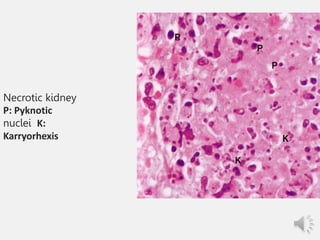
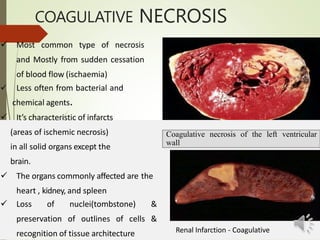
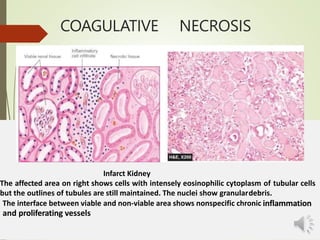
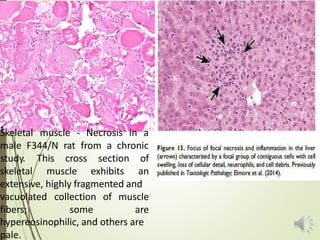
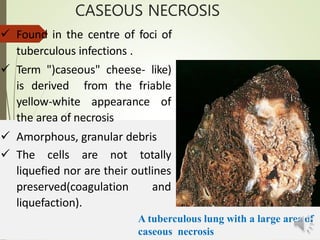
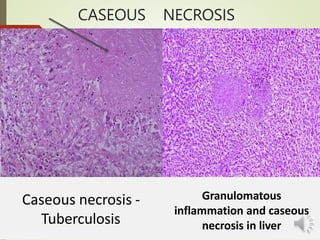
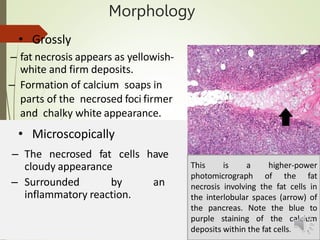
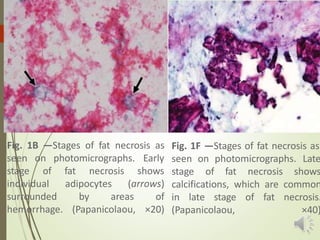
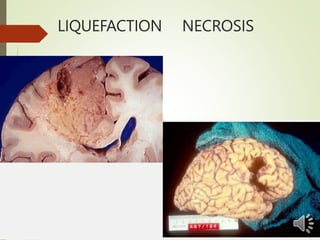
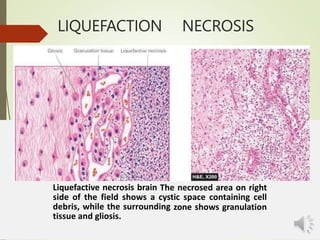
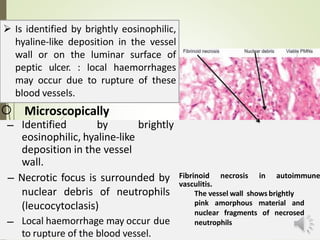
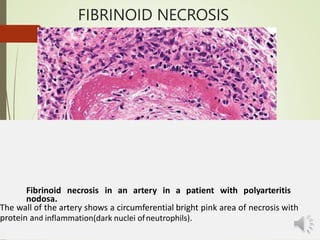
Necrosis is the death of cells and living tissue. It is characterized by cellular swelling, breakdown of organelles, and denaturation of proteins. The main types of necrosis include coagulative, caseous, fat, liquefactive, and fibrinoid necrosis. Coagulative necrosis occurs from ischemia and results in preservation of cell outlines. Caseous necrosis is seen in tuberculosis and has a cheesy appearance. Fat necrosis involves destruction of fat cells. Liquefactive necrosis causes tissue liquefaction by hydrolytic enzymes. Fibrinoid necrosis features deposition of fibrin-like material in blood vessels. Necrosis can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, calcification, or cyst formation over time.