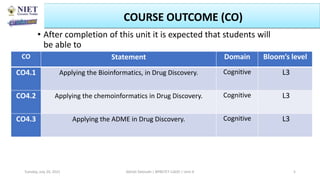
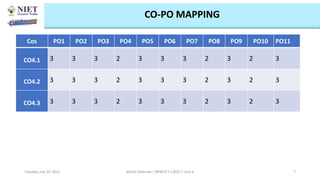
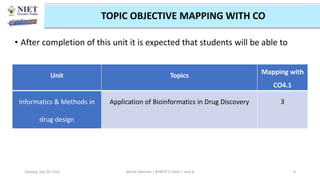
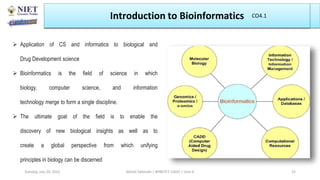
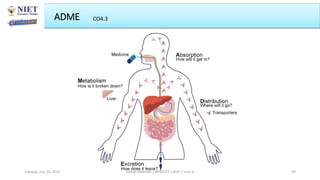
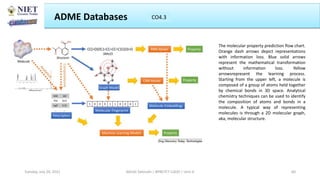
The document outlines a course on informatics and methods in drug design, focusing on bioinformatics, chemoinformatics, and ADME databases for pharmacy students. It describes the learning objectives, course outcomes, and the importance of these fields in optimizing drug discovery processes. Additionally, it highlights specific techniques and tools used in computer-aided drug design and virtual high-throughput screening.