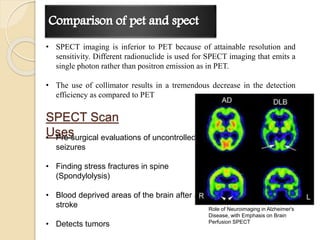
Single Photon Emission Tomography (SPECT) is a diagnostic tool used to detect single photons from radionuclide tracers, aiding in the reconstruction of 3D images for medical evaluations, including tumor detection and bone scans. The technique relies on gamma-ray photons emitted from radiopharmaceuticals and typically utilizes thallium-activated sodium iodide detectors with a specific radiopharmaceutical for imaging. While SPECT provides valuable functional information, it is generally inferior to Positron Emission Tomography (PET) in terms of resolution and sensitivity.