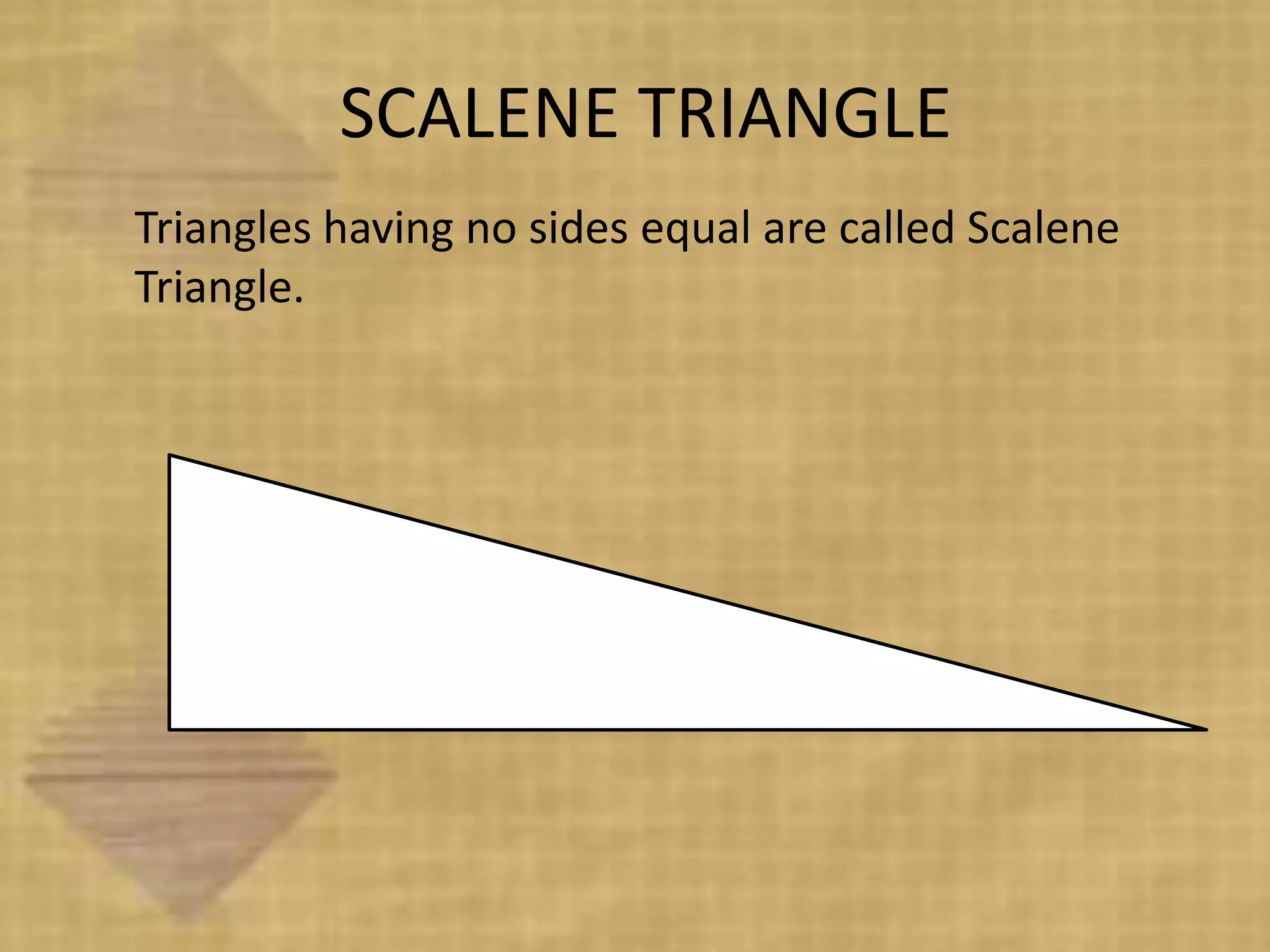
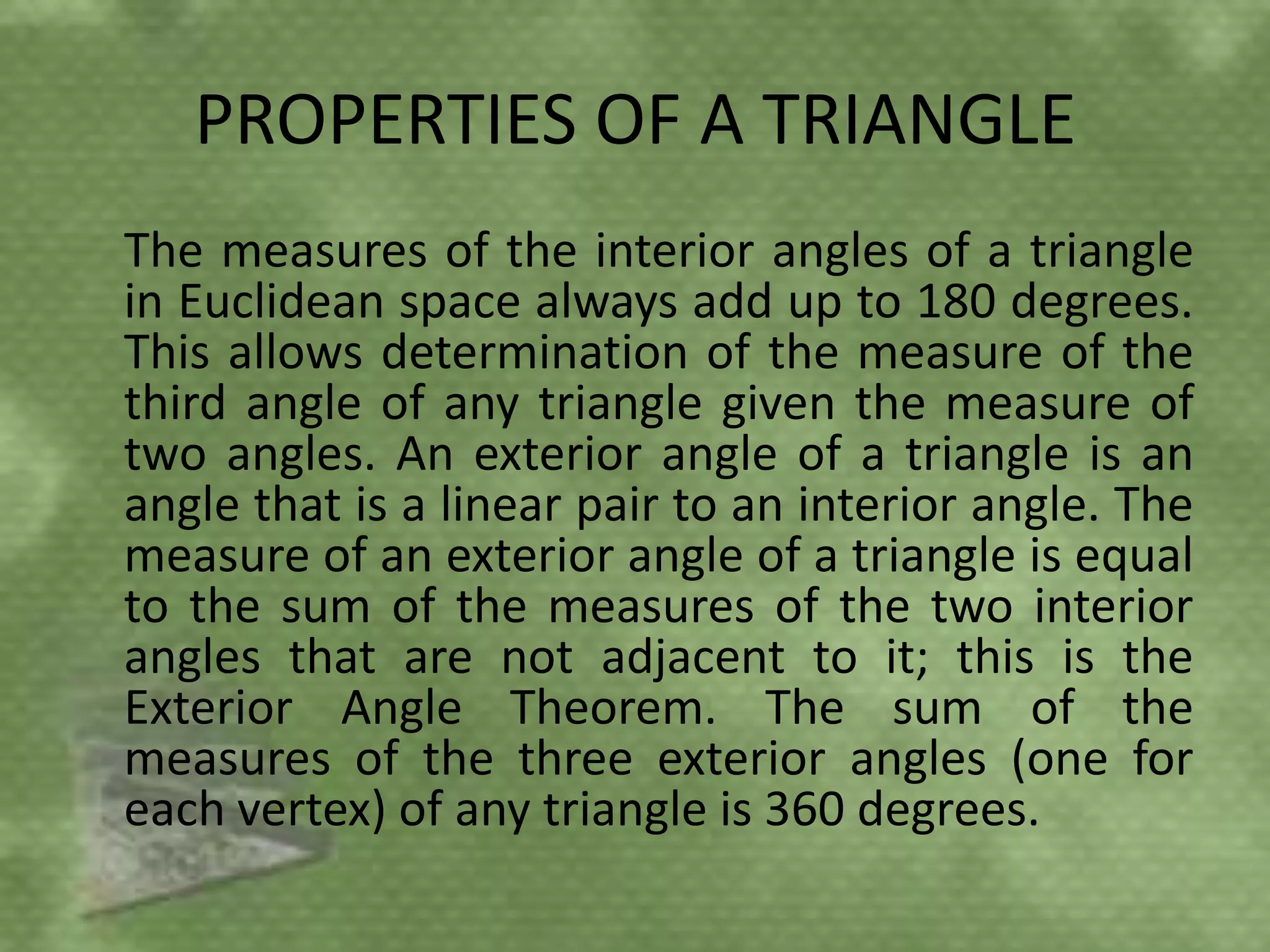
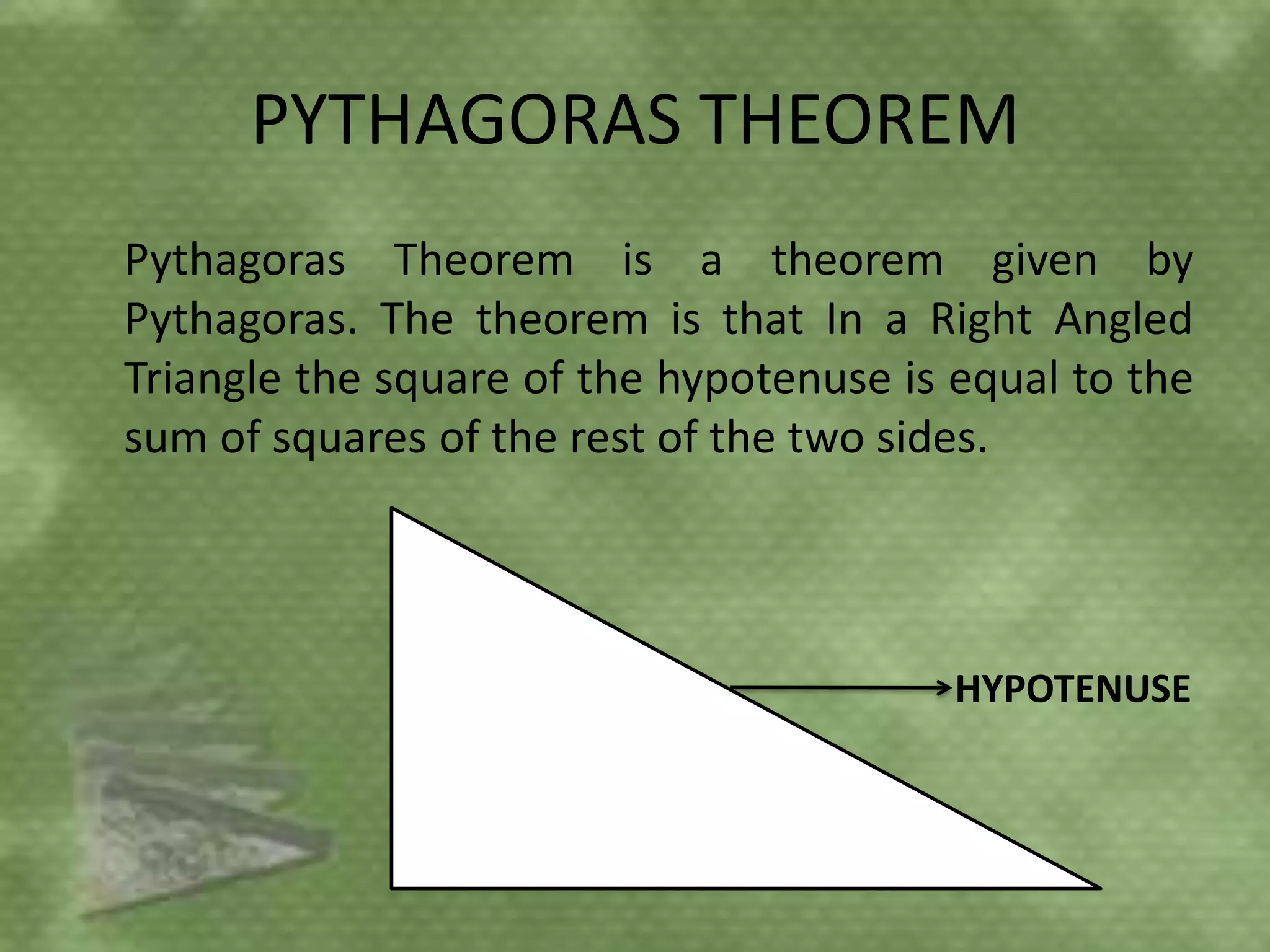
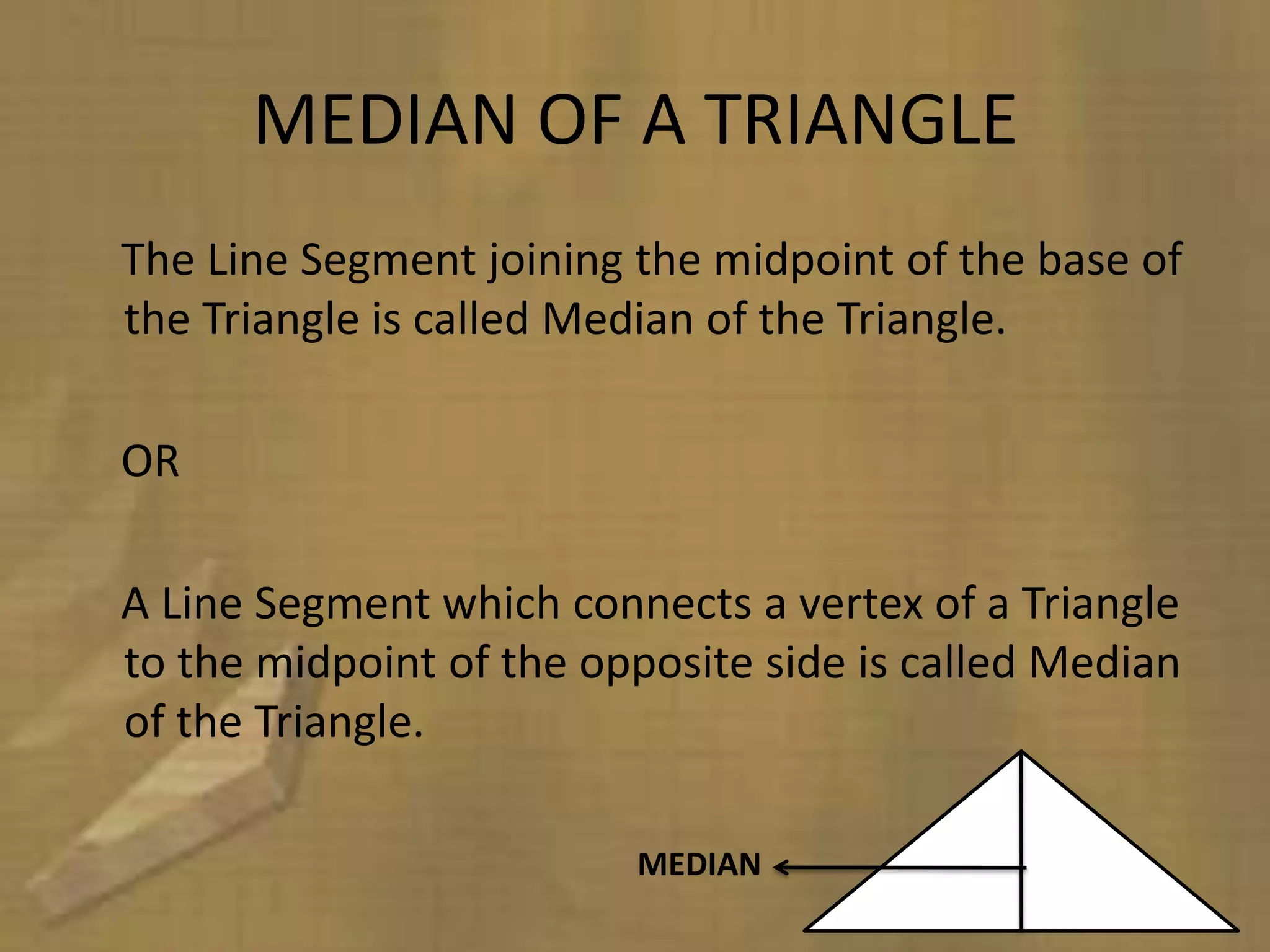
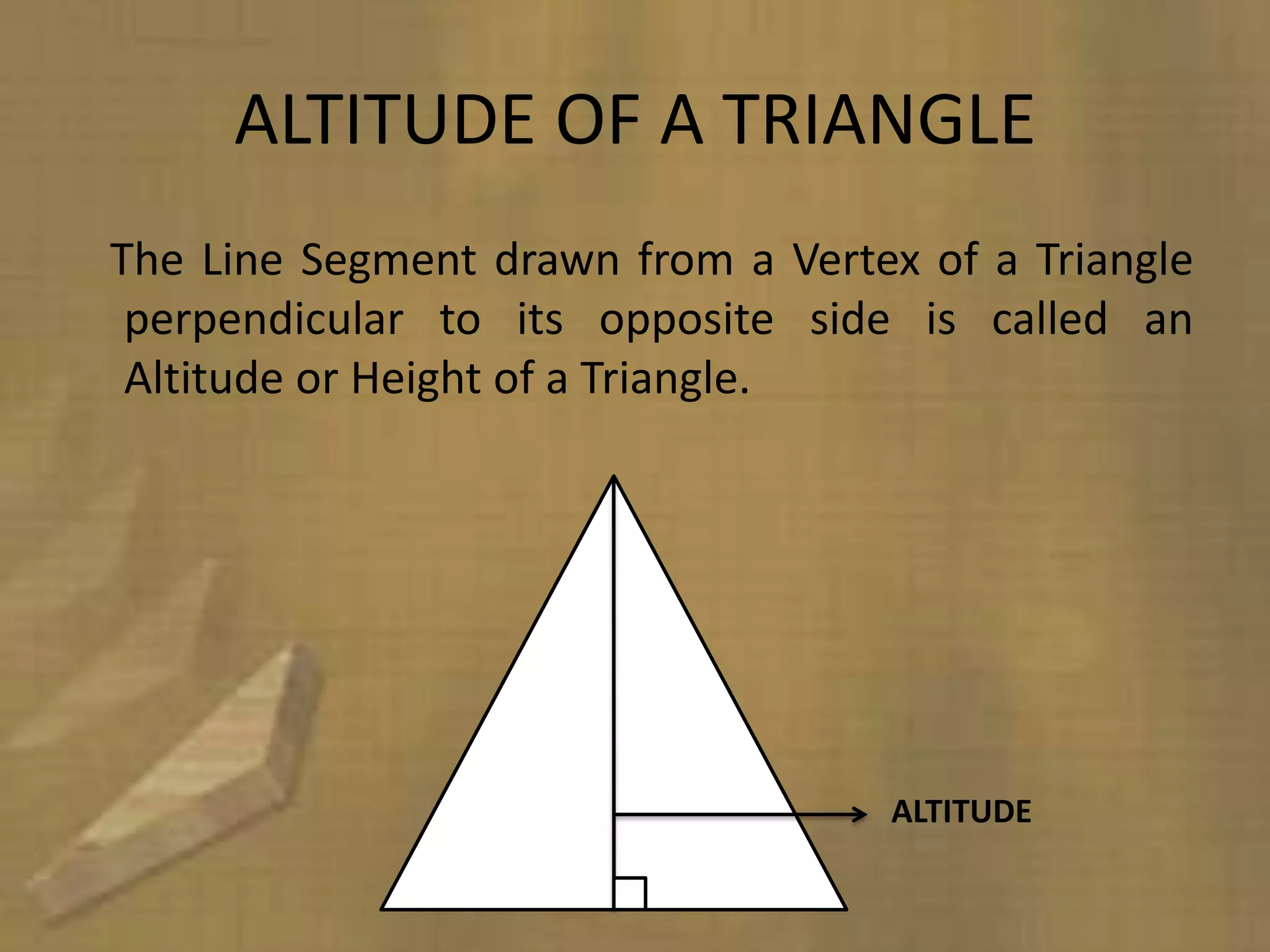
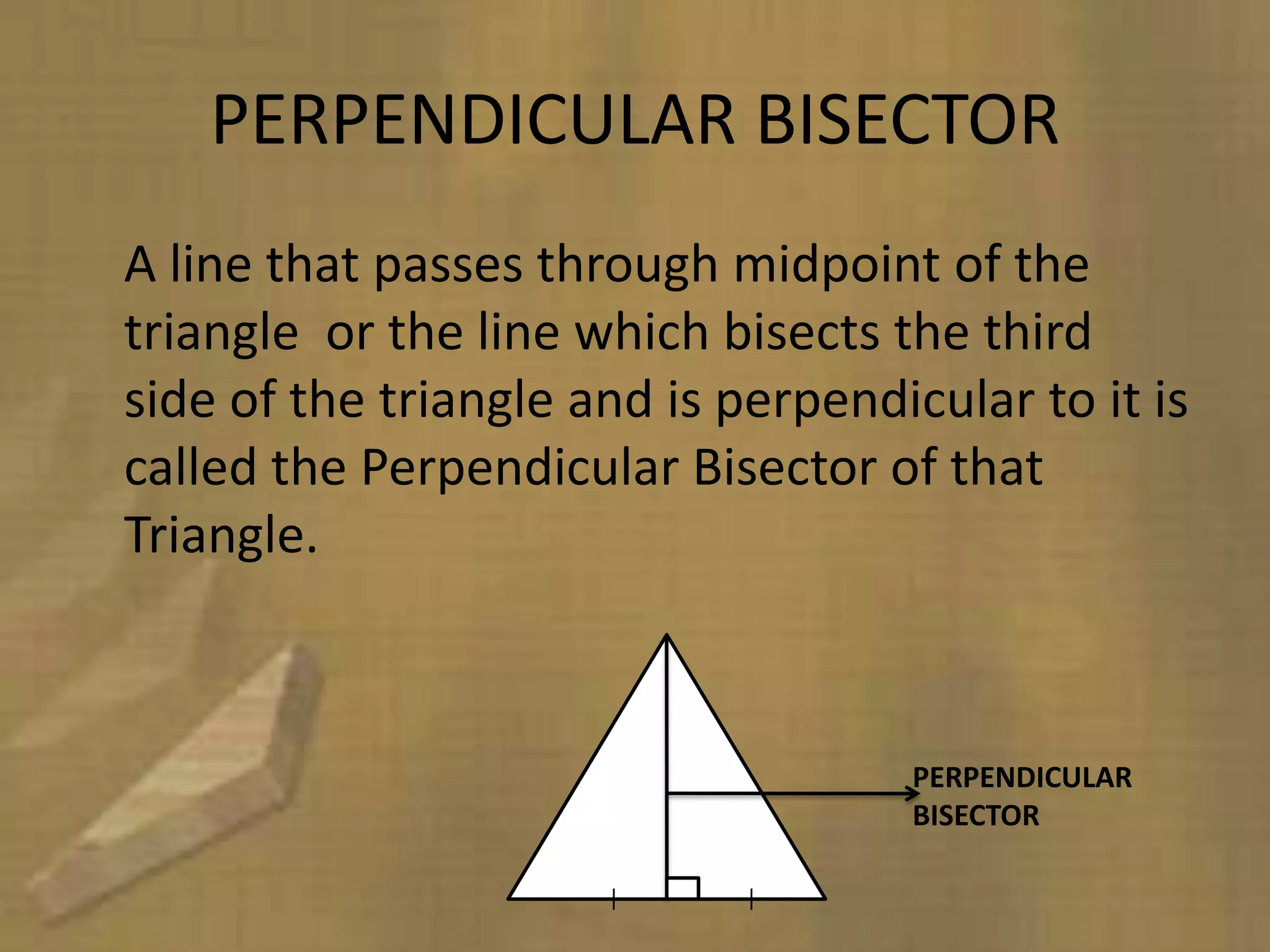
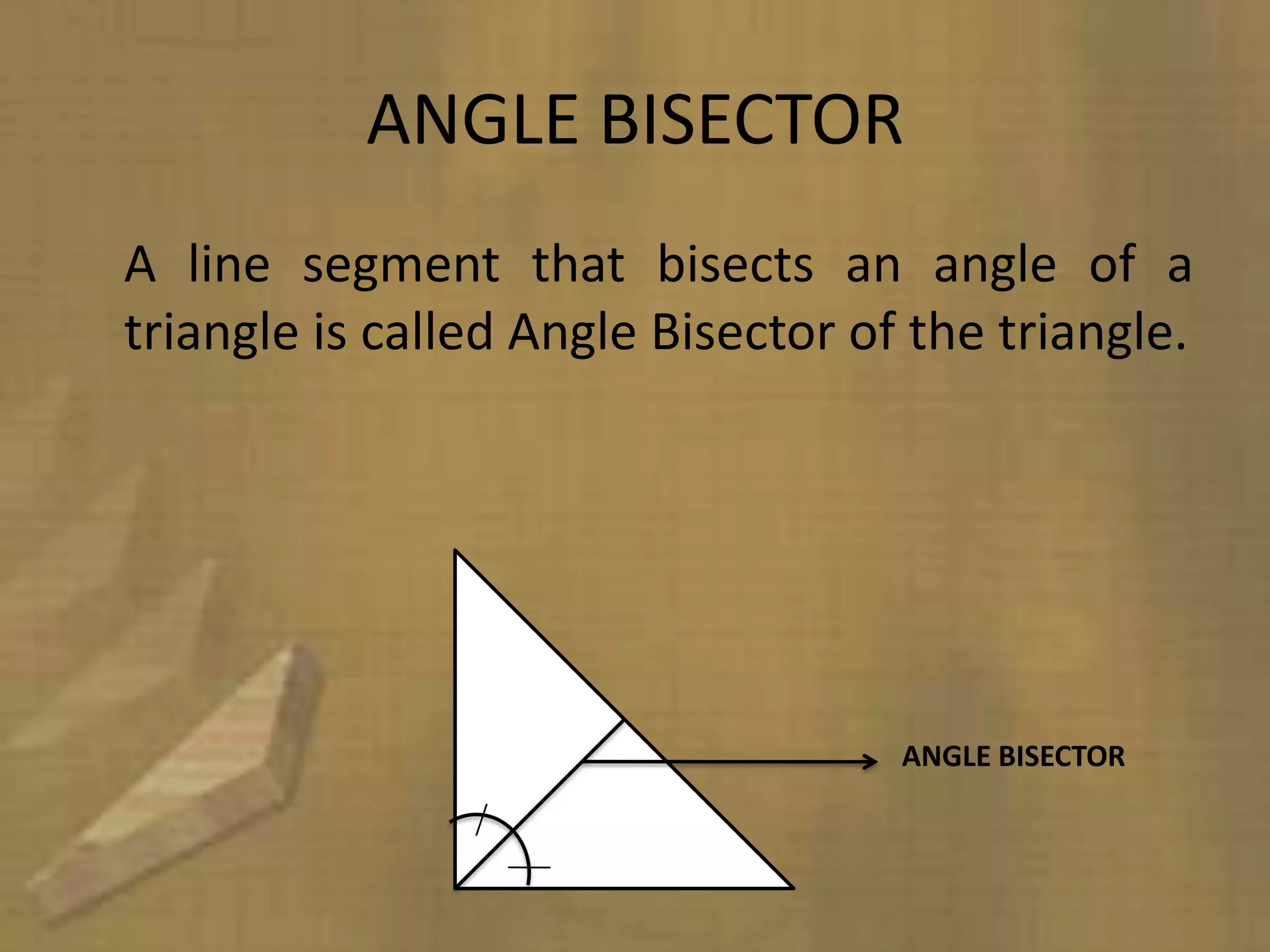
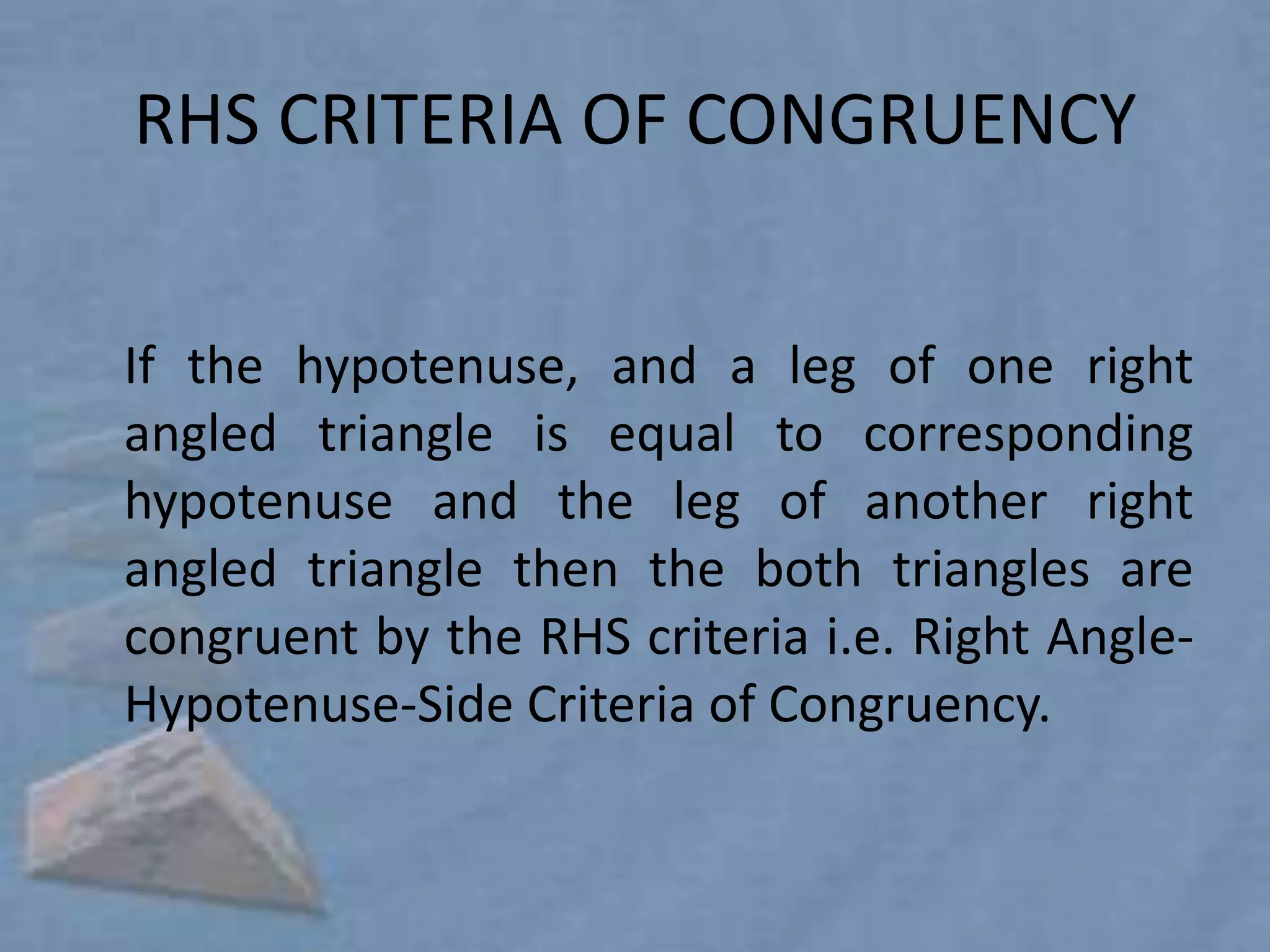
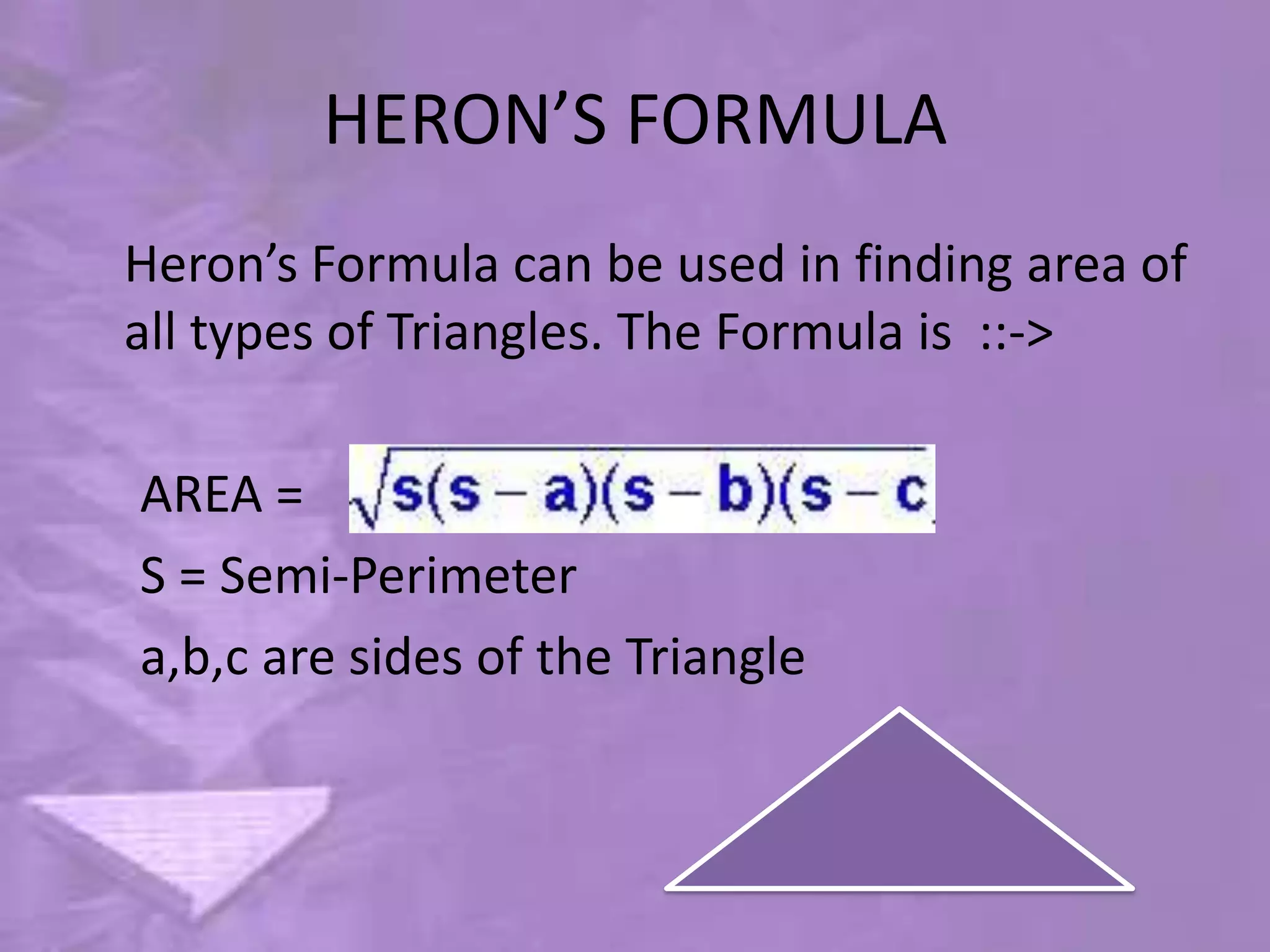
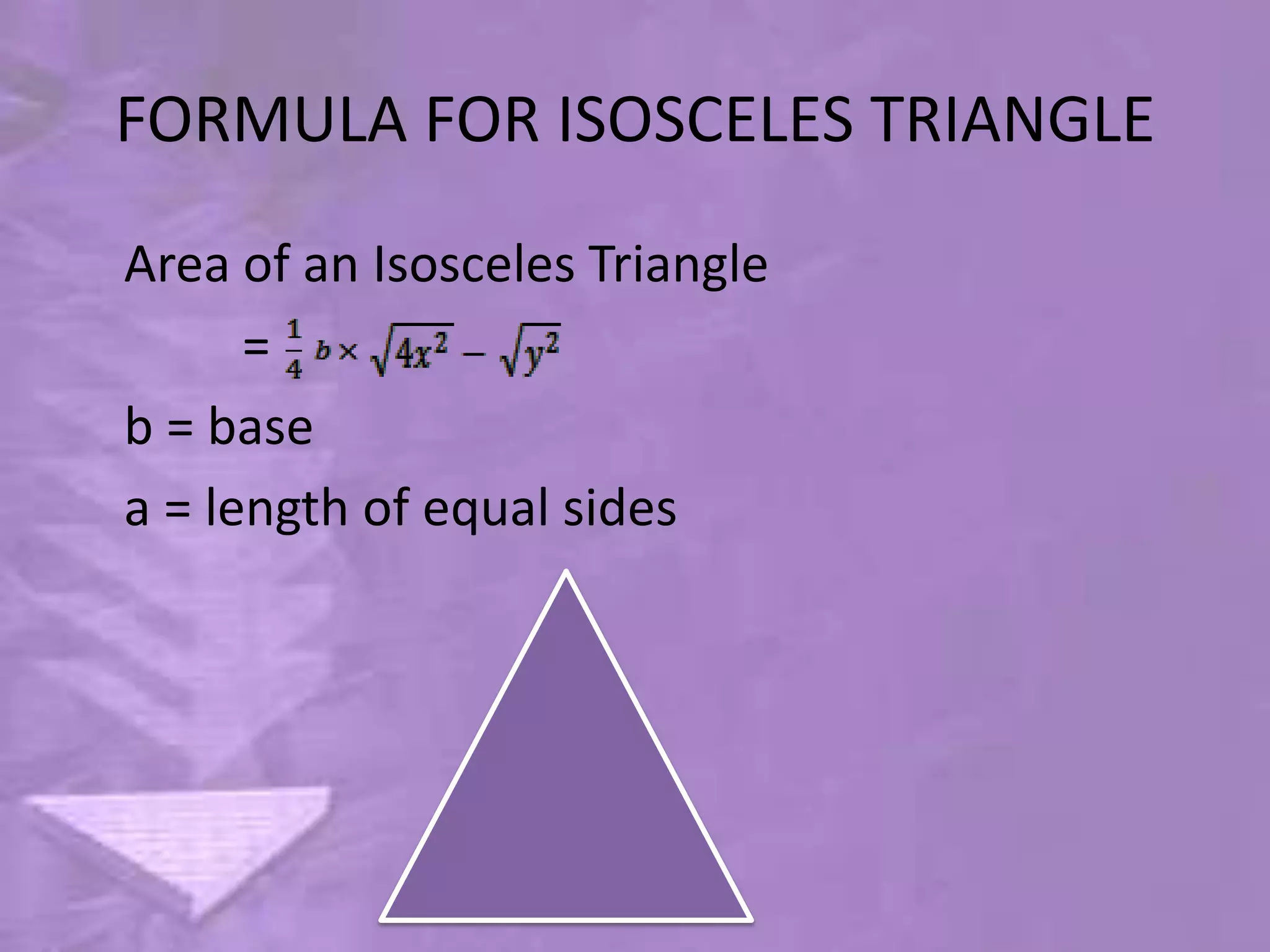
Triangles are three-sided polygons that have three angles and three sides. There are three main types of triangles based on side lengths: equilateral (all sides equal), isosceles (two sides equal), and scalene (no sides equal). The interior angles of any triangle always sum to 180 degrees. Important triangle properties include the exterior angle theorem, Pythagorean theorem, and congruency criteria like SSS, SAS, ASA. Common secondary parts are the median, altitude, angle bisector, and perpendicular bisector. The area of triangles can be found using Heron's formula or other formulas based on side lengths and types of triangles.