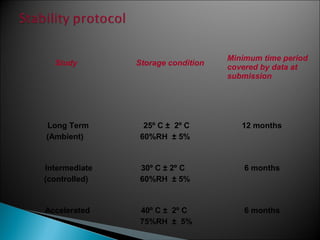
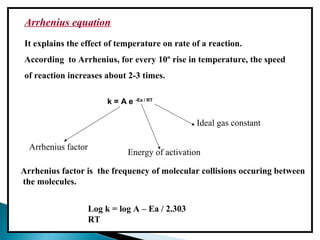
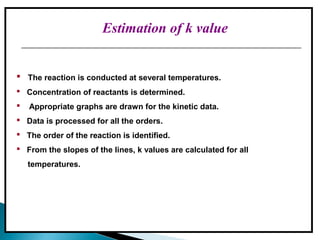
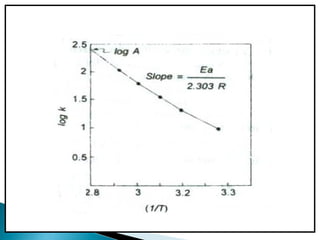
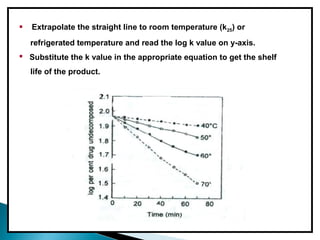
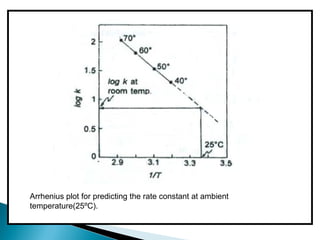
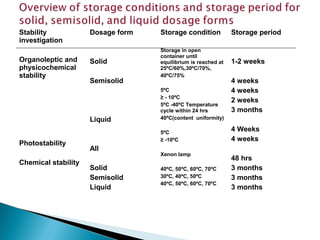
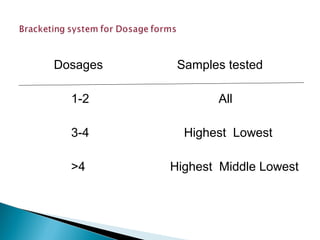
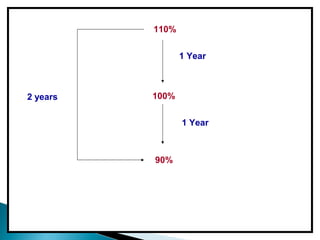
Accelerated stability testing exposes pharmaceutical products to elevated temperatures and humidity to rapidly determine their shelf life. Samples are stored at conditions like 40°C/75%RH and tested over time. The Arrhenius equation relates reaction rate constants at different temperatures, allowing prediction of shelf life at normal storage conditions from accelerated data. Limitations include reactions not dependent on temperature alone and products losing integrity at high stresses.