- Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes tuberculosis and infects around 1.7 million people annually, causing over 9 million new cases and 1.7 million deaths per year. An estimated 500,000 people are infected with multidrug resistant strains.
- Risk of infection and disease is highest among socioeconomically disadvantaged people with poor housing and nutrition. Tuberculosis is transmitted via respiratory aerosols from people with active, untreated tuberculosis.
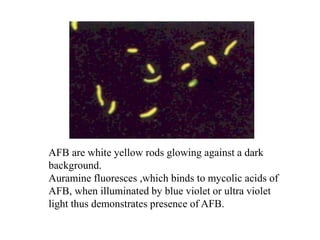
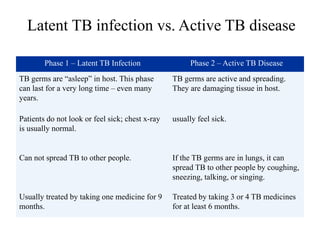
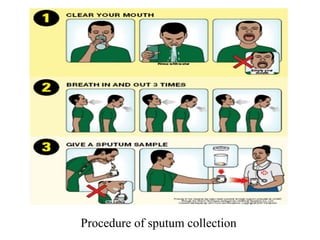
- Laboratory diagnosis involves microscopy, culture, and molecular techniques using sputum, gastric washings, urine, tissues or other clinical samples. Staining methods like Ziehl-Neelsen identify acid-fast bacilli. Culturing is needed for species identification and drug



















































![• Isolation of mycobacteria from clinical samples :
1. Homogenization : liquefaction of nonsterile samples
with N-acetyl-L-lysine .
2. Decontamination : by 4% NaOH followed by
neutralization with 14% potassium dihydrogen
orthophosphate buffer (color change red to orange
yellow) or 3% oxalic acid followed by neutralization
with 2% NaOH (color change yellow to
orange).[indicator-phenol red]
3. Centrifugation : 1500-2000g for 20 minutes.
4. Neutralization.
5. Inoculation of culture media.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/75f63d3c-d203-42f5-9310-b3bfb454d607-161115172957/85/Mycobacterium-tuberculosis-56-320.jpg)