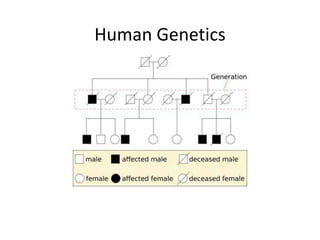
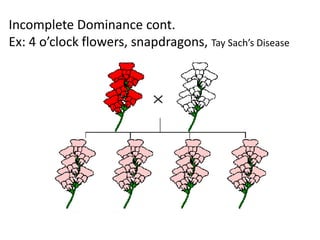
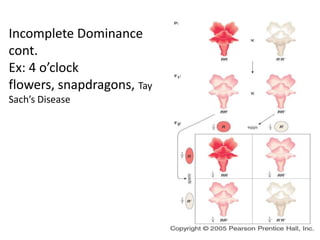
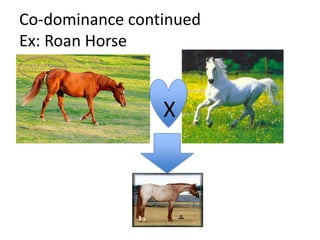
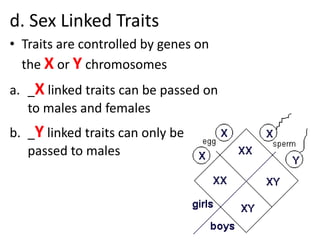
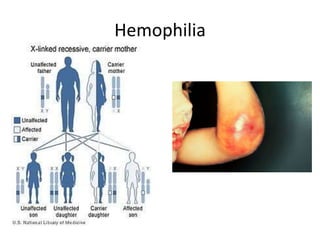
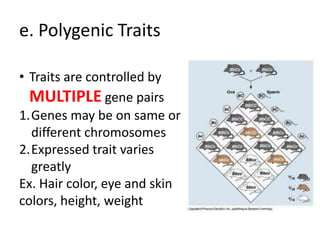
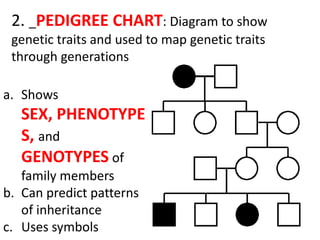
The document discusses 5 patterns of human inheritance: complete dominance, incomplete dominance, co-dominance, sex-linked traits, and polygenic traits. It provides examples for each pattern including Mendelian genetics (BB, Bb, bb), blending of traits in flowers, expression of both parental alleles in horses, traits on the X/Y chromosomes, and traits influenced by multiple gene pairs like hair/eye color. The document also describes how karyotypes and pedigree charts are used to study inheritance in families by examining chromosomes and mapping genetic traits through generations.