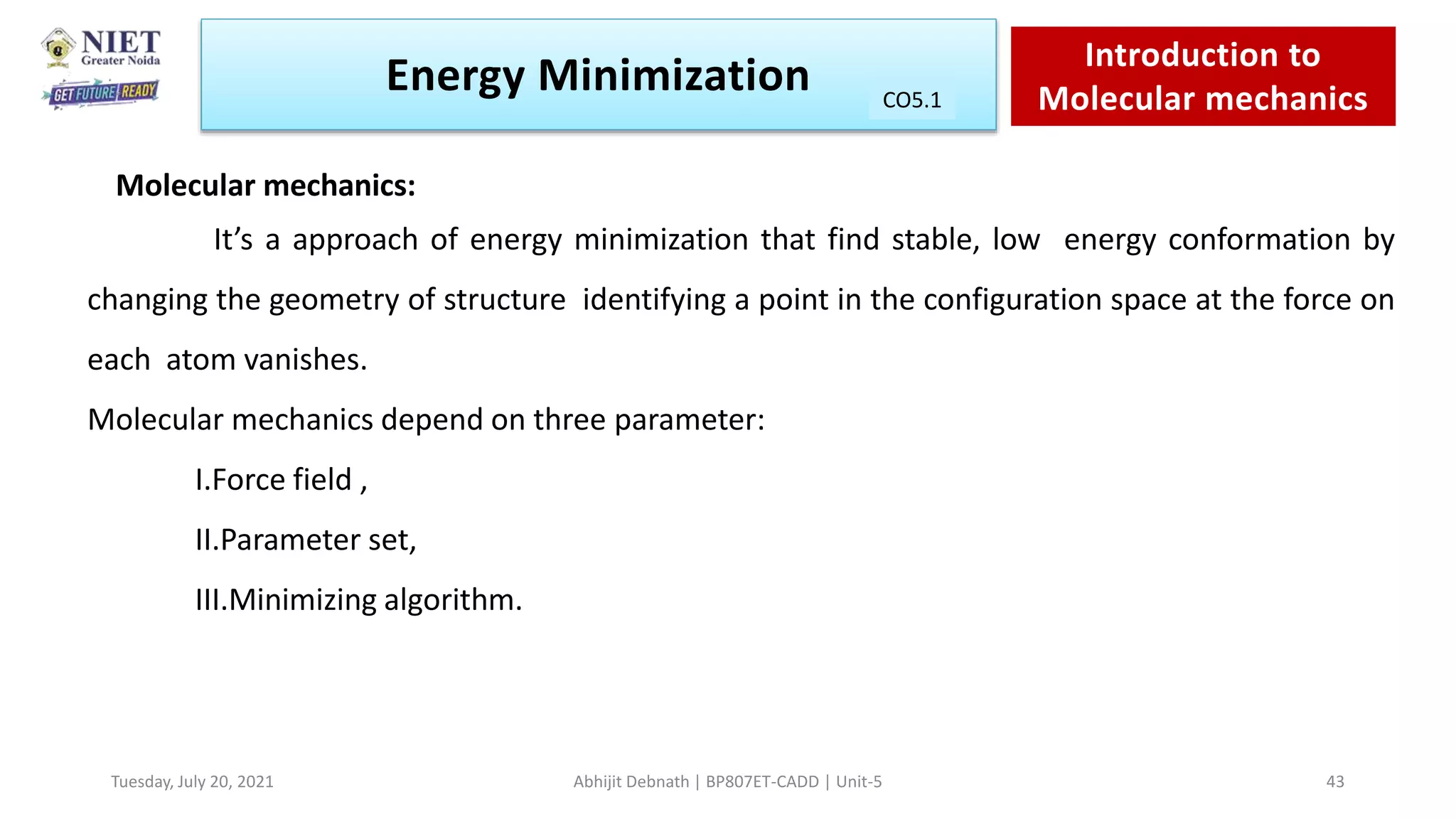
The document outlines a course on molecular modeling, primarily focusing on the principles of molecular mechanics and quantum mechanics. It aims to equip students with the knowledge necessary for applying molecular modeling techniques in drug discovery, supported by objectives and course outcomes mapped to various program outcomes. Key topics include energy minimization methods, conformational analysis, and the applications of quantum and molecular mechanics in computational chemistry.




























![It is set of function & constant used to described potential energy of the molecule.
General form of force field equation ;
Epot = ∑Ebon+ ∑Eang+ ∑Etor + ∑Eoop+ ∑ Enb + ∑Eel
Where;
Epot : The total steric energy
Ebon : The energy resulting from changing the bond length from it’s initial value calculated by Hook’s law for
deformation spring E=1/2kb(b-b0)2
[ kb-force constant for bond, b0-equilibrium bond length ,b-current bond length]
Eang: The energy resulting from deforming a bond angle from it’s original val.
Etor : Deforming the torsinal or dihydral angle
Eoop: Is the out of plane bending component of the steric energy
Enb : Energy arising from non-bonded interaction
Eel : Energy arising from coulombic forces
4
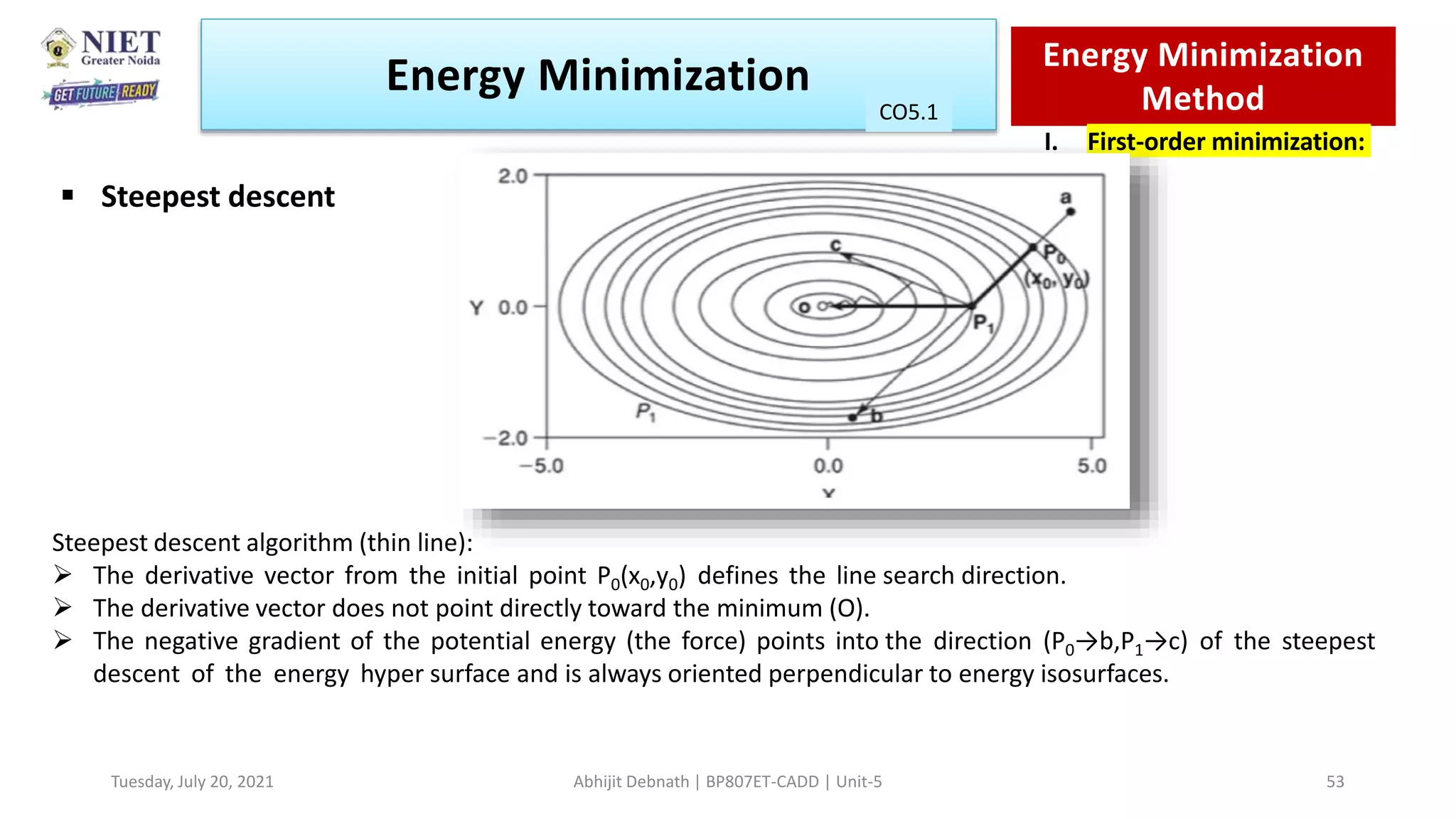
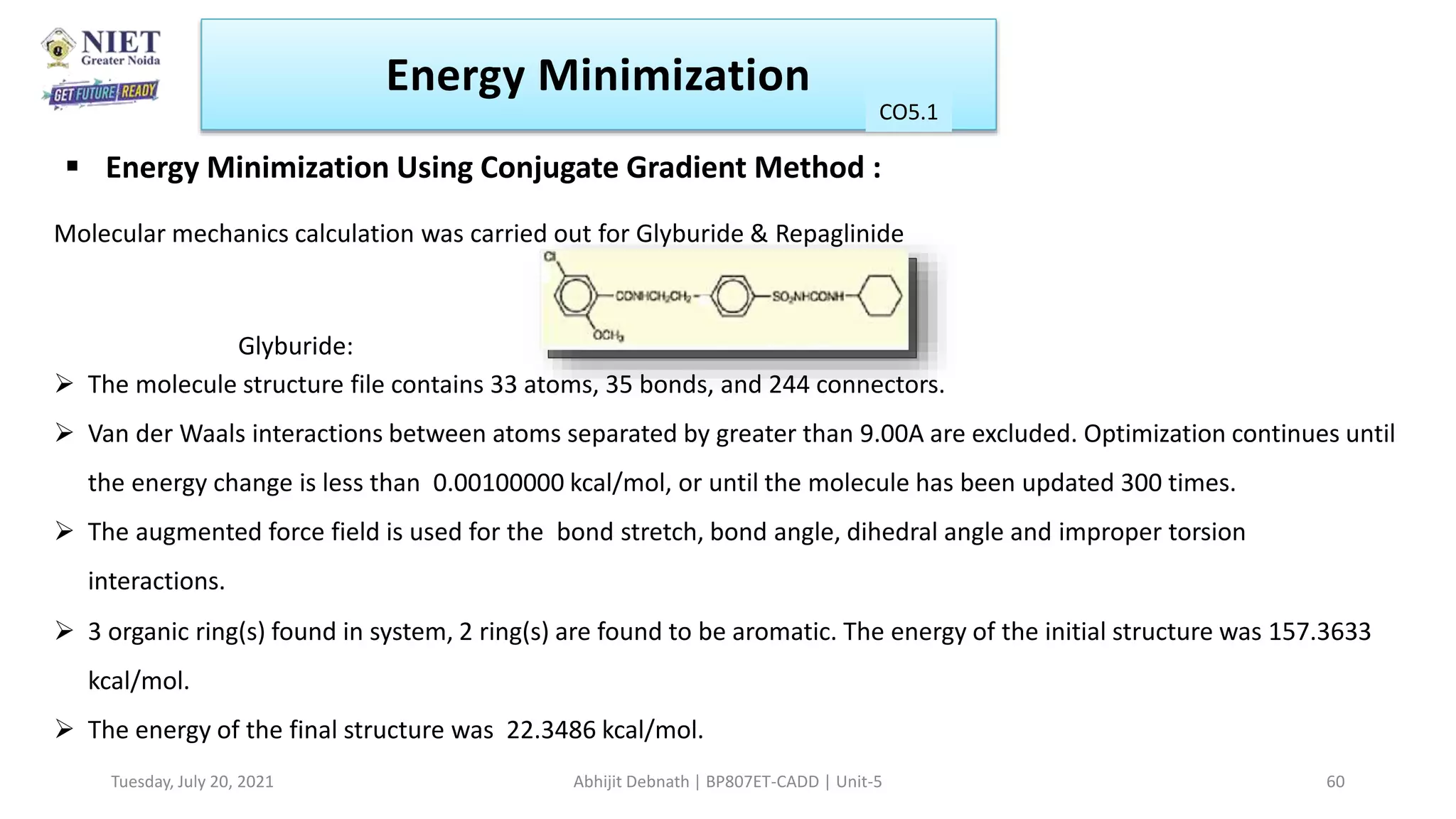
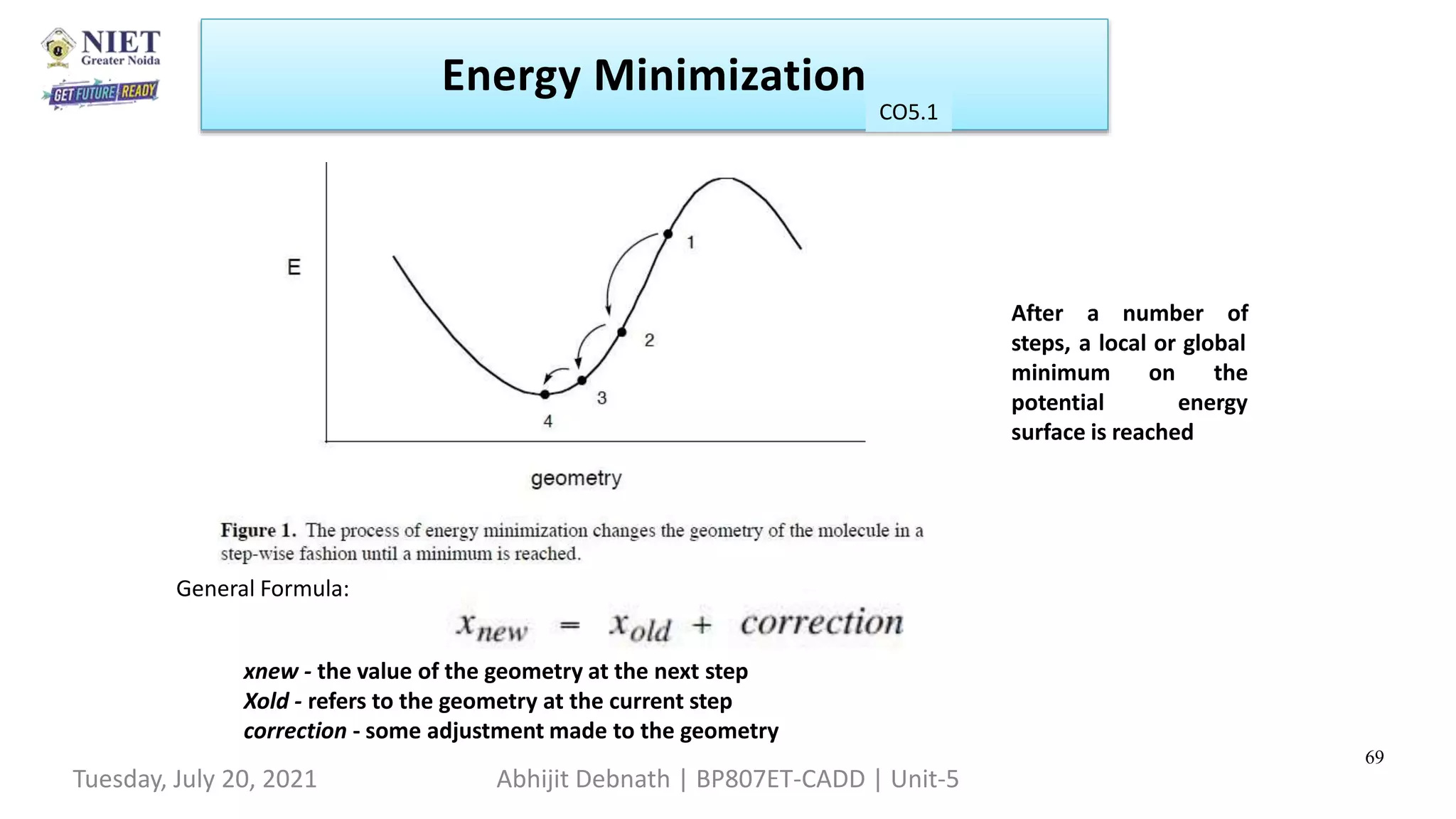
Energy Minimization
I ) Force field
CO1
Tuesday, July 20, 2021 Abhijit Debnath | BP807ET-CADD | Unit-5 44
CO5.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caddunit5-210720130756/75/Molecular-Modeling-44-2048.jpg)