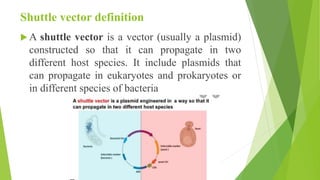
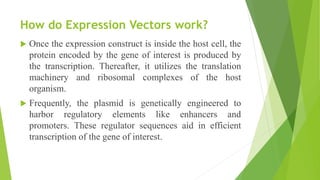
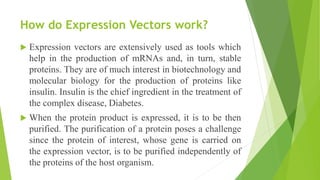
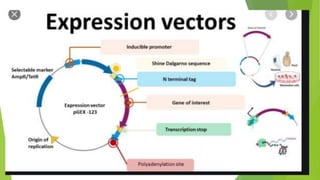
Shuttle vectors are DNA molecules designed to propagate in two different host species, allowing for the introduction and reproduction of foreign DNA in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. They incorporate two origins of replication to function in both cell types and can facilitate the cloning of genes in organisms like E. coli and yeast. Expression vectors, on the other hand, are engineered to not only introduce but also express genes efficiently within host cells, crucial for producing proteins such as insulin for medical applications.