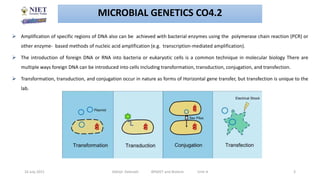
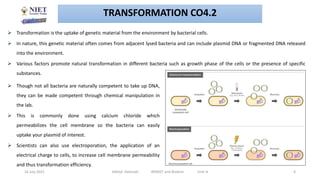
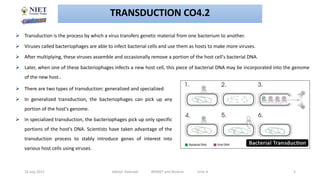
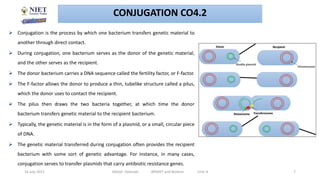
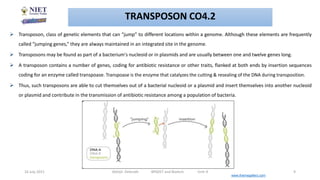
This document discusses various techniques in microbial genetics including transformation, transduction, conjugation, plasmids, and transposons. Transformation involves the uptake of genetic material like DNA by bacterial cells. Transduction occurs when viruses called bacteriophages transfer genetic material between bacteria. Conjugation is the transfer of genetic material like plasmids through direct contact between bacteria. Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules that are distinct from chromosomal DNA and often provide genetic advantages to bacteria. Transposons are genetic elements that can move to different locations in a genome and contribute to the spread of traits like antibiotic resistance.