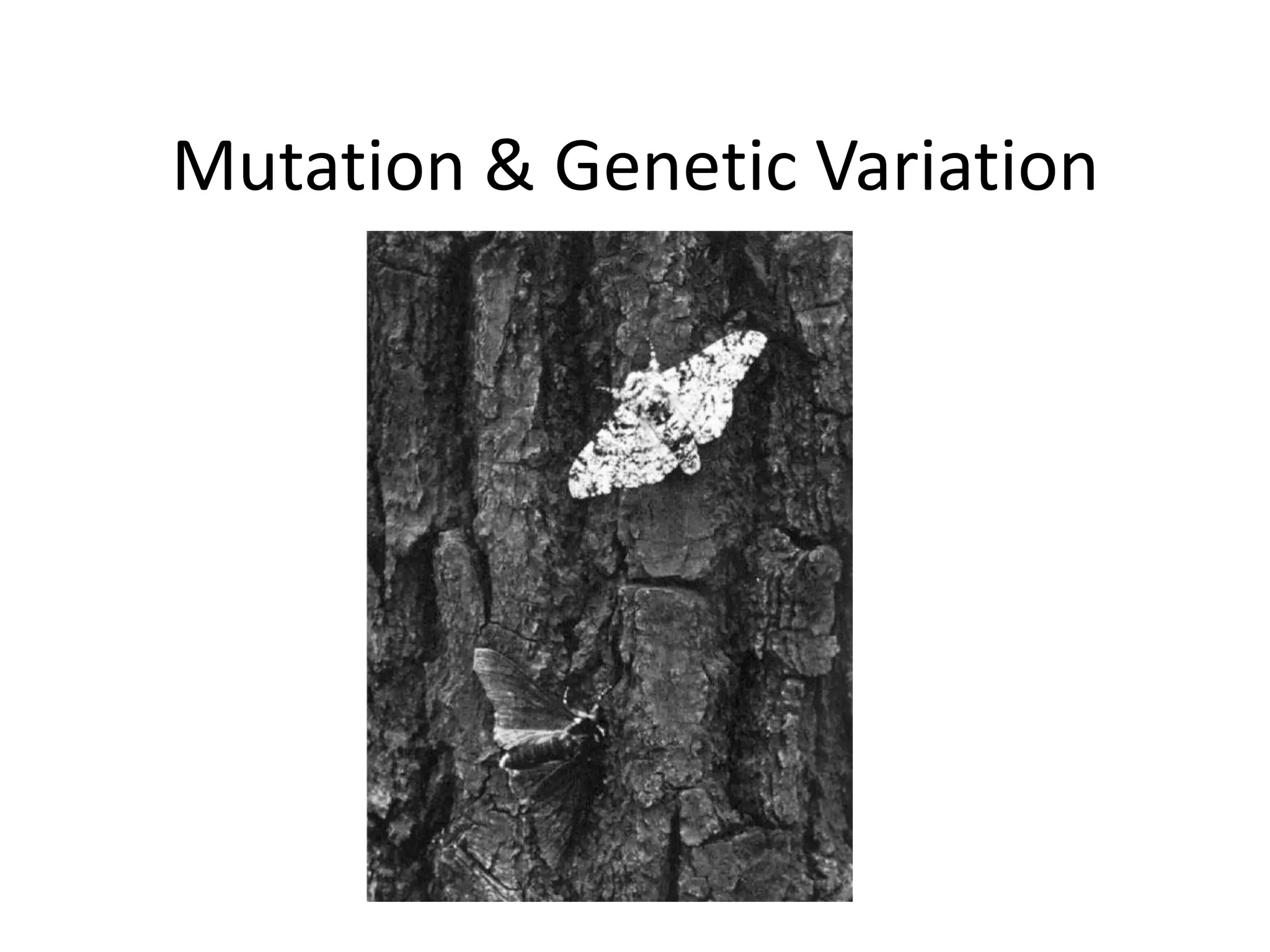
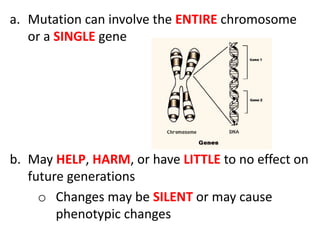
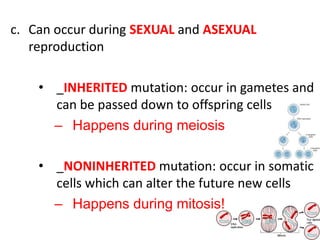
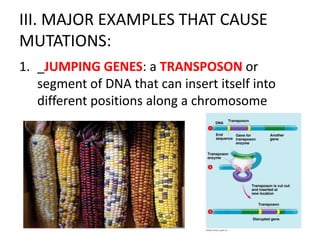
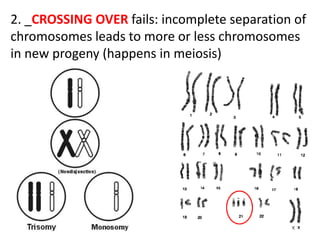
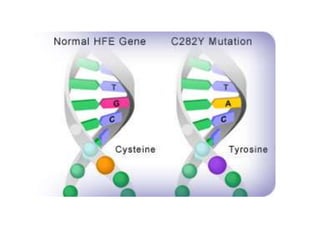
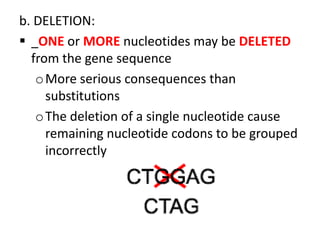
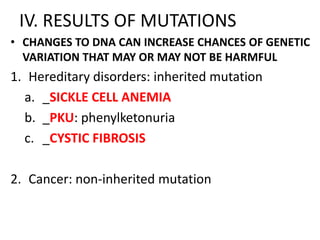
Mutations are changes or alterations in the DNA sequence that can disrupt genes and alter protein production. Mutations can occur during sexual or asexual reproduction and be inherited or non-inherited. Causes of mutation include heredity, carcinogens like chemicals and radiation, and chance mistakes during DNA replication. Major types of mutations include transposons that insert into chromosomes, crossover failures in meiosis, and single gene mutations like substitutions where nucleotides are replaced or deletions where nucleotides are removed. The results of mutations can include genetic variation and hereditary disorders or cancer depending on if they are inherited or non-inherited.