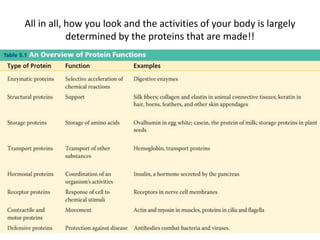
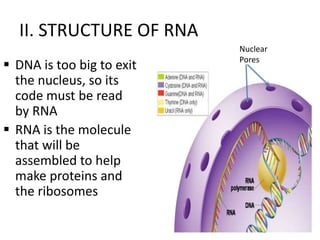
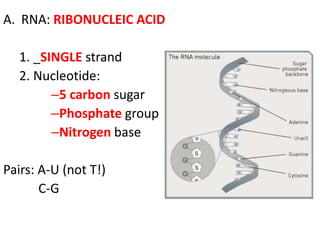
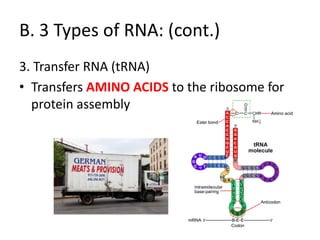
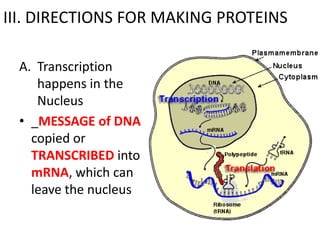
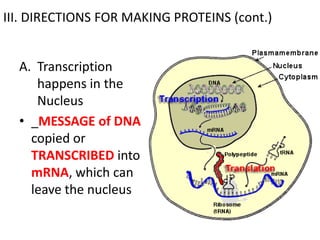
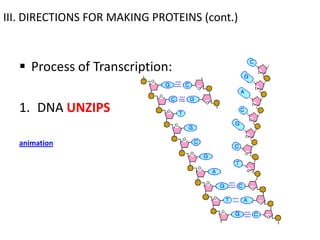
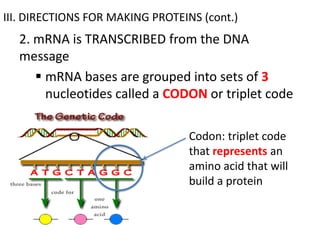
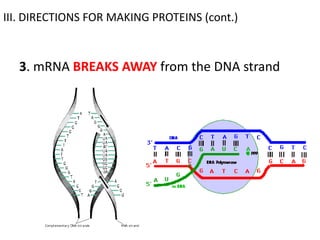
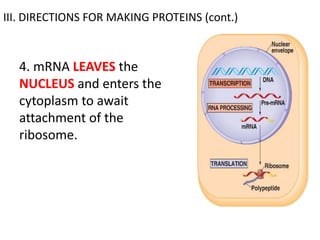
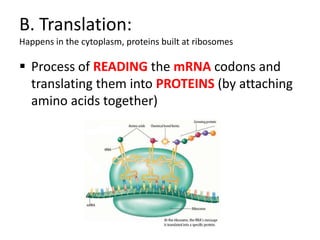
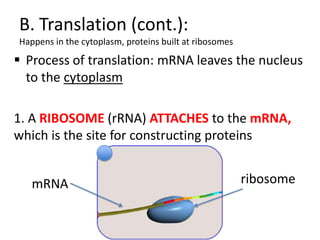
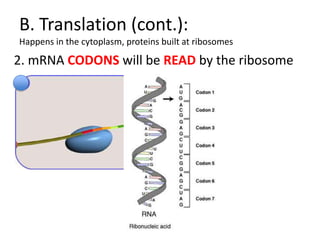
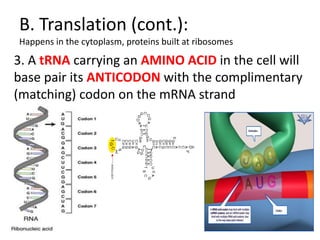
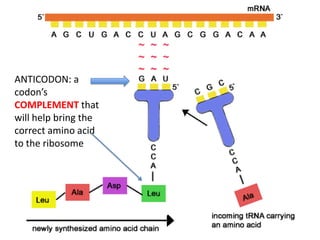
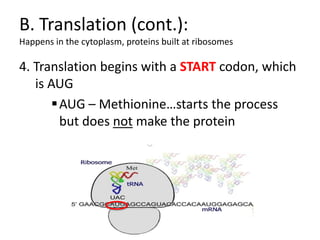
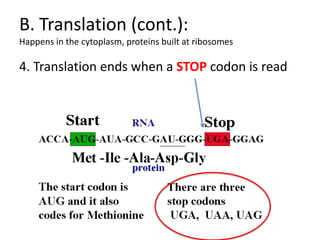
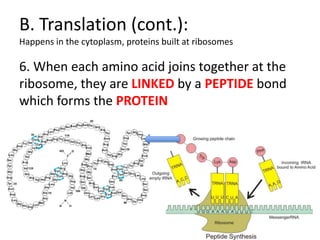
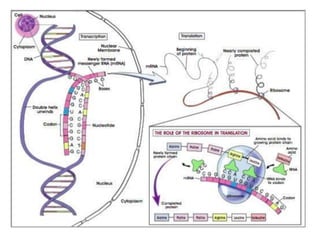
The genetic message of DNA is transcribed into mRNA and then translated into proteins. During transcription, the DNA unwinds and mRNA is produced that carries the protein code out of the nucleus. There are three types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA and tRNA. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm where ribosomes read the mRNA codons and join amino acids specified by each codon into proteins via peptide bonds. tRNA molecules match amino acids to codons to enable protein assembly according to the DNA's genetic instructions.