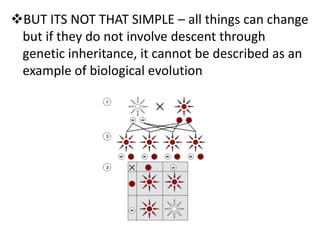
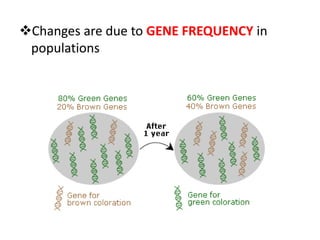
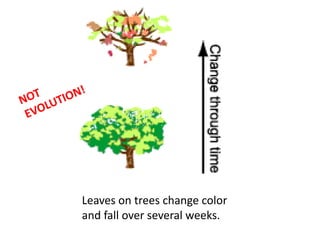
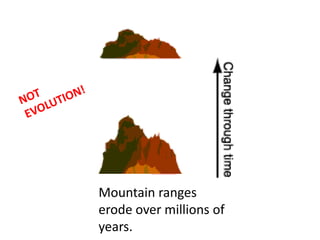
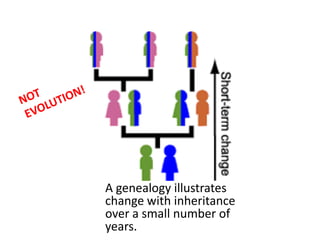
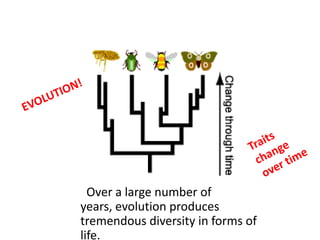
This document provides evidence for biological evolution from several sources:
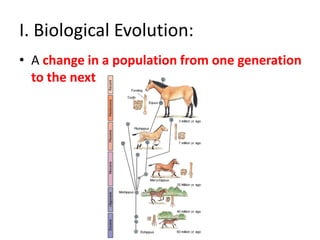
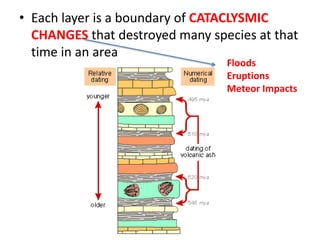
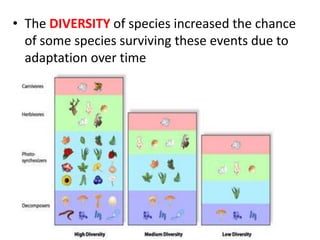
- Fossil records show succession of organisms over time and increased diversity after catastrophic events.
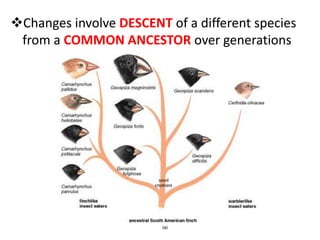
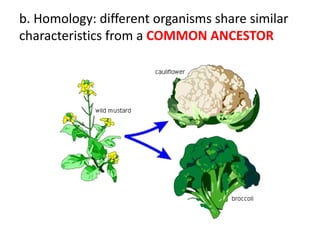
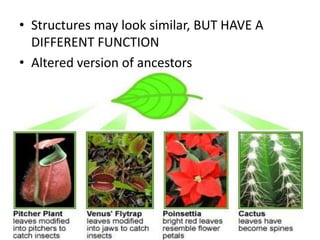
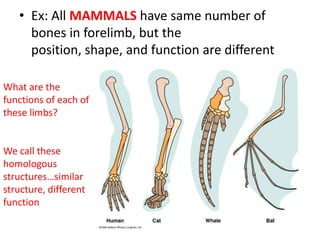
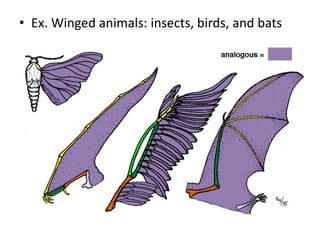
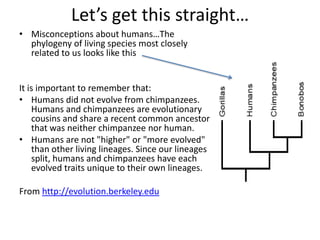
- Homology and analogy demonstrate that structures in different species share common ancestry or adaptations to environment.
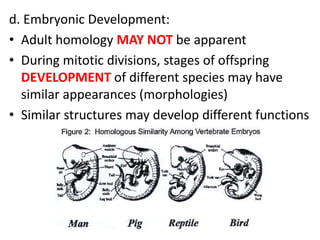
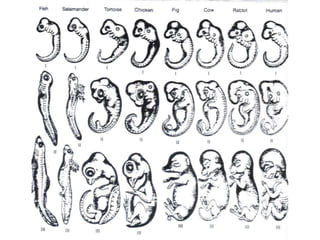
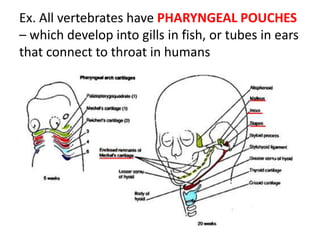
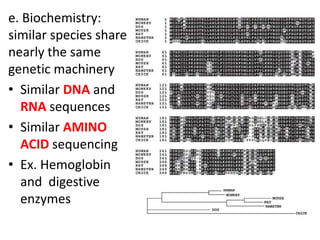
- Embryonic development and biochemistry reveal similar genetic machinery and developmental stages across species.