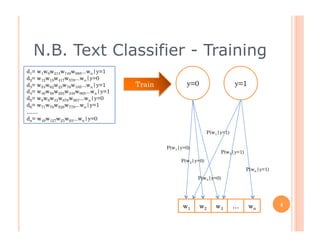
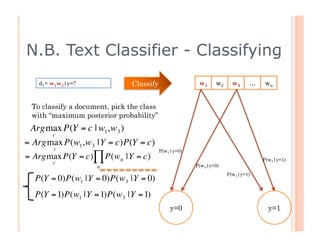
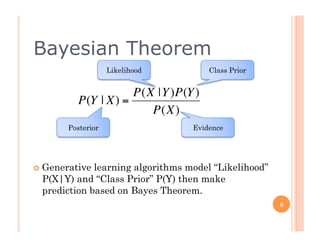
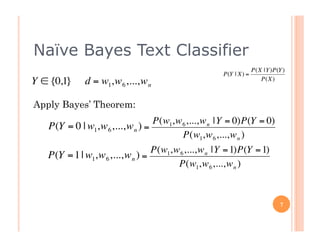
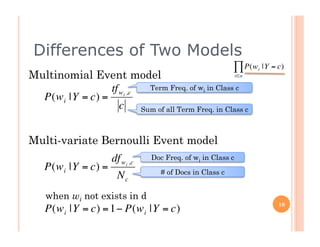
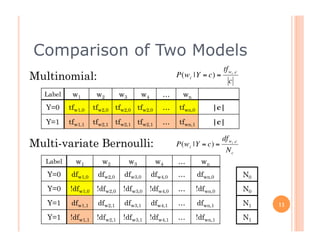
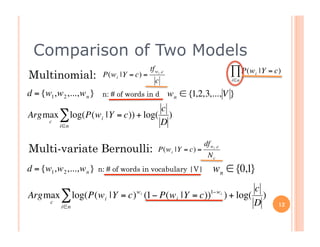
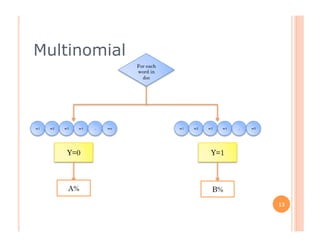
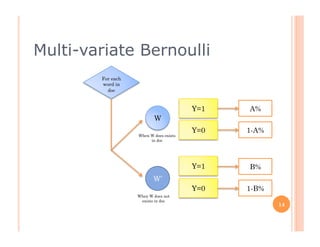
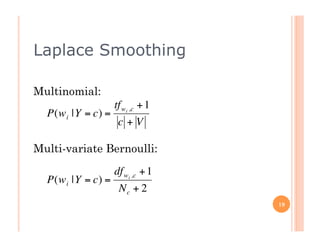
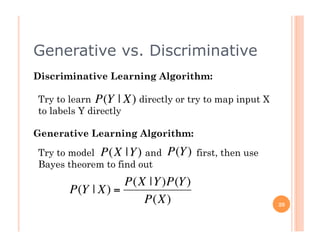
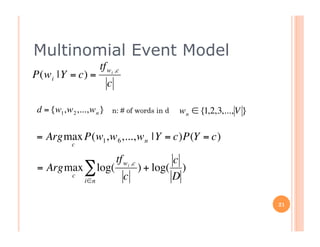
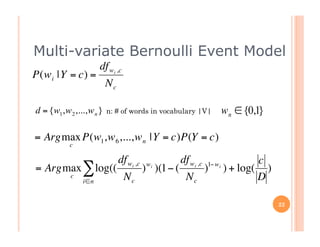
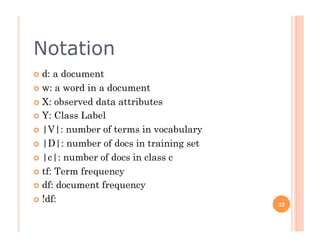
The document outlines the workings of naïve Bayesian text classifiers and the two main event models: multinomial and multi-variate Bernoulli. It discusses performance characteristics, successful applications such as spam filtering and news categorization, and provides insights on estimating likelihood and model comparisons. Additionally, it notes the importance of choosing the appropriate model based on data characteristics and offers guidance on both generative and discriminative learning approaches.