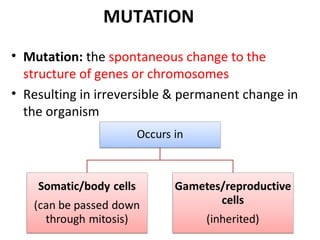
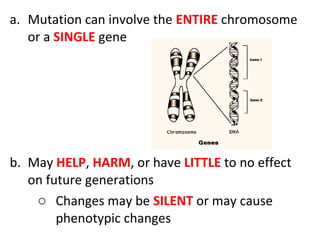
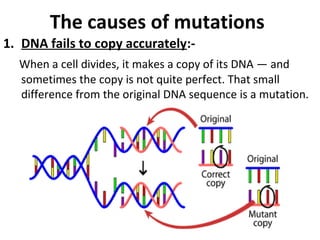
1. Mutations can occur at the gene or chromosomal level and can be caused by errors in DNA replication or exposure to mutagens like radiation or chemicals.
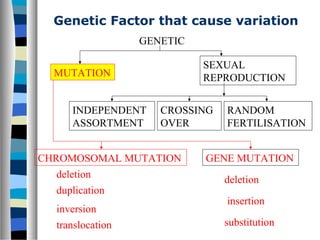
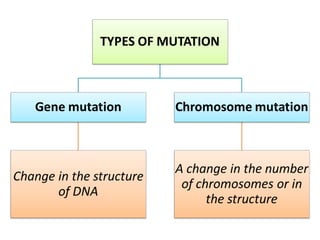
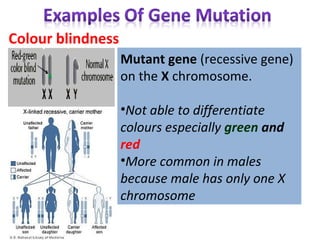
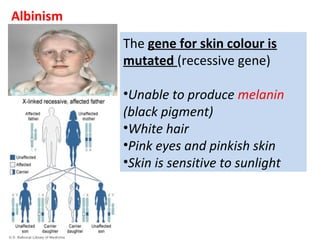
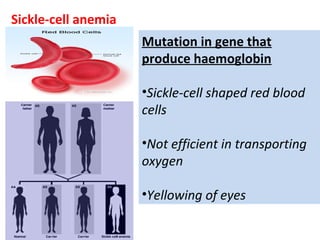
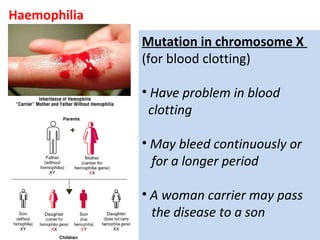
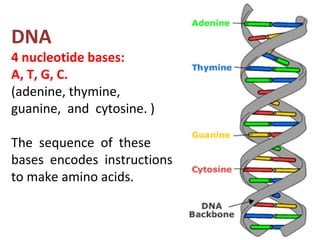
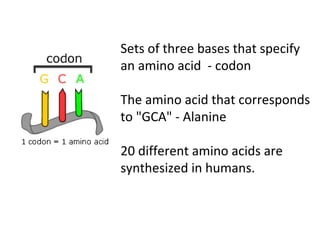
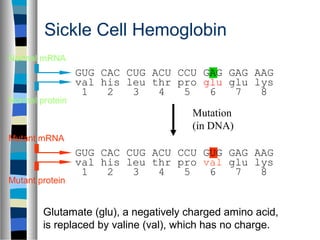
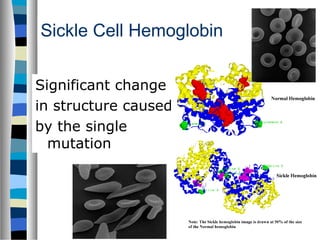
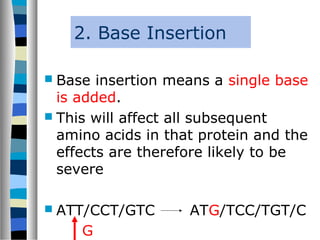
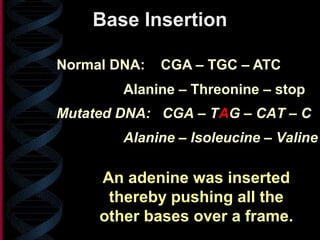
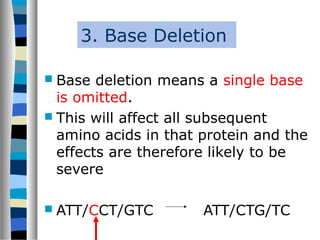
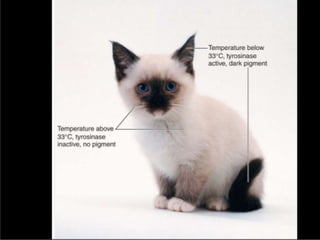
2. Gene mutations include substitutions, insertions, and deletions of DNA bases and can range from having little to no effect to causing genetic disorders, depending on where they occur.
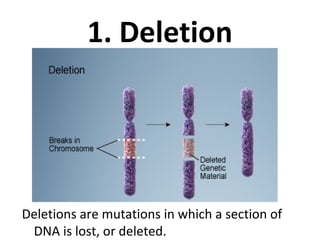
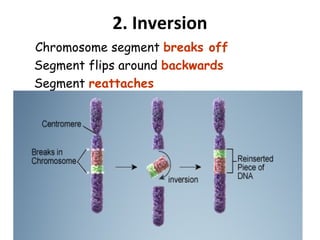
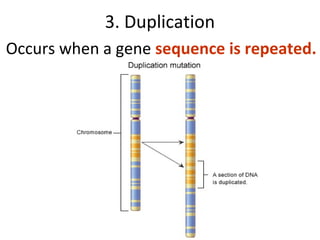
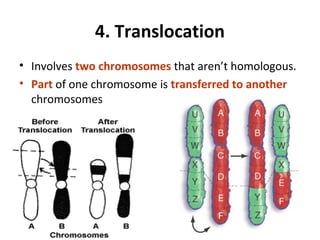
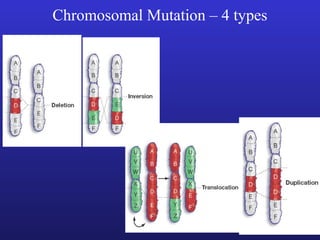
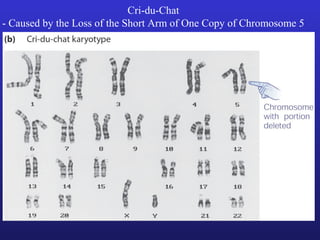
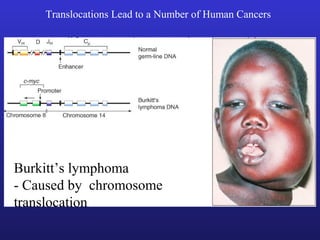
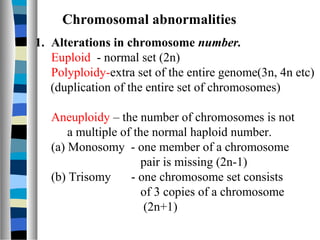
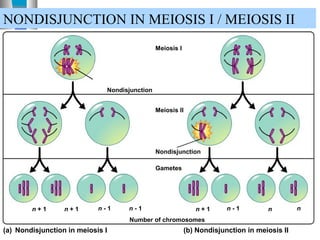
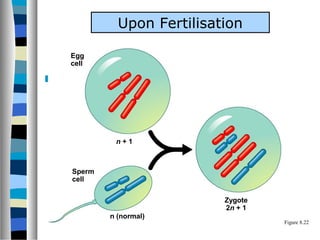
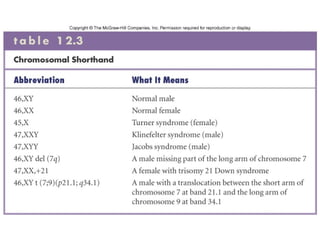
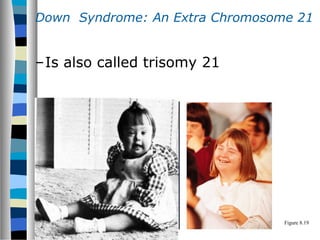
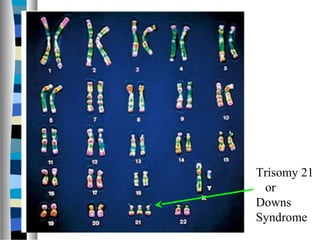
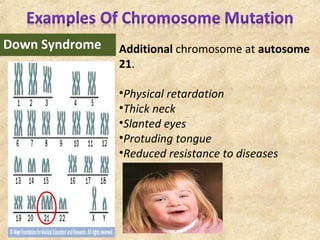
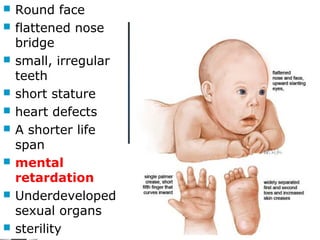
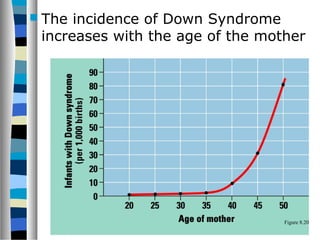
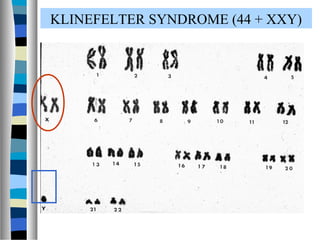
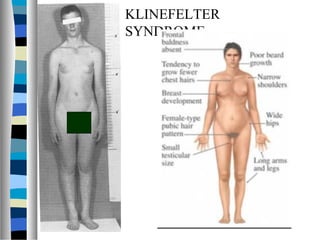
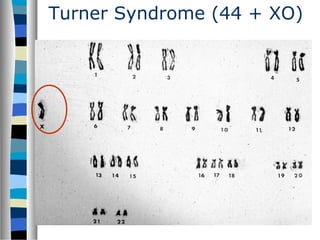
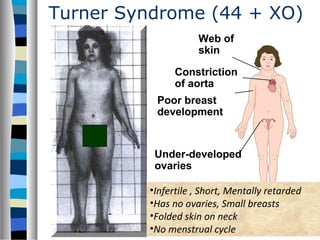
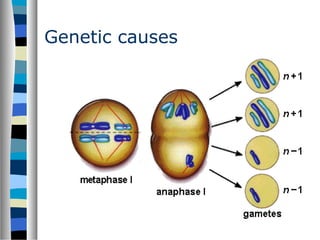
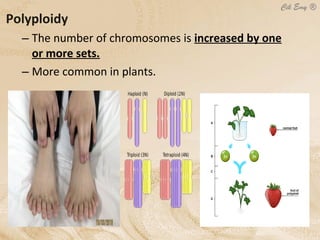
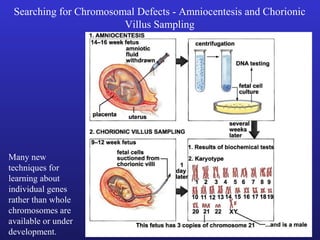
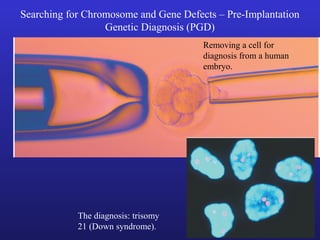
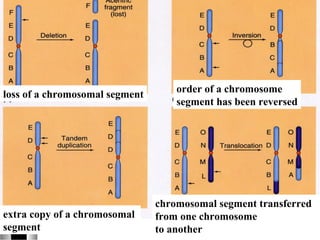
3. Chromosomal mutations involve changes in chromosome structure or number, such as deletions, inversions, duplications, and translocations, and can also cause genetic disorders.