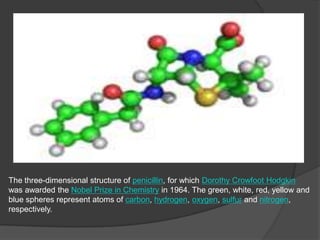
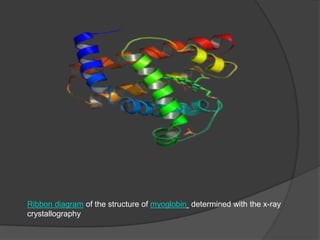
Protein engineering involves modifying protein structure using recombinant DNA technology or chemical treatment to improve function for use in medicine, industry, and agriculture. The objectives of protein engineering are to create superior enzymes for specific chemical production, produce enzymes in large quantities, and produce superior biological compounds. Protein engineering aims to alter properties like kinetic properties, thermostability, stability in nonaqueous solvents, substrate specificity, and cofactor requirements to meet industrial needs. Common methods for protein engineering include mutagenesis, selection, and recombinant DNA technology.