This document discusses the importance of preformulation studies, specifically focusing on partition coefficient, dissociation constant, and solubility. It defines these key terms and explains their significance in determining drug absorption and developing drug formulations. The partition coefficient indicates a drug's lipophilicity and ability to cross cell membranes. The dissociation constant and Henderson-Hasselbalch equation are used to predict drug ionization and site of absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Solubility is critical for bioavailability and influences formulation strategies to increase or decrease a drug's aqueous solubility. Understanding these physicochemical properties is essential for designing an optimal drug delivery system.










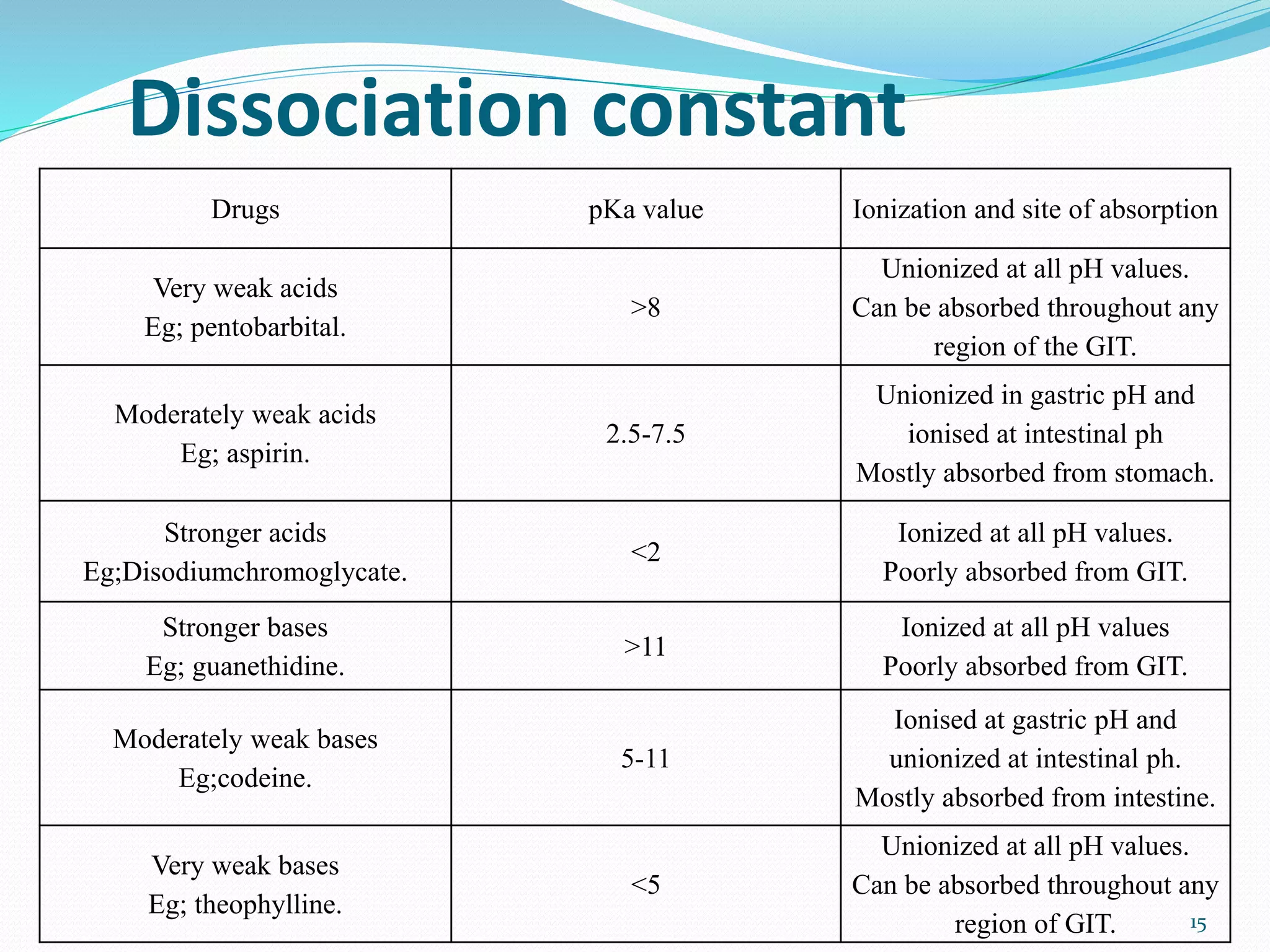
![Dissociation constant:
At a particular ph the relative concentration of
unionised and ionised species in a drug solution can
be estimated with the help of Henderson-hasselbalch
equation;
For acidic drugs- pH= pKa + log [ionised
drug]/[unionised drug]
For basic drugs- pH= pKa + log [unionised
drug]/[ionised drug]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importanceofpartitioncoefficientsolubilityanddissociation-170306172541/75/Importance-of-partition-coefficient-solubility-and-dissociation-on-pre-formulation-studies-12-2048.jpg)











![Reference
Lachman, Leon, and Herbert A Liebermann. The Theory
and Practice Of Industrial Pharmacy. New Delhi: CBS
Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd., 2012.
Tripathi, D.K. Industrial Pharmacy, A Comprehensive
Approach. Giriraj lane, Sultan Bazar,
Haydrabad.:PharmaMed Press, 2015.
Aulton, Michael E. Aulton's Pharmaceutics. Edinburgh:
Churchill Livingstone, 2007.
Academia.edu. CHAPTER – 1 Preformulation Studies
[Internet]. 2015 [cited 11 November 2015]. Available from:
http://www.academia.edu/7720904/CHAPTER_1_Preform
ulation _Studies
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importanceofpartitioncoefficientsolubilityanddissociation-170306172541/75/Importance-of-partition-coefficient-solubility-and-dissociation-on-pre-formulation-studies-26-2048.jpg)
