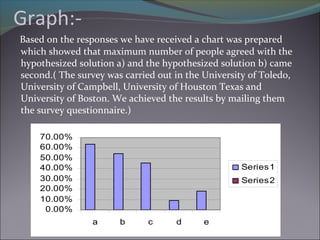
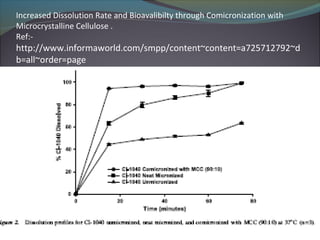
The document discusses the micronization process in the pharmaceutical industry, highlighting its objectives, factors influencing the process, and case studies of drug recalls due to micronization issues. It emphasizes the importance of controlling particle size to improve bioavailability and outlines critical problems faced by companies, including the need for regulatory compliance. A survey conducted at several universities indicated support for proposed solutions to enhance micronization effectiveness and quality assurance.












![letter1) FDA issued a 483 to a leading pharmaceutical company for
failing to comply with cGMP regulations governing manufacturing
equipment used in Micronization.
“Failure to qualify manufacturing equipment such as the liquid
filler, homogenizer and colloidal mill, which were used to
manufacture all liquid finished products at your facility [21 CFR
211.68(a)].”
Ref:--http://www.fda.gov/foi/warning_letters/s6357c.htm
According to you which kind of strategies or corrective actions
should be followed by the company?: (Pl select the 2 most
appropriate corrective actions.)
1)A full review of all lots within expiration in the market to assure
that the released drug products have their appropriate identity,
strength, quality, and purity.
2)To validate the reprocessing procedure and the extent of the
validation.
3)To recall the drug from the market.
4)To provide written procedures for conducting periodic product](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/micronization2003-12588686383593-phpapp01/85/Micronization-2003-14-320.jpg)