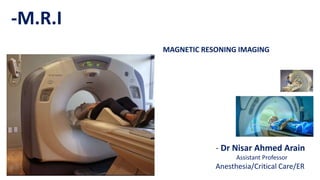
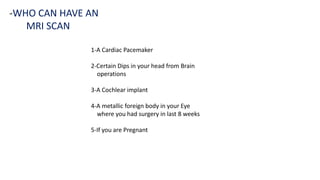
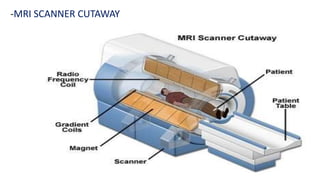
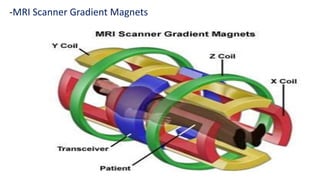
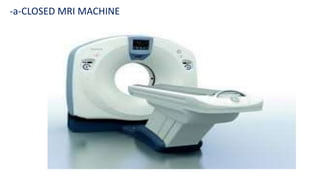
1. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and tissues in the body.
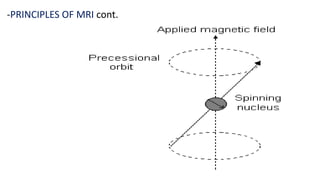
2. MRI scanners use powerful magnets and radio waves to align hydrogen atoms in the body and produce signals that can be used to generate cross-sectional images of organs and tissues.
3. The first human MRI was performed in 1977 and took 5 hours to produce an image, whereas modern MRI machines can generate high-quality images much more quickly.