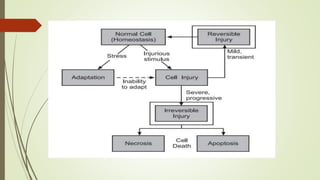
Necrosis is cell death caused by external factors like lack of oxygen, toxins, burns or trauma. There are several types of necrosis including coagulative where tissue structure is preserved, liquefactive where cells are digested, and gangrenous which often involves bacterial infection. Necrotic cells appear eosinophilic on staining and show features like nuclear dissolution or fragmentation. Clinical signs include pain, swelling and spreading skin redness.