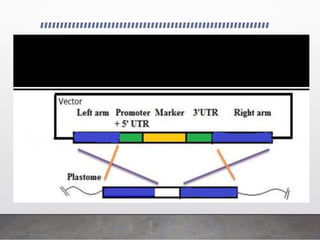
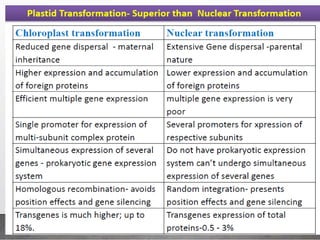
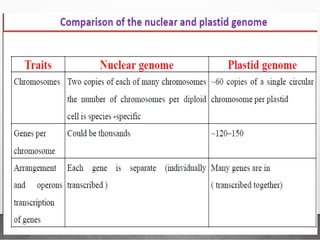
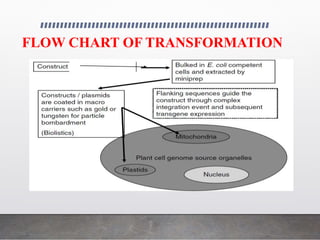
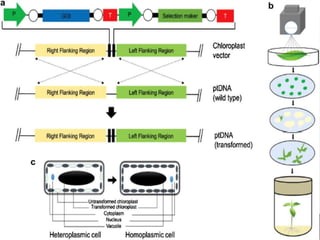
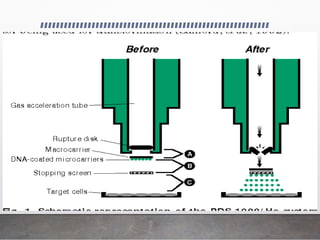
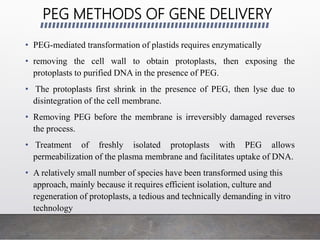
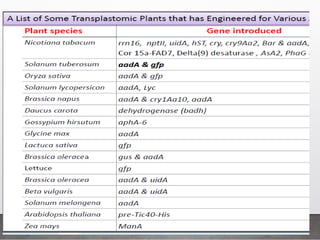
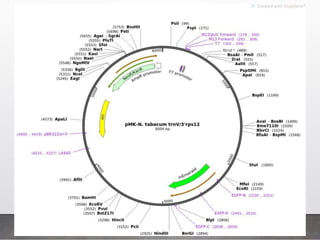
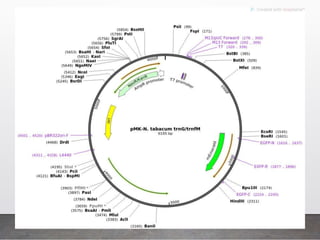
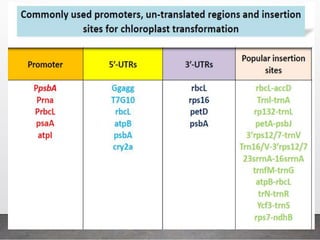
Chloroplast transformation allows for the integration of foreign genes into the chloroplast genome. This is beneficial as it provides high levels of transgene expression without epigenetic effects or position effects. Chloroplast transformation requires a chloroplast specific expression vector, a method for DNA delivery such as biolistics, and an efficient selection marker such as spectinomycin resistance. Successful transformation is confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analysis showing integration of the transgene into the chloroplast genome. Applications of chloroplast transformation include production of biopharmaceuticals, vaccines, industrial enzymes, and biomaterials as well as phytoremediation.