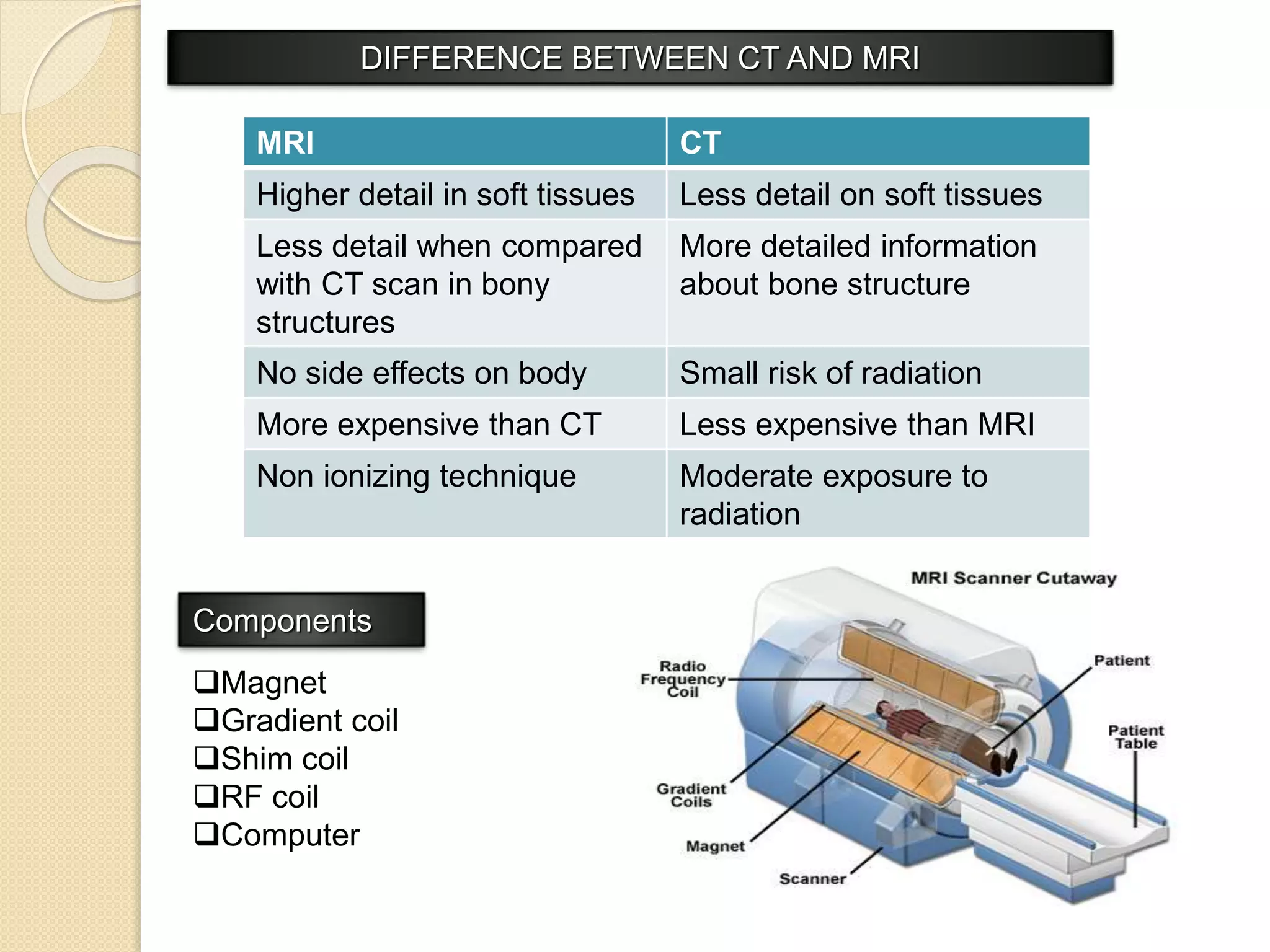
The document discusses Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), a technique used to visualize the interior of the human body using magnetic fields and radio waves. MRI offers advantages such as detailed soft tissue imaging, real-time 3D views, and non-radiative methods, making it particularly effective for detecting pre-cancerous cells. It contrasts MRI with CT scans, highlighting differences in detail, exposure to radiation, and costs.