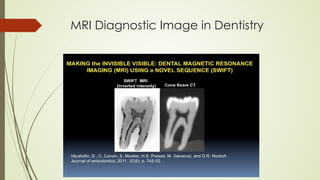
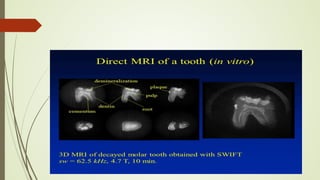
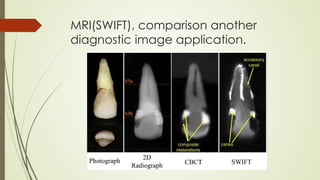
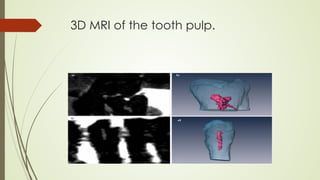
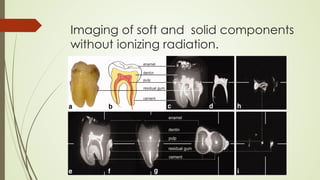
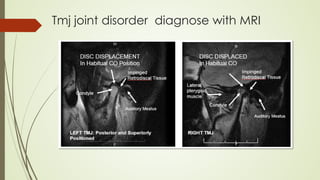
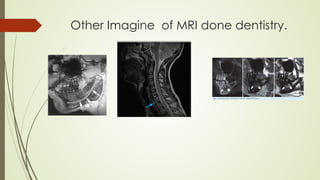
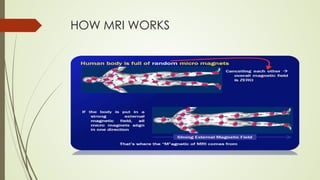
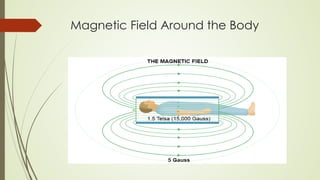
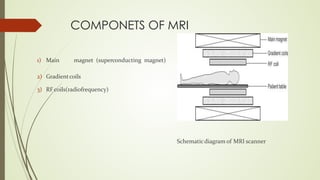
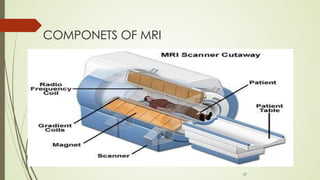
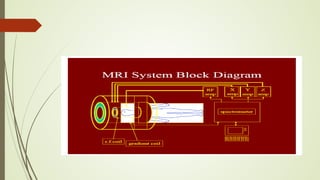
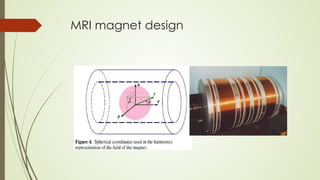
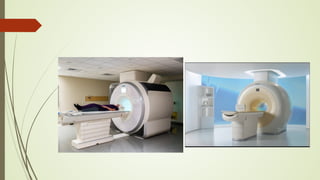
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the inside of the body. It was first developed in the 1970s and allows doctors to diagnose issues without exposing patients to radiation. An MRI scan works by aligning hydrogen atoms in the body using magnetism and radio waves. This causes the atoms to emit signals that are picked up by antennas and used by a computer to construct cross-sectional images of tissues and organs. MRI is useful for dental applications as it can image soft tissues like tooth pulp and the temporomandibular joint with high resolution, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.