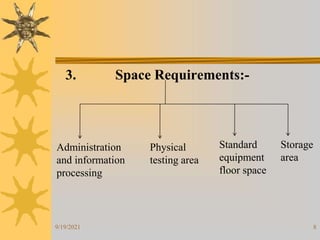
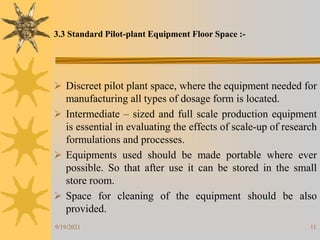
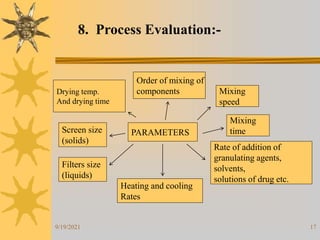
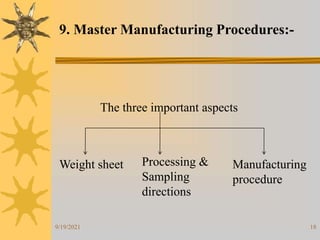
This document provides information on pilot plants and scale-up in the pharmaceutical industry. It defines pilot plants as where lab-scale formulas are transformed into viable products through reliable manufacturing procedures. The significance of pilot plants is that they allow examination of formulas to determine suitability for batch scale-up and process modification. General considerations for pilot plants include having appropriate personnel, space, equipment, and procedures to support good manufacturing practices and product validation. The document also discusses advantages like quality control observation and material sourcing, as well as disadvantages such as potential reduced interaction between formulation and production teams.