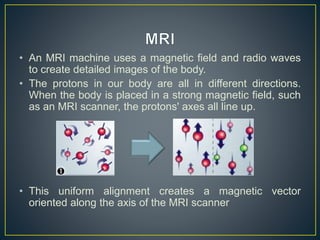
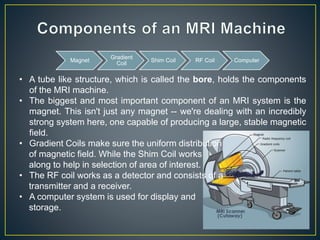
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. An MRI machine contains a powerful magnet that aligns hydrogen atoms in the body. Radio waves are then used to produce signals from the hydrogen atoms, which are detected by antennas and used to construct an image on a computer. MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues and organs in the body without using ionizing radiation.