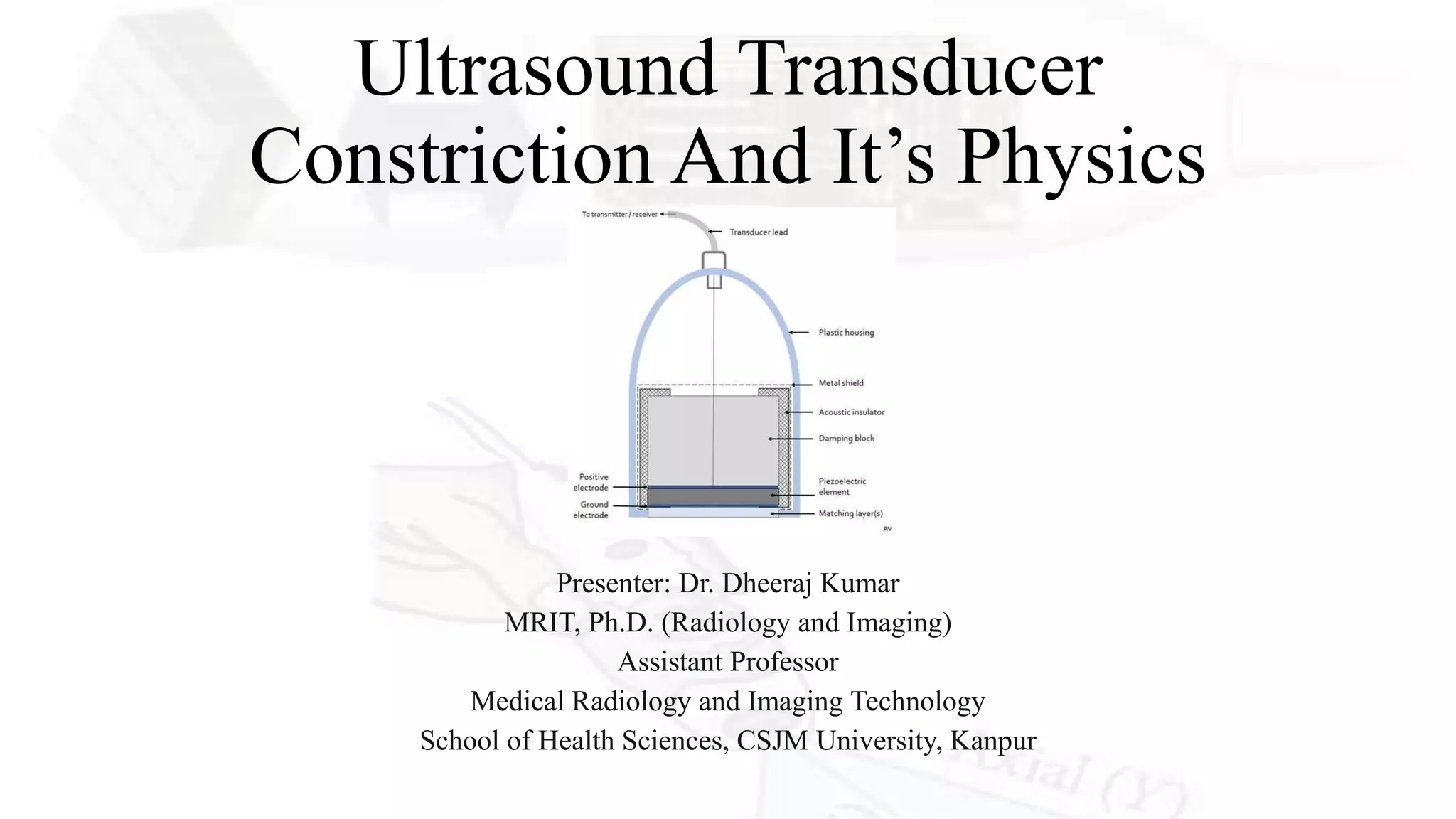
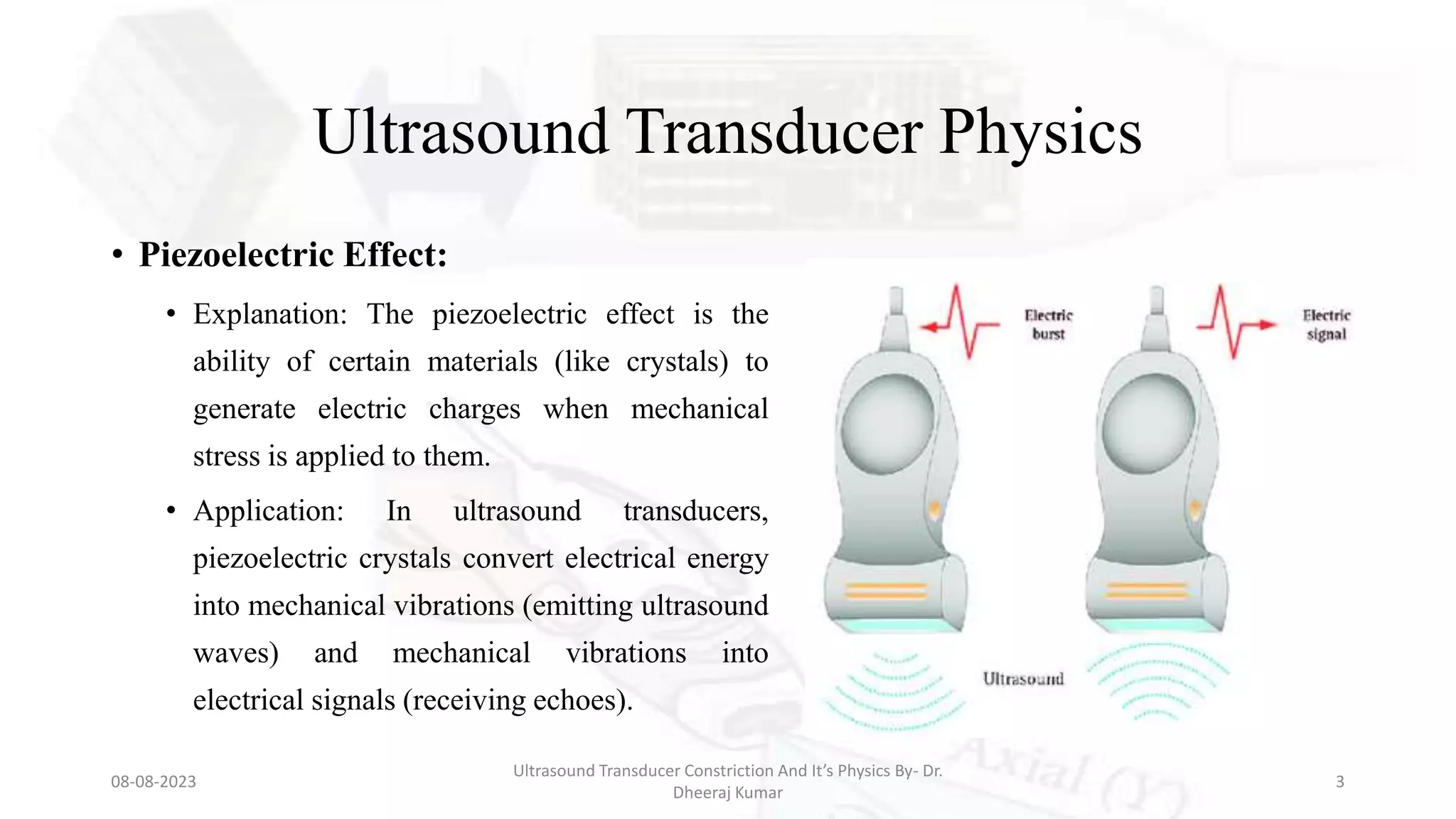
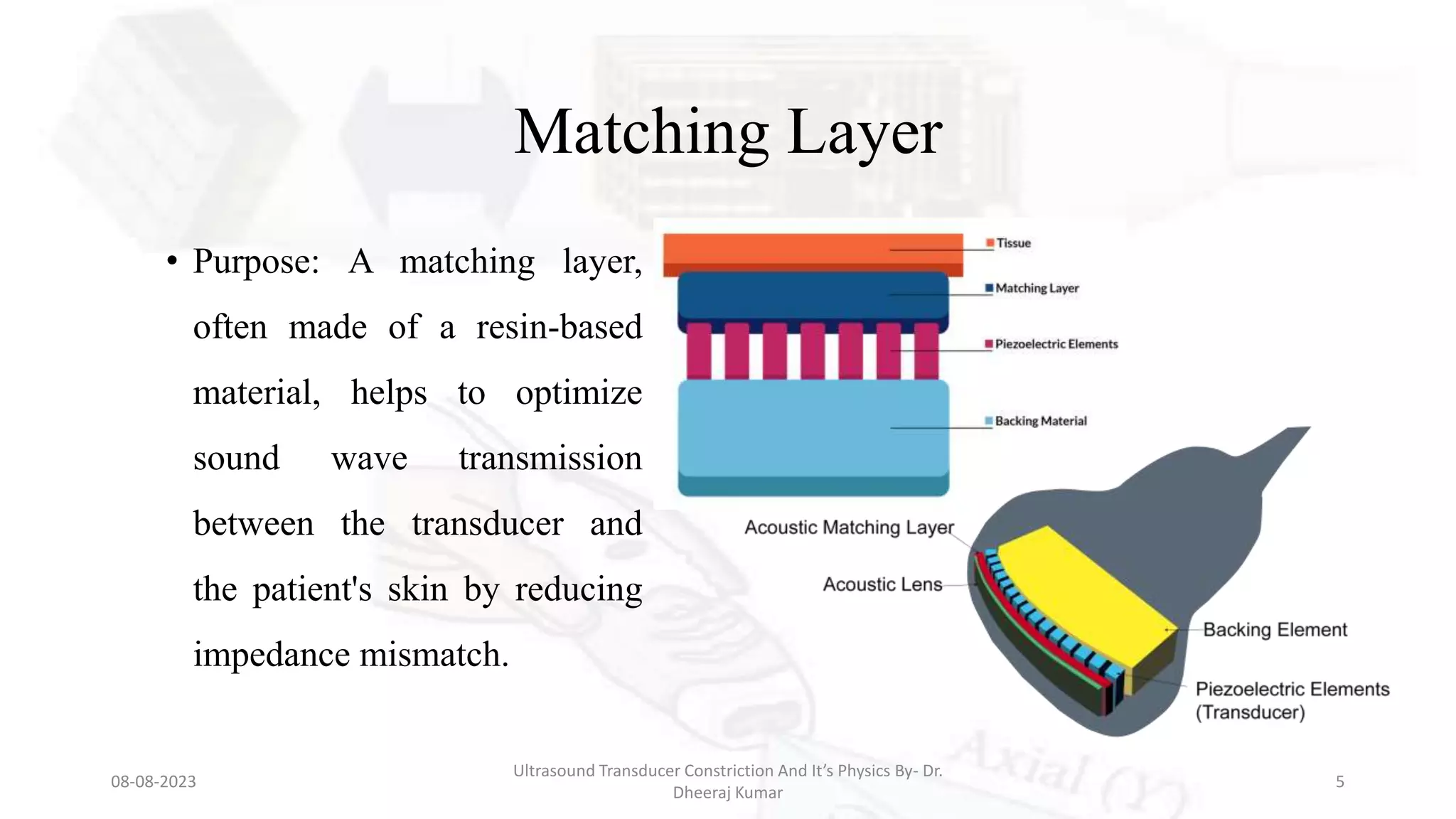
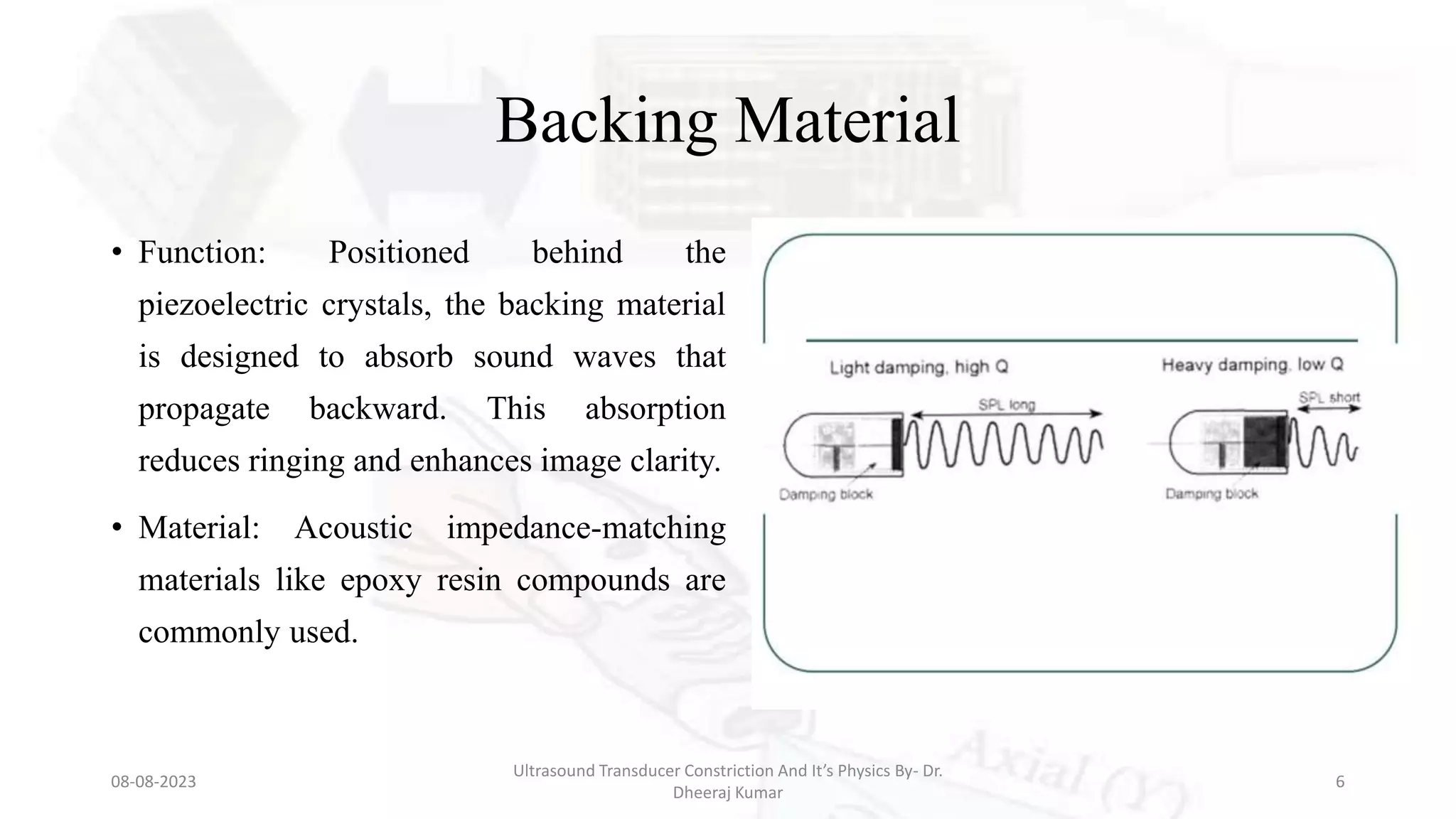
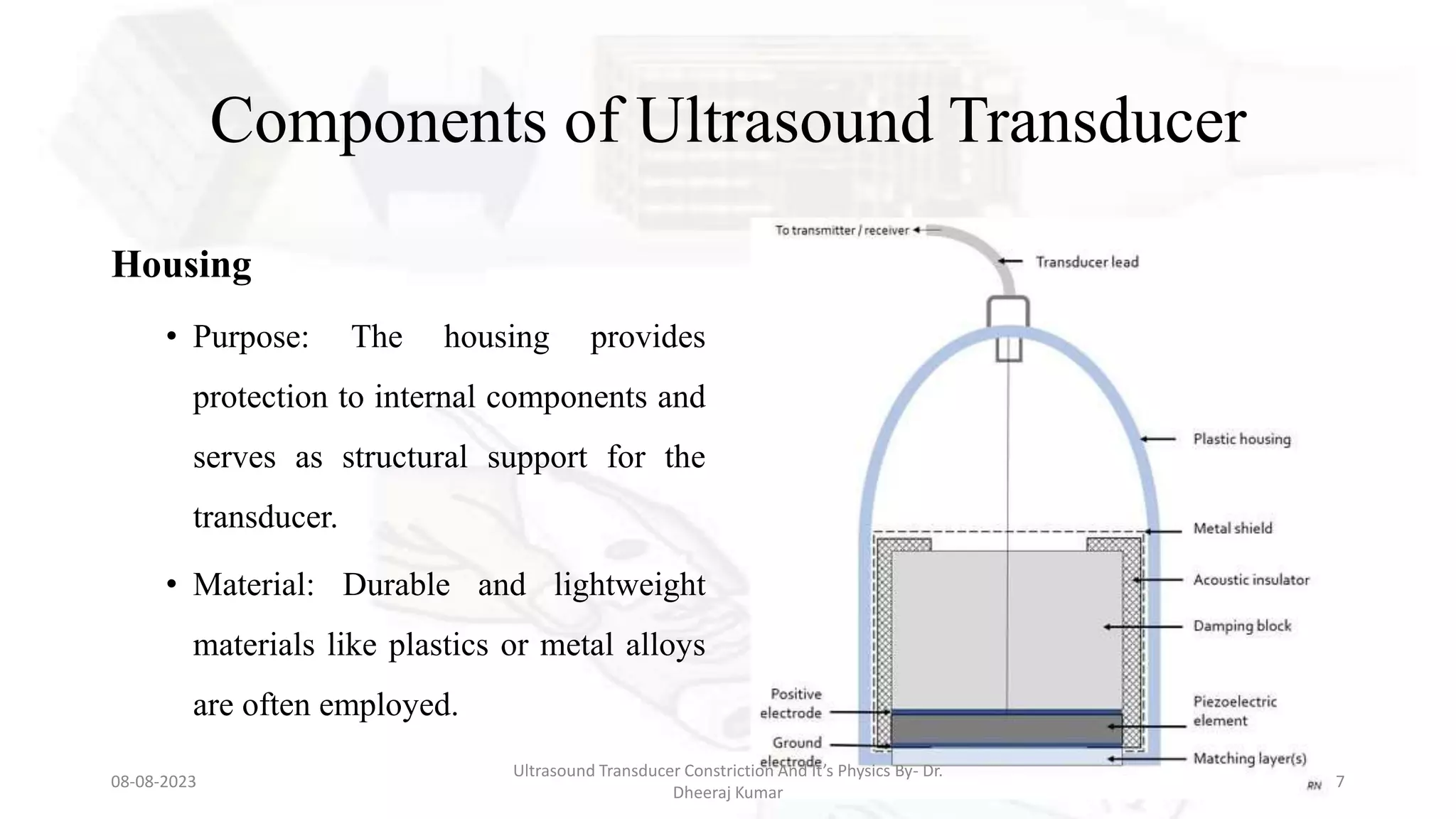
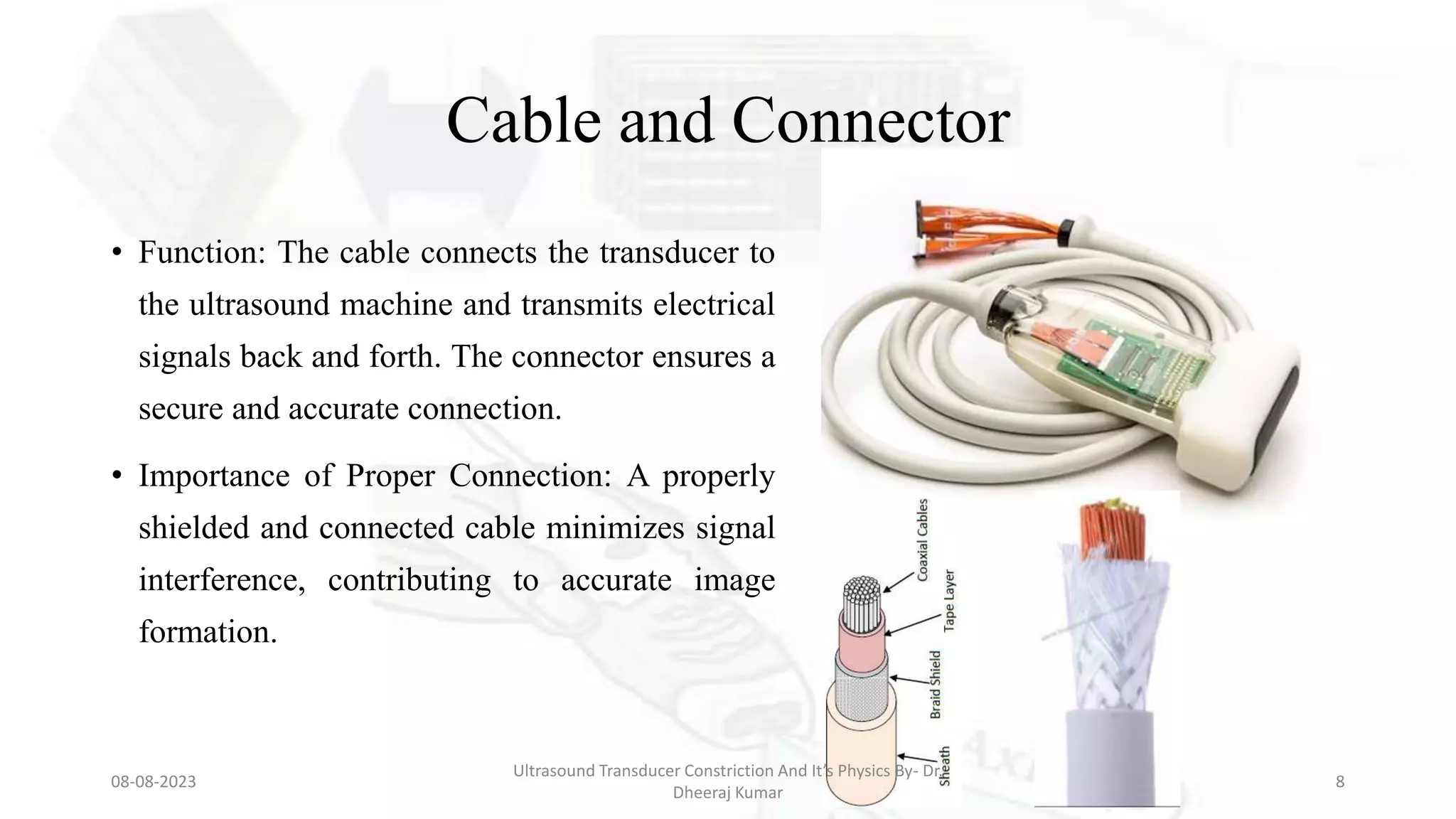
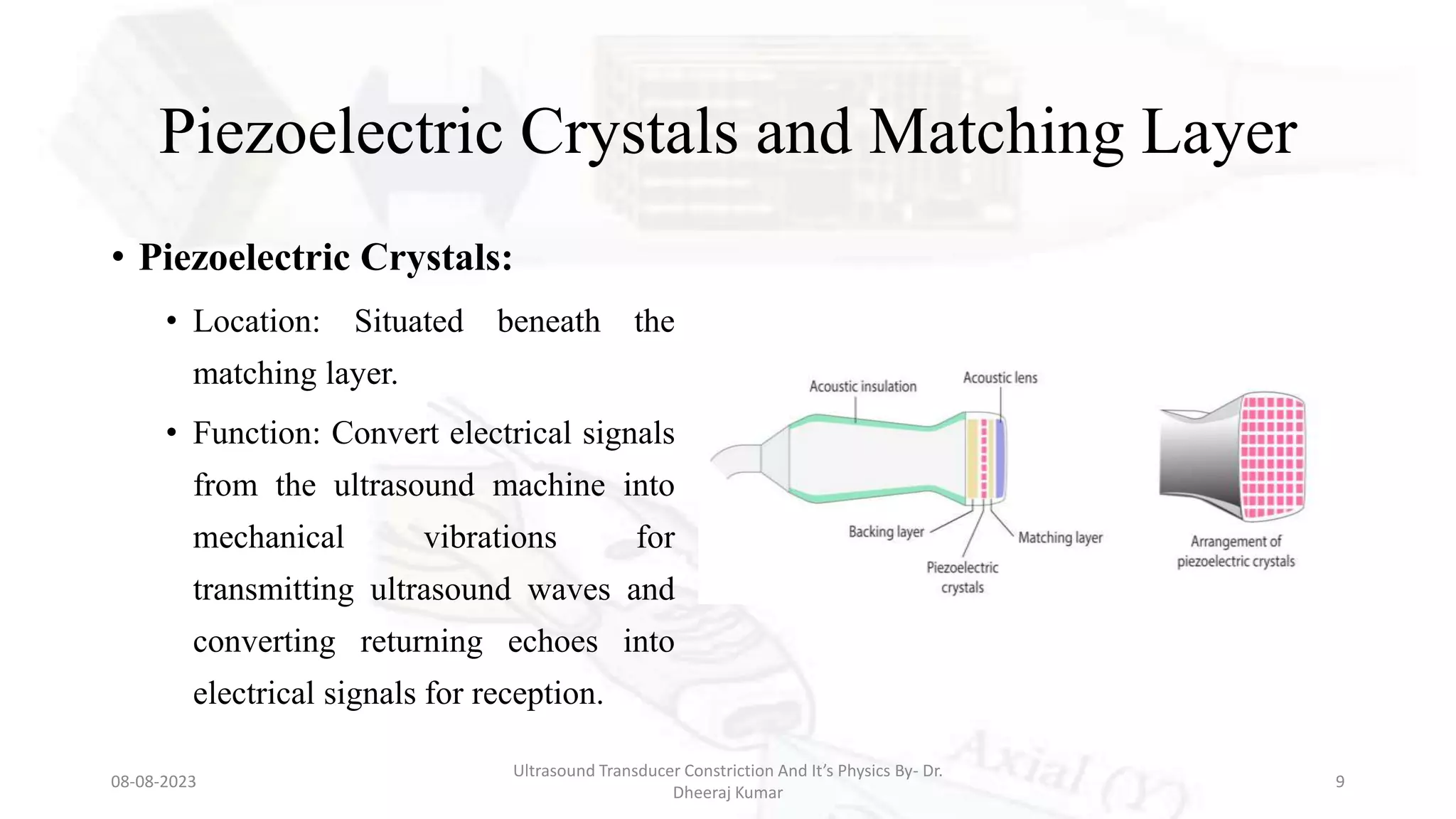
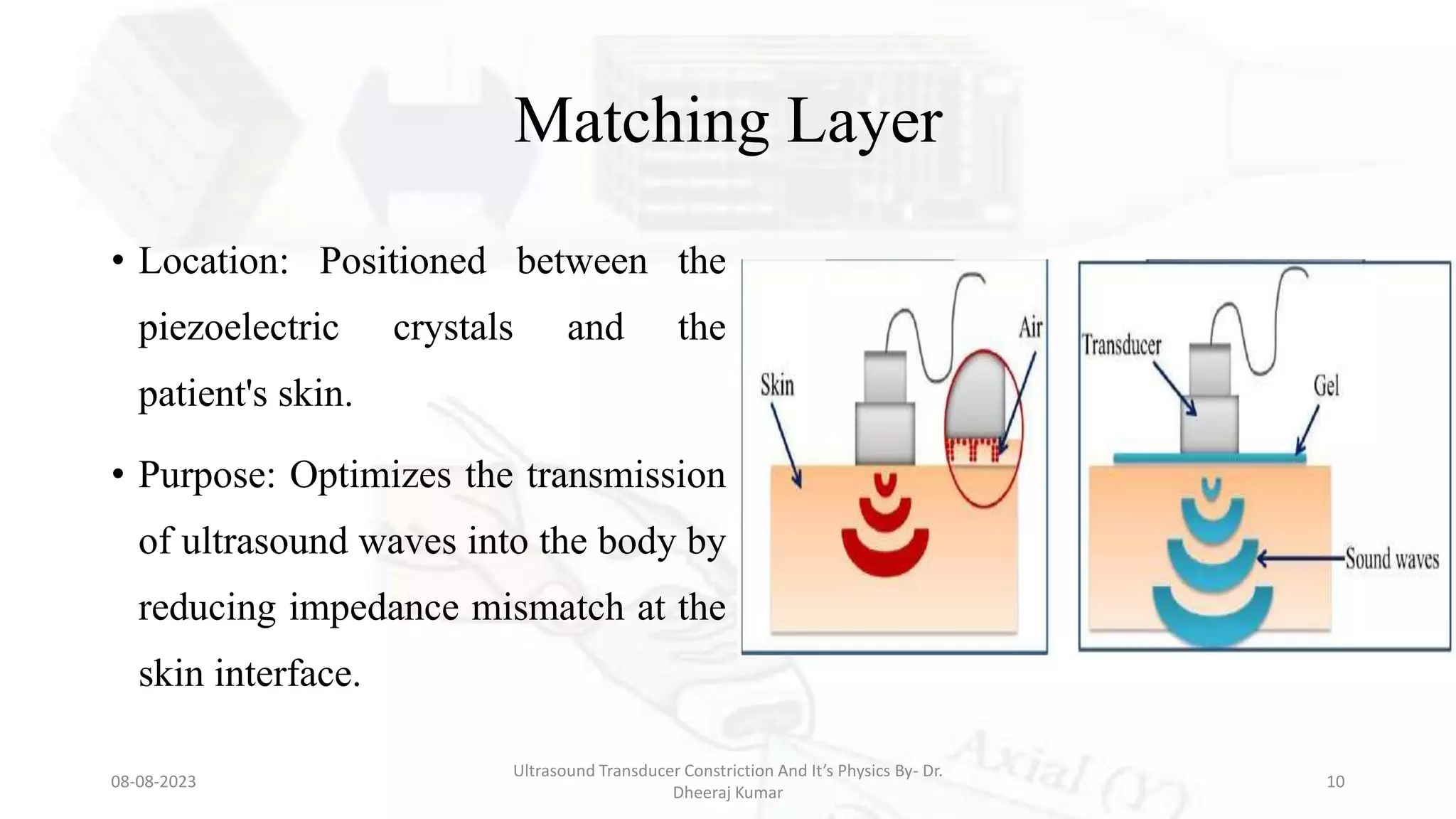
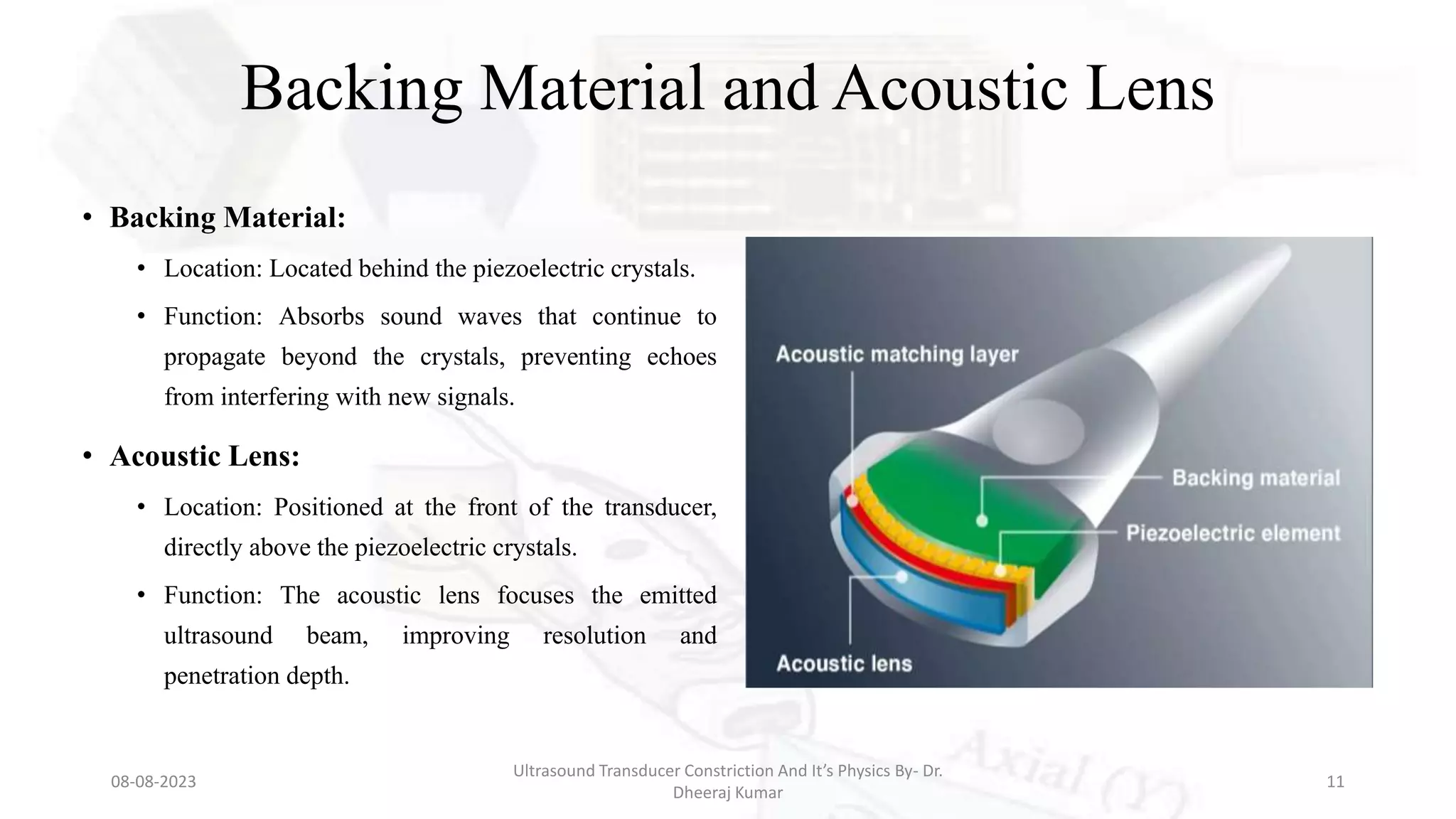
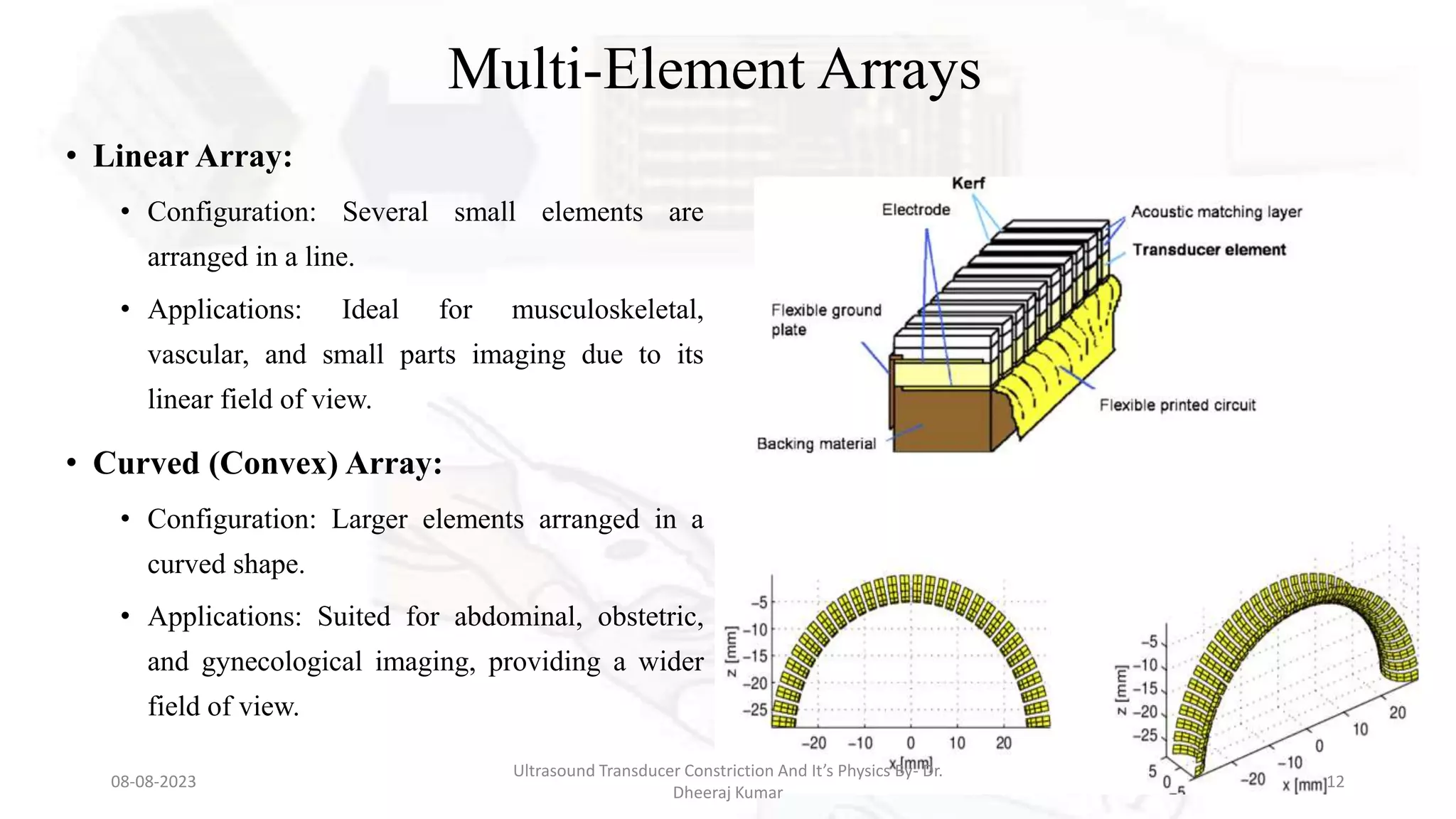
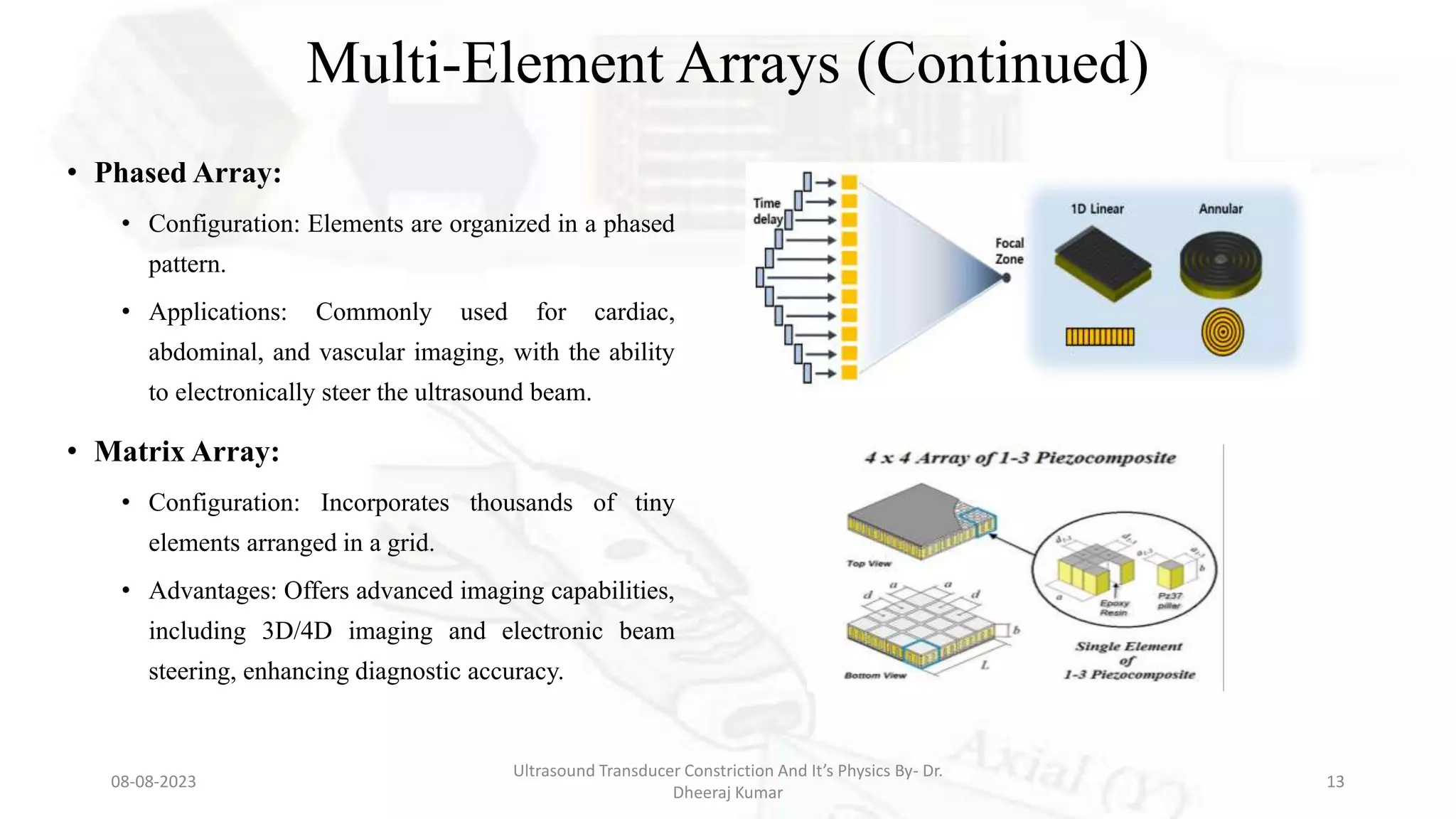
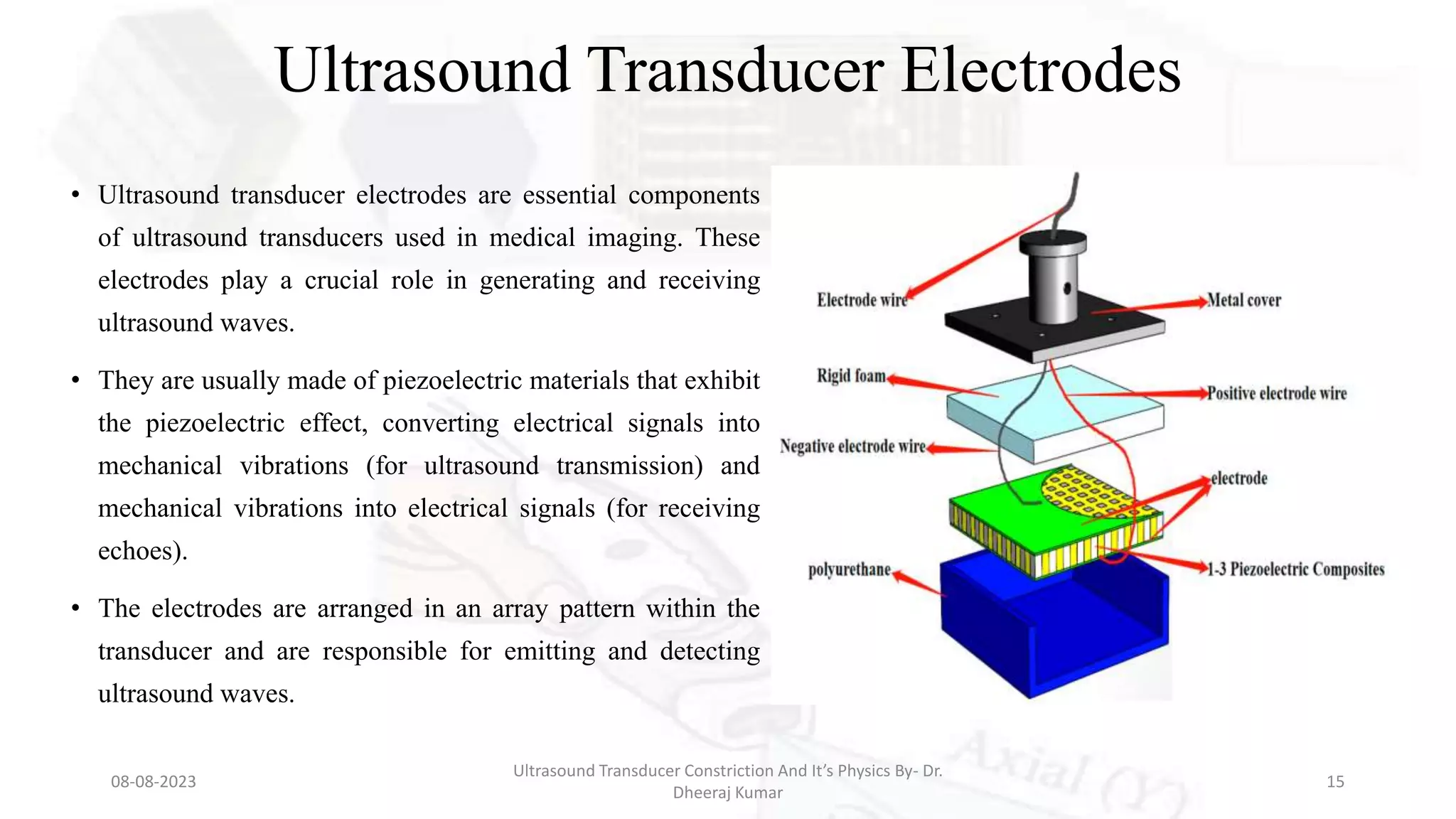
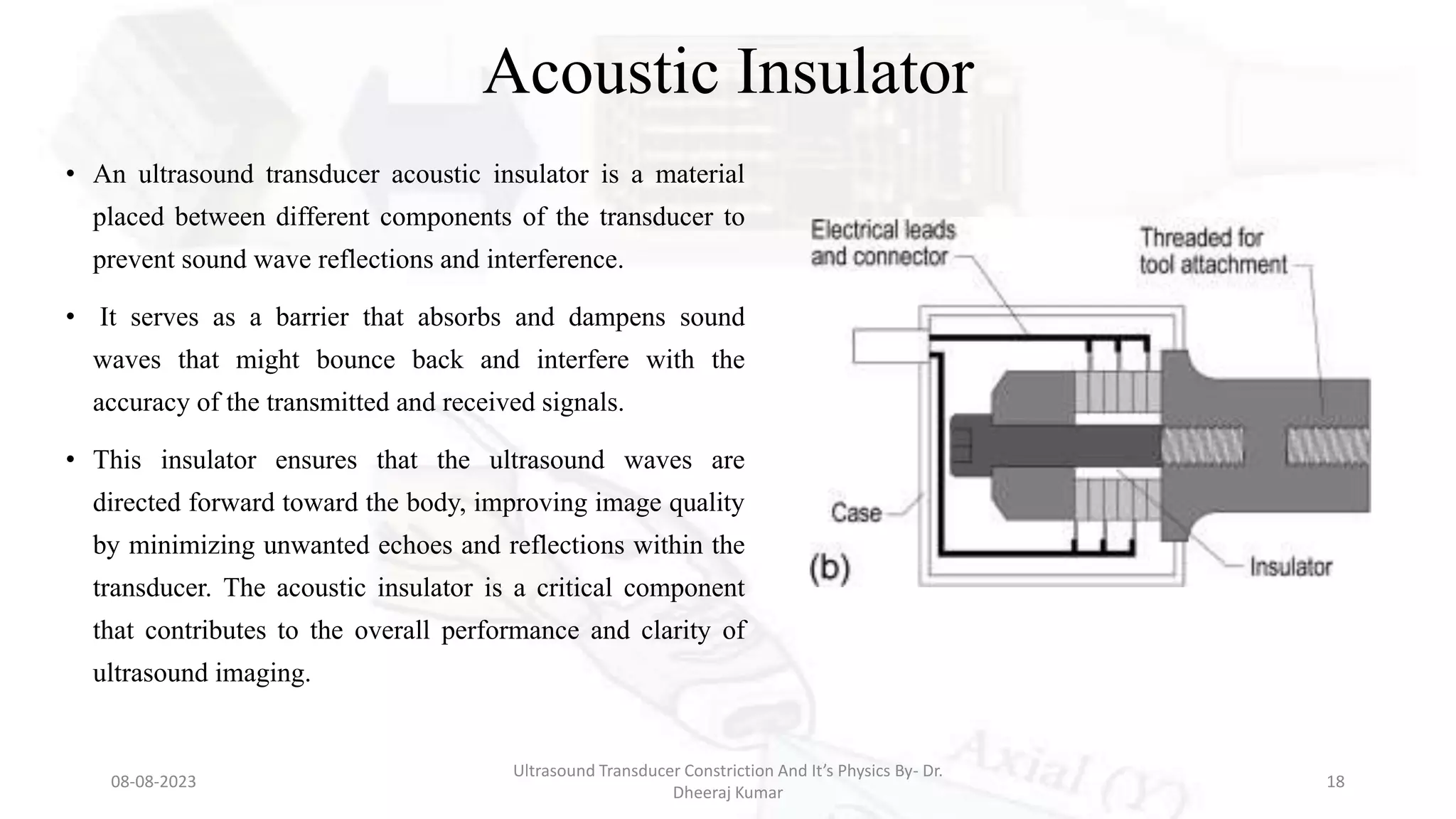
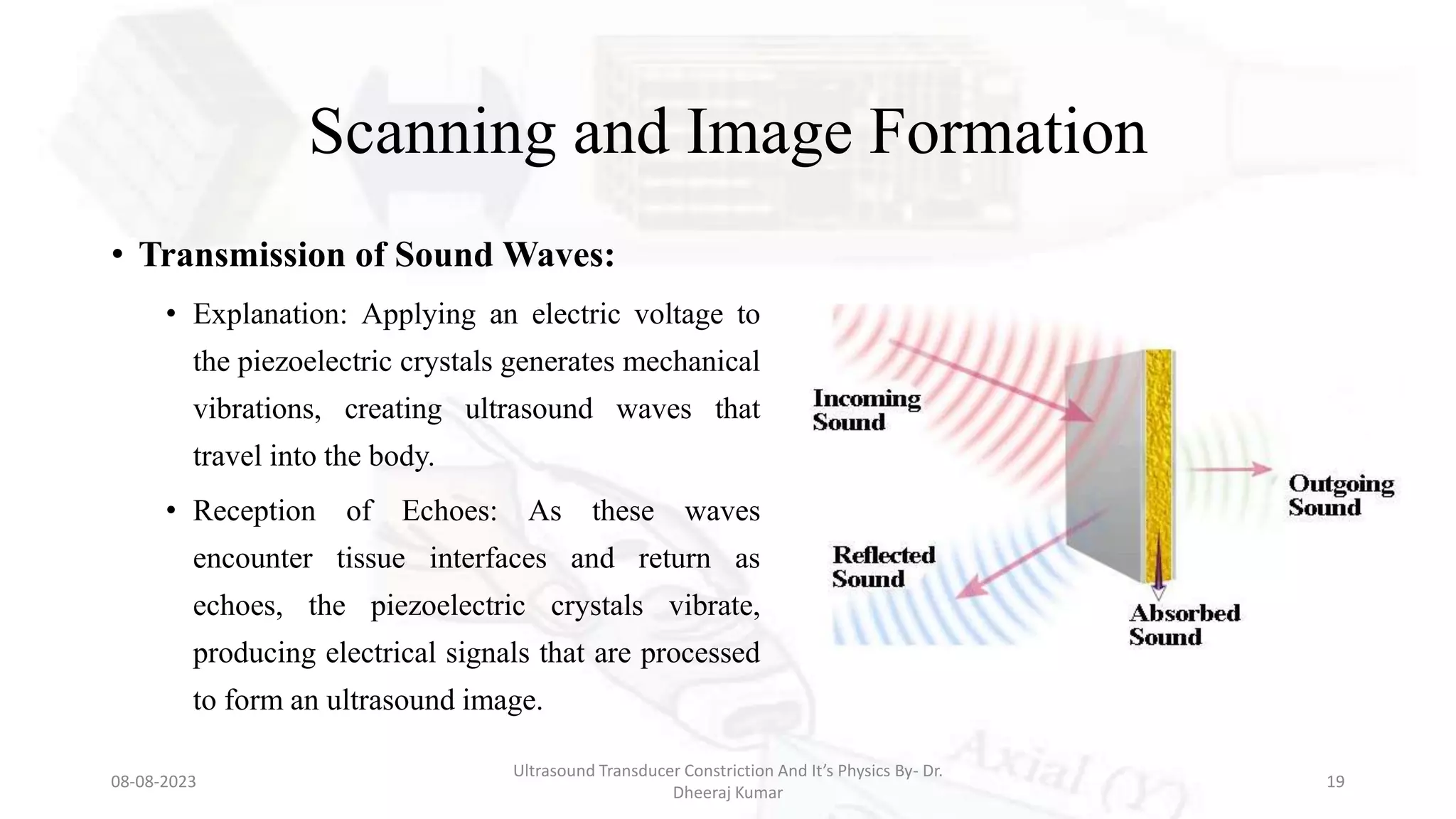
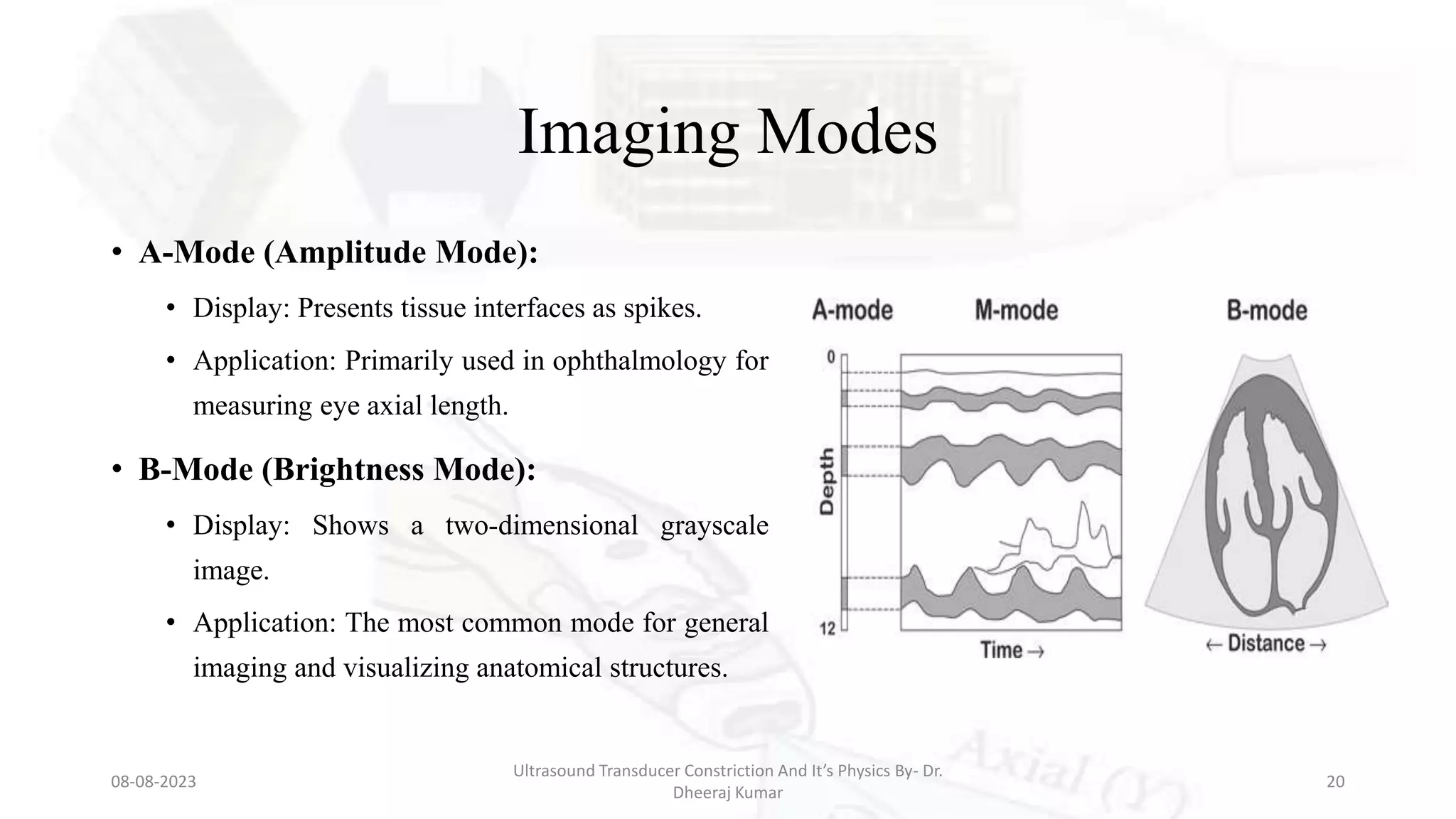
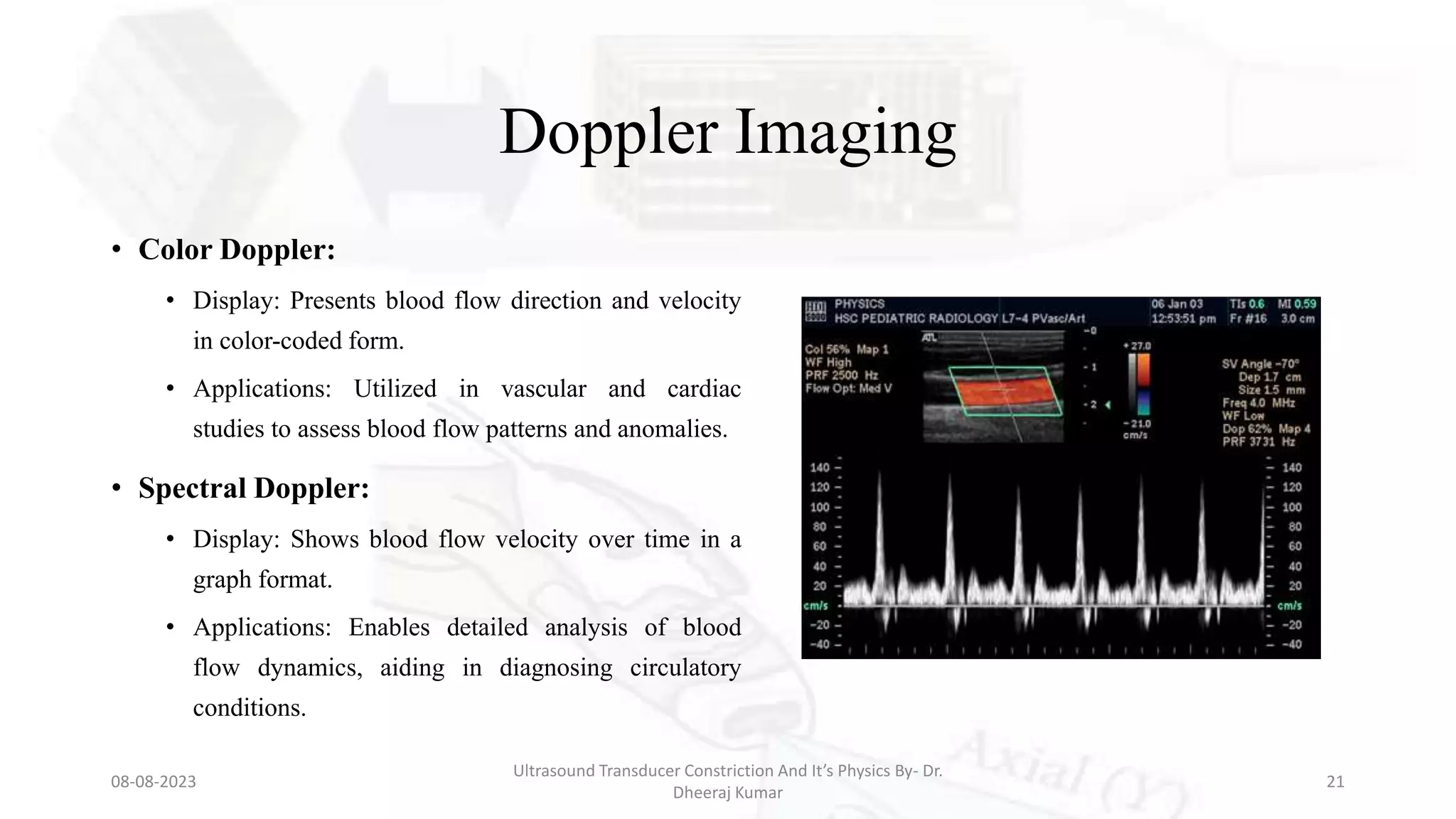
This document presents an overview of ultrasound transducers, detailing their definition, physics, materials, and key components essential for medical imaging. It covers the piezoelectric effect, construction materials like piezoelectric crystals, and the function of various components such as matching layers and backing materials. The presentation emphasizes the importance of understanding transducer mechanics for radiology students and discusses advancements in ultrasound technology for improved diagnostic accuracy.