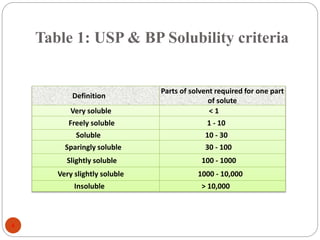
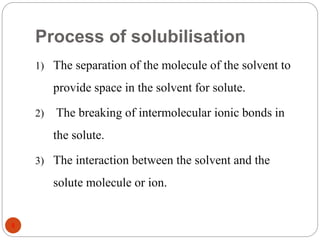
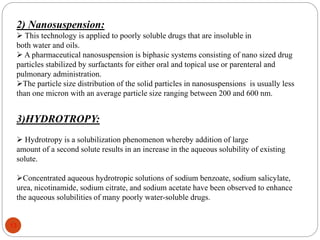
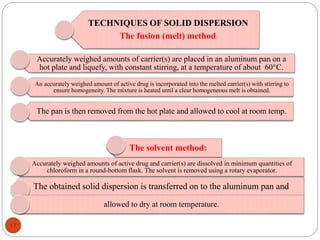
This document discusses various techniques for enhancing the solubility of drugs, including particle size reduction, hydrotropy, cosolvency, solubilization by surfactants, solid dispersions, pH adjustment, high pressure homogenization, supercritical fluid recrystallization, sonocrystallization, complexation, spray drying, inclusion complex formation, liquisolid technique, microemulsions, and self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Particle size reduction techniques like micronization and nanosuspensions increase surface area to enhance dissolution rate and solubility. Other techniques utilize excipients like surfactants, cosolvents, and polymers to solubilize drugs.