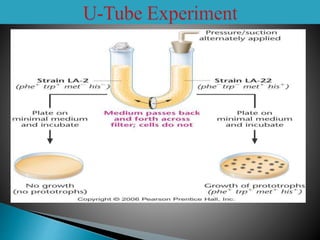
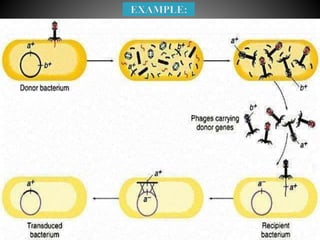
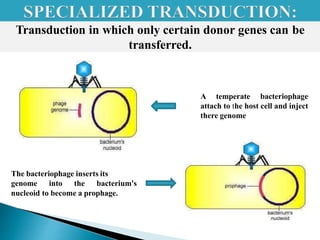
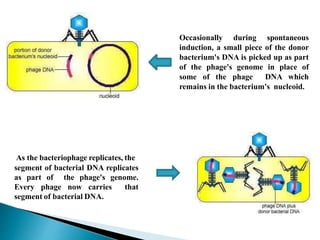
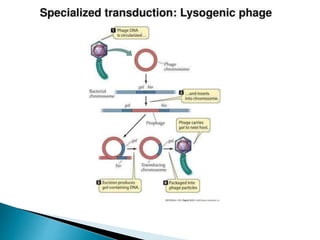
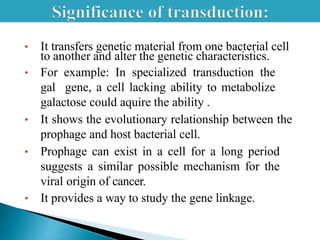
Transduction is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells via bacteriophages and can either be generalized or specialized. It was first discovered in 1952 by Zinder and Lederberg, who demonstrated genetic exchange in auxotrophic strains of Salmonella. This process alters genetic characteristics and has implications for understanding gene linkage and potential origins of viral-induced cancers.