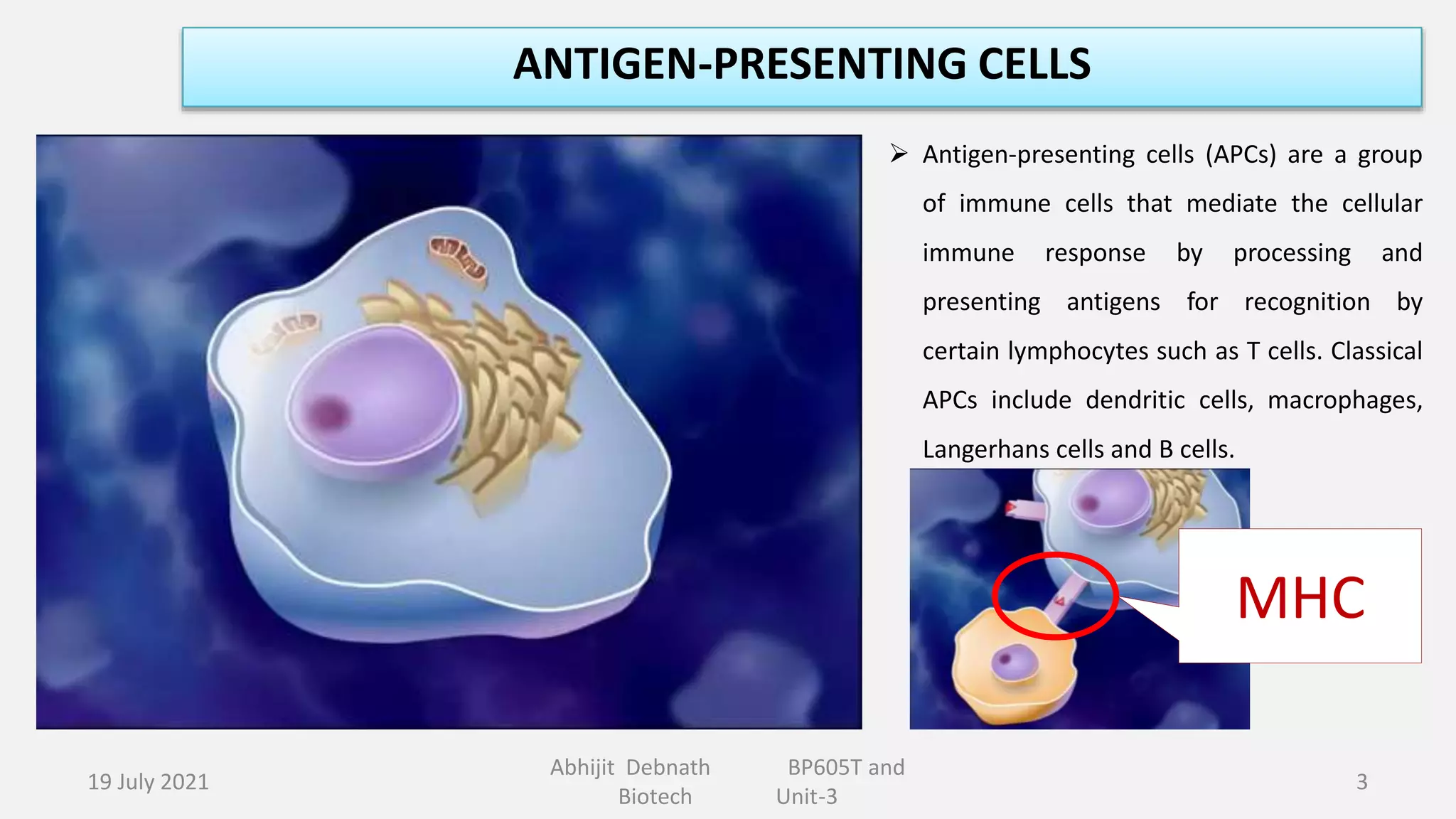
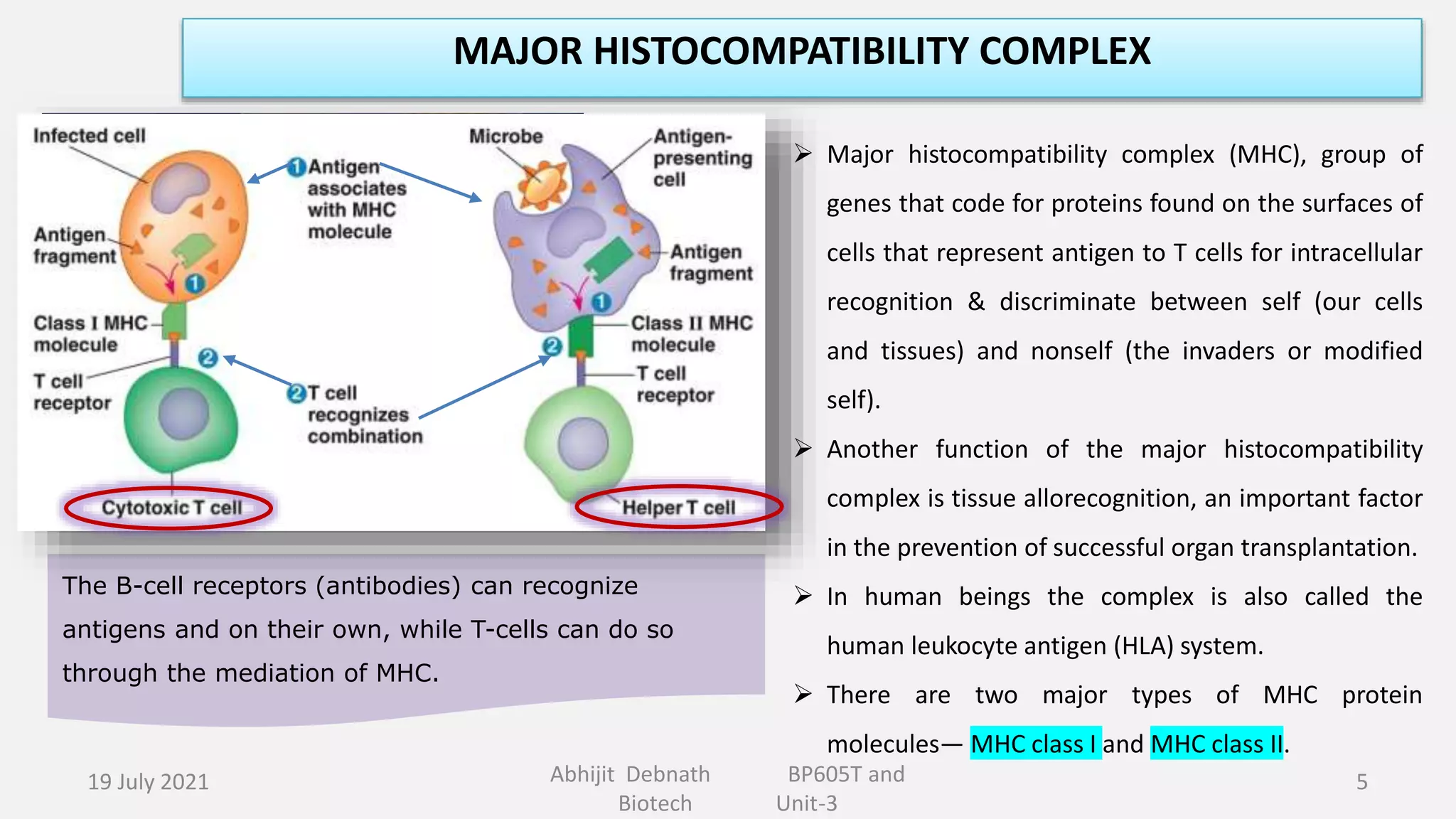
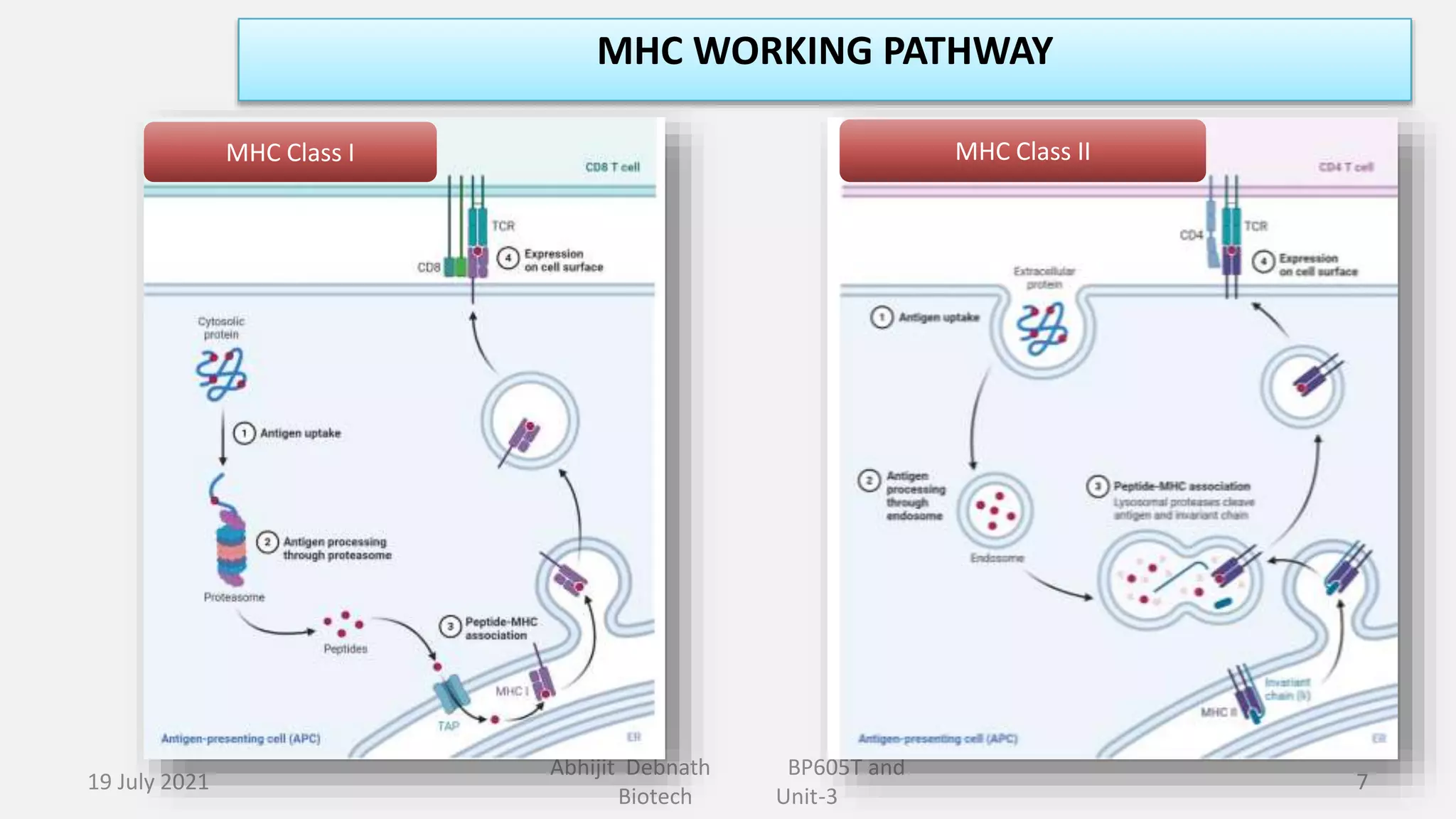
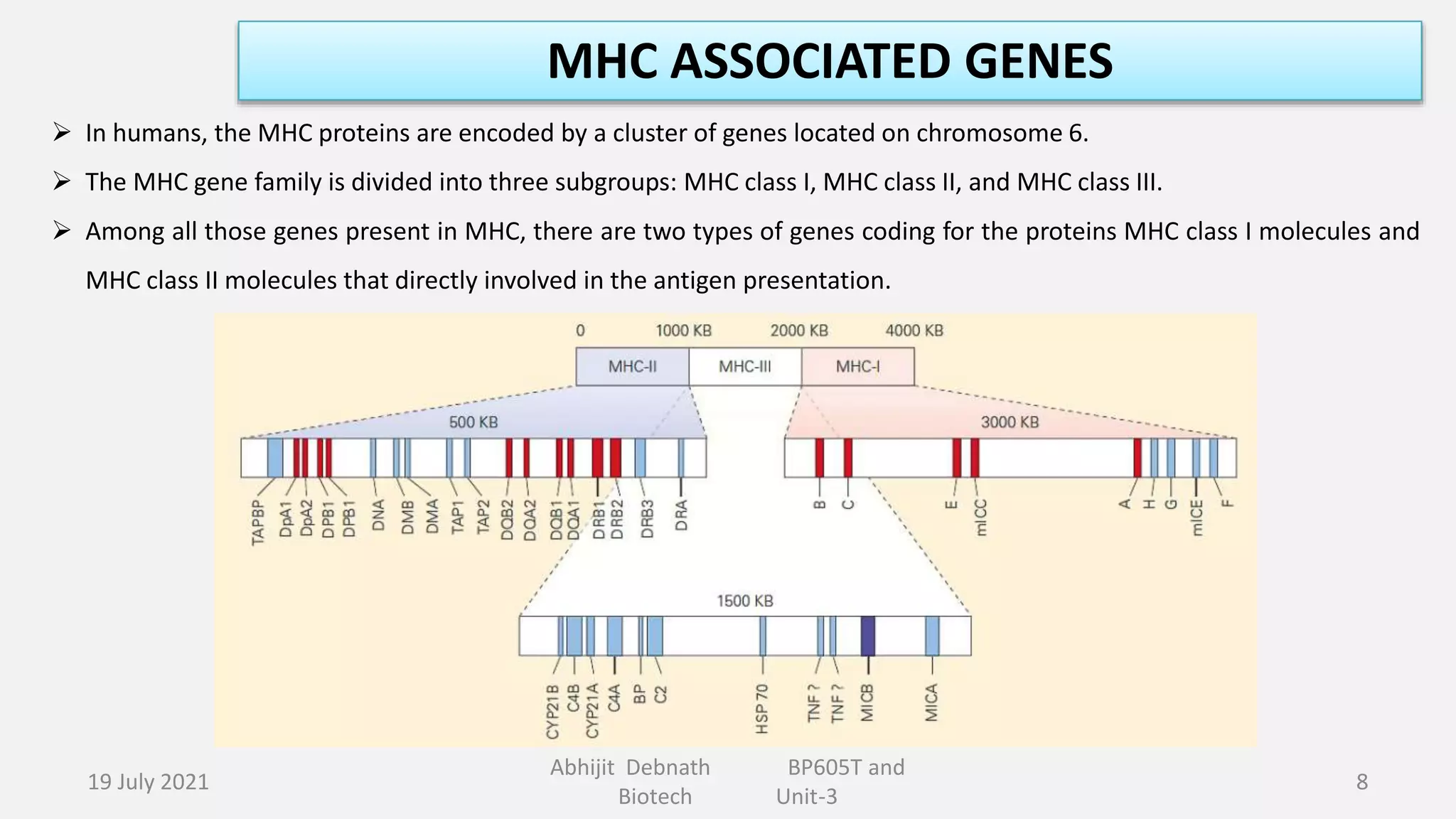
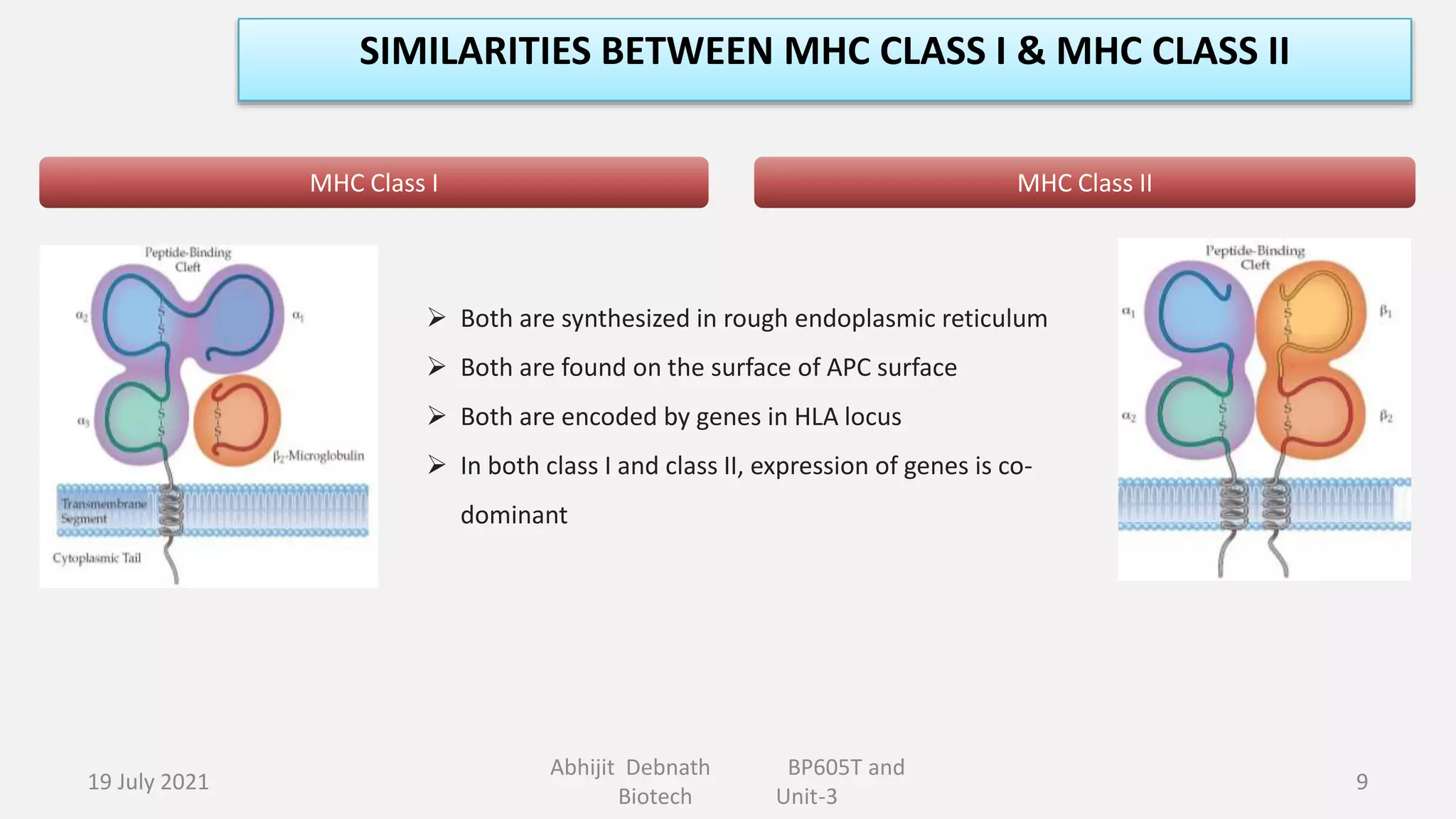
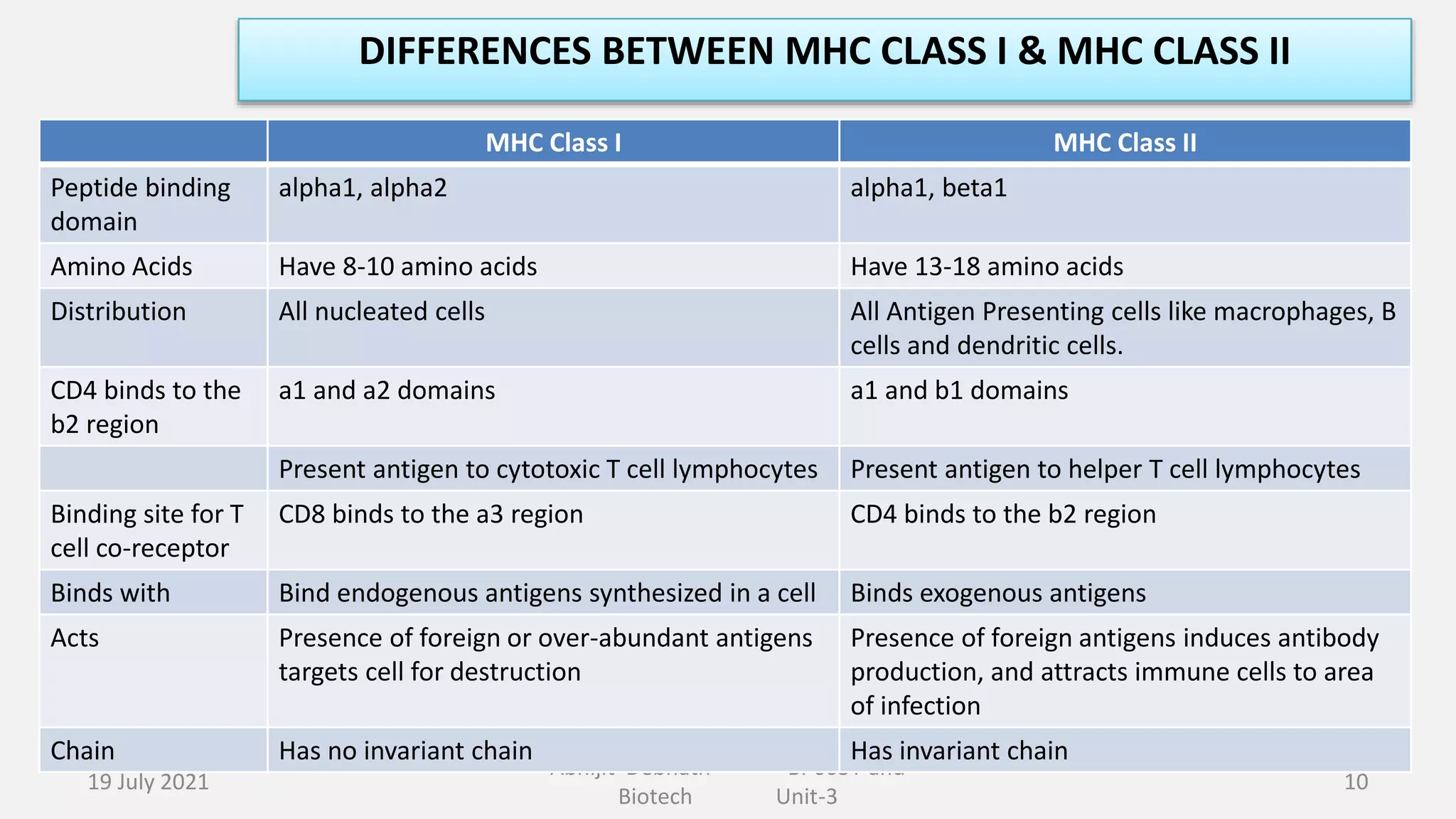
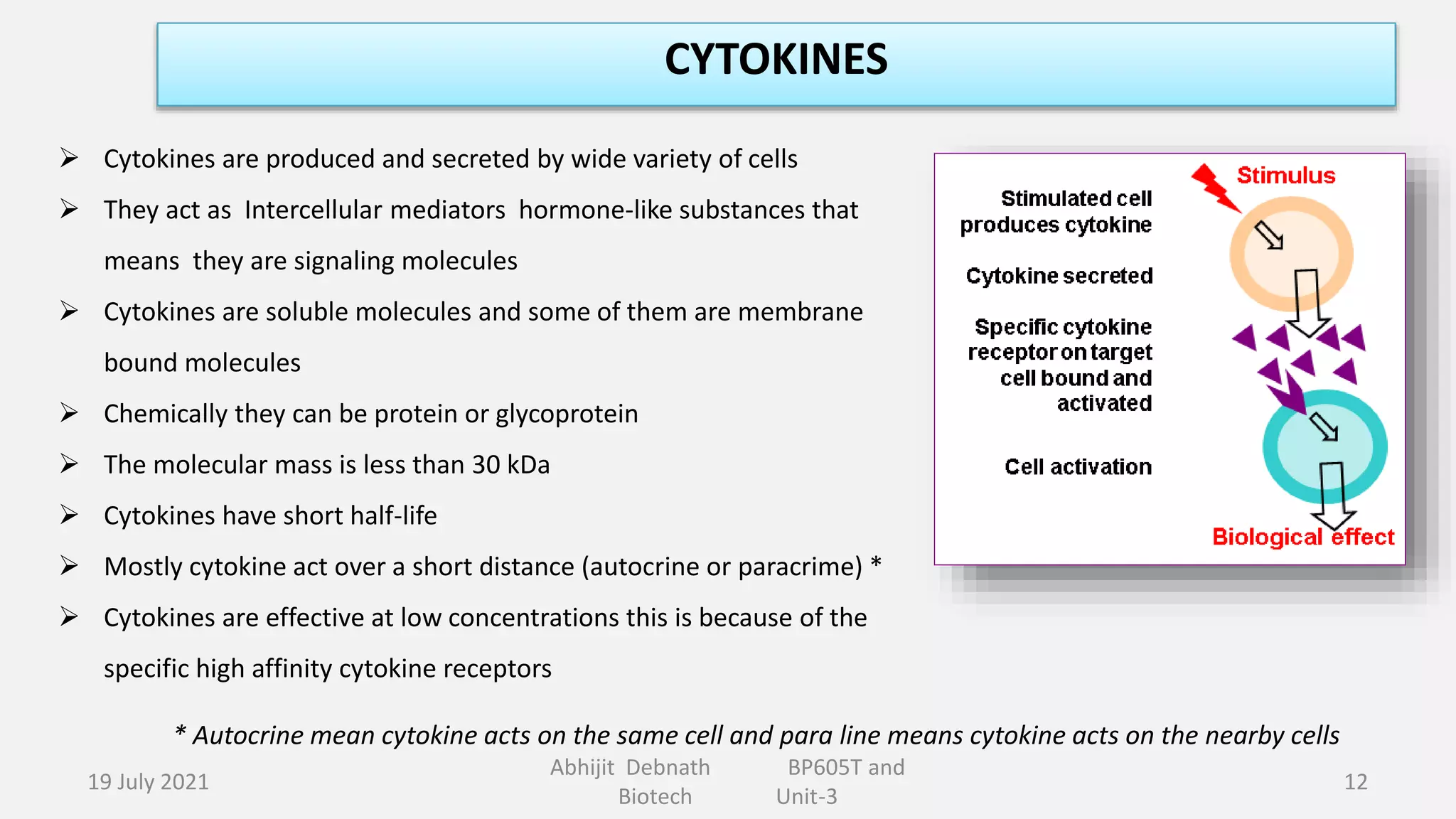
This document contains lecture notes on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and related topics from a biotechnology course. It discusses antigen-presenting cells, the structure and function of MHC class I and II molecules, similarities and differences between the two classes, MHC-associated genes, and important immune signaling molecules like cytokines, interleukins, interferons, and chemokines. Diagrams are included to illustrate MHC pathway and types of interferons. The notes provide an overview of key concepts in MHC and immunology for students in the biotechnology course.