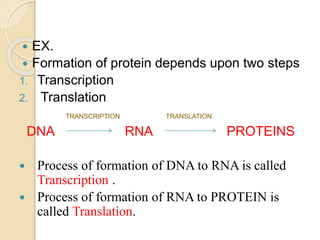
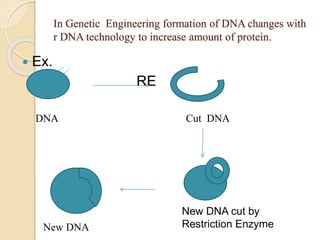
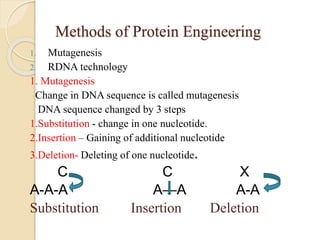
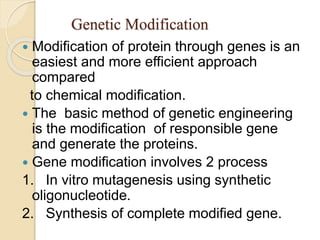
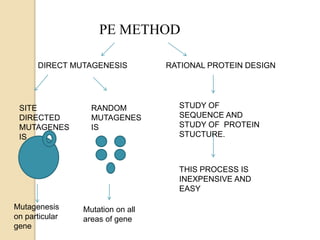
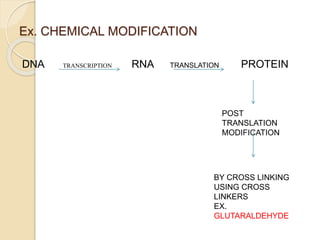
Protein engineering is the process of designing new proteins or enzymes with desirable functions. It involves modifying amino acid sequences through methods like site-directed and random mutagenesis, as well as recombinant DNA technology. The goal is to produce proteins in large quantities, or create enzymes with improved properties like thermal stability, activity in non-aqueous solvents, or altered substrate binding. Protein engineering has applications in pharmaceuticals, food/detergent industries, environmental remediation, and other areas.