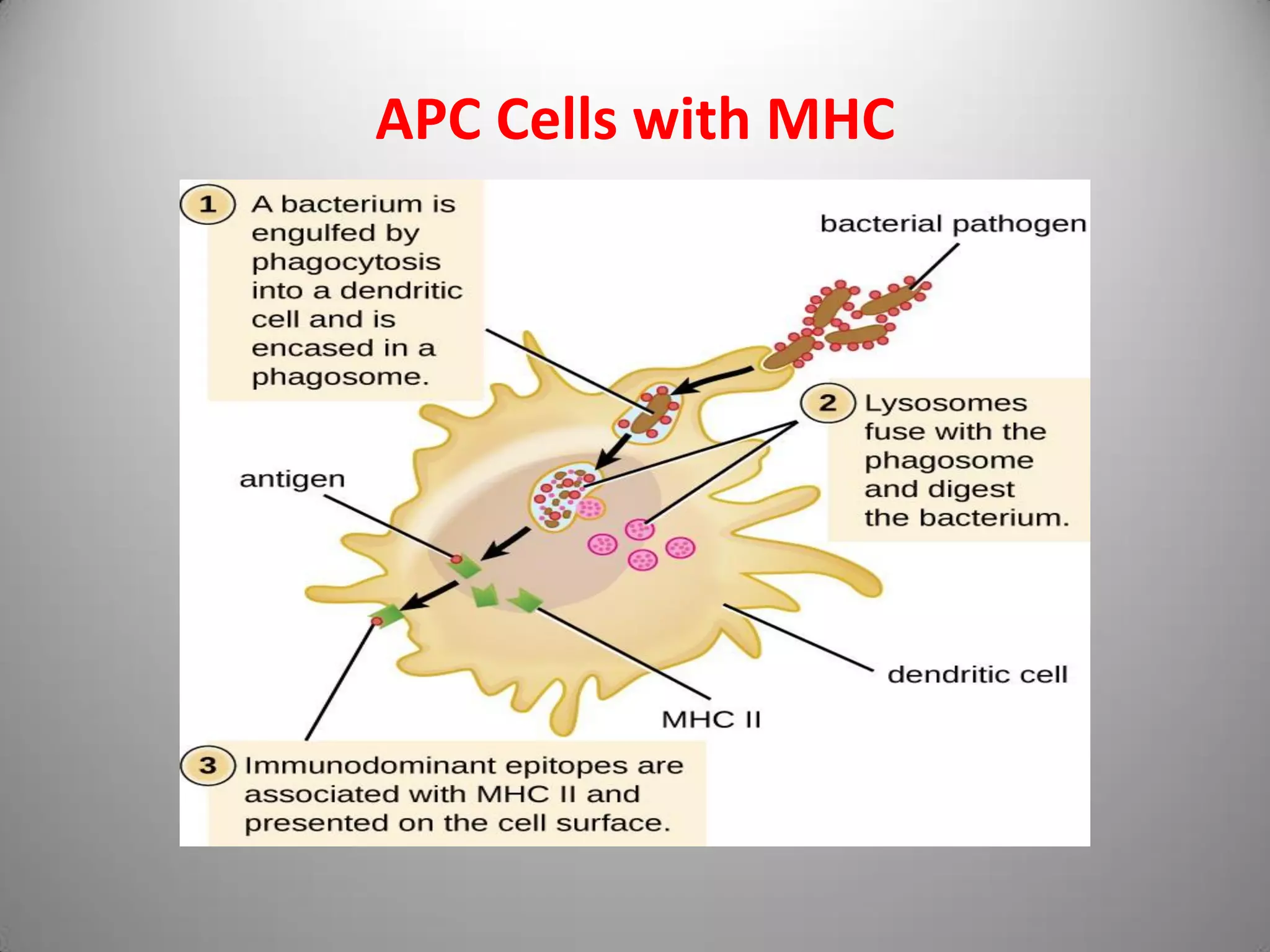
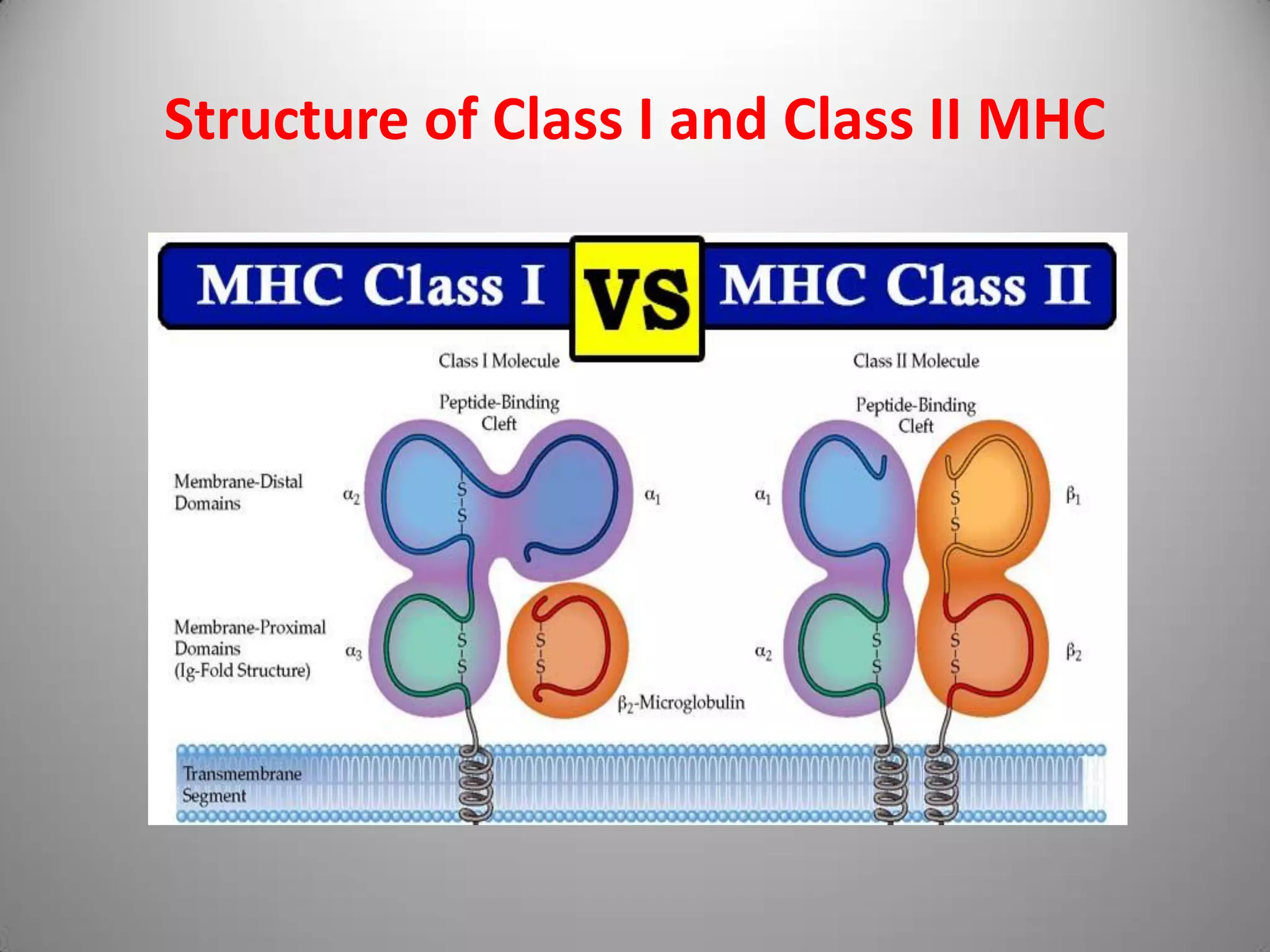
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) antigens are a set of cell surface proteins essential for the acquired immune system to identify foreign molecules. MHC antigens bind to pathogen antigens and display them on the cell surface for identification by T-cells. MHC is a cluster of genes on chromosome 6 in humans that encodes these antigens. There are three classes of MHC - Class I presents antigens to CD8 T-cells on all nucleated cells, Class II presents antigens to CD4 T-cells on antigen presenting cells like macrophages, and Class III plays a role in immune function through complement and cytokines. MHC antigens act as antigen presenting structures and play important roles in immune responses, transplantation tissue matching, and autoimmune diseases.