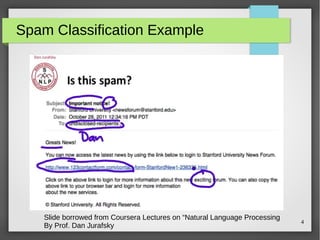
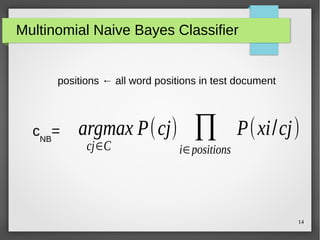
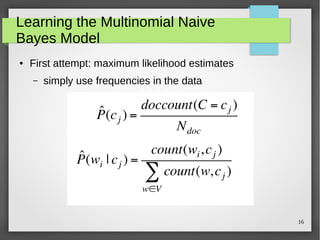
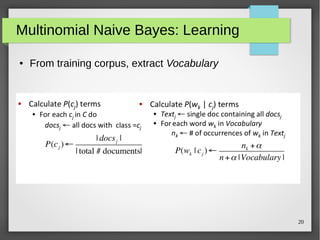
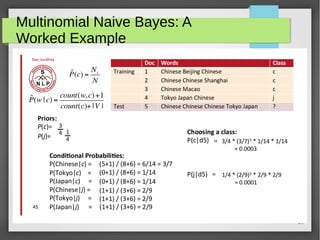
The document discusses text classification and sentiment analysis, outlining their definitions, methods, and applications. It covers classifiers like Naive Bayes, along with their assumptions and parameter estimation techniques, as well as the challenges faced in sentiment analysis. Additionally, it highlights specific applications across various domains, such as politics and product reviews, and mentions sentiment lexicons used in research.