The document discusses matrices and their types and applications. It defines a matrix as a rectangular arrangement of numbers, expressions or symbols arranged in rows and columns. It describes 10 different types of matrices including row, column, square, null, identity, diagonal, scalar, transpose, symmetric and equal matrices. It also discusses three algebraic operations on matrices: addition, subtraction and multiplication. Finally, it provides examples of how matrices are used in economics to calculate costs of production, in geology for seismic surveys, and in robotics and automation to program robot movements.


![It is an collection of element which is arranges in rows and columns
MATRIX
It is the combination of linear equation
It is represented by these symbols : () , [] , l l](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrixanditsapplication-161031032013/85/Matrix-and-it-s-application-3-320.jpg)
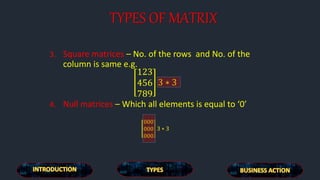
![TYPES OF MATRIX
1. Row matrices – A matrices which has only one row
called row matrices e.g.-
[123]1*3
2. Column matrices – A matrices which has only one
column is called column matrices e.g. –
1
2
3
3 ∗ 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrixanditsapplication-161031032013/85/Matrix-and-it-s-application-4-320.jpg)









![ACTION OF MATRIX
Step 1
.40 .30
A = .20 and B = .25
.10 .35
Step 2
The cost of manufacturing x1 dollars worth of A are given by x1*A and the costs of
manufacturing x2 dollars worth of B are given by x2.B. Hence the total costs for both
products are simply given by their products once again,
.40 .30
[ x1 ] .20 + [ x2 ] .25 = x1*A + x2*B.
.10 .35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrixanditsapplication-161031032013/85/Matrix-and-it-s-application-15-320.jpg)


