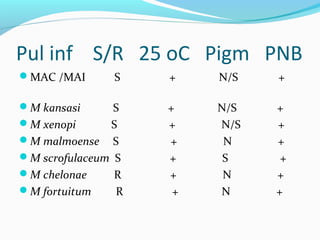
Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It has historically been a major global health problem, infecting one third of the world's population and killing millions each year. M. tuberculosis can be detected by acid-fast staining and grows very slowly, taking weeks to culture. Treatment requires a multi-drug regimen over several months to prevent the development of drug resistance. Despite efforts to control the disease, it remains a significant cause of illness and death worldwide.