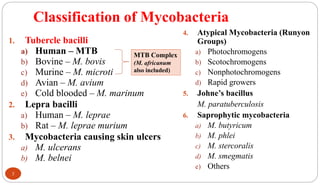
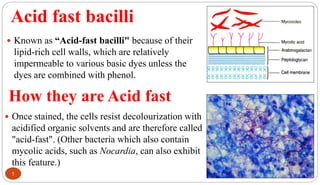
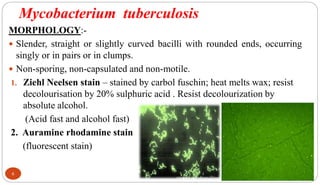
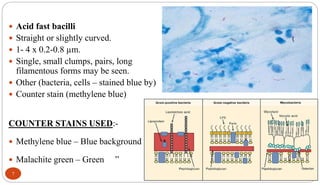
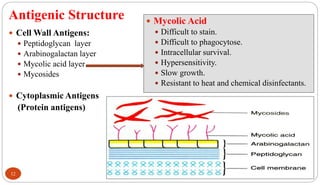
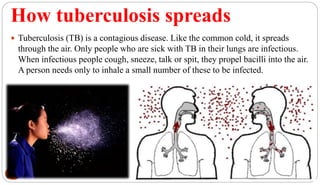
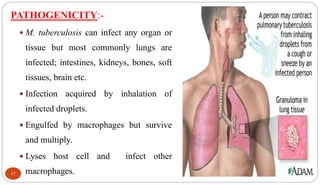
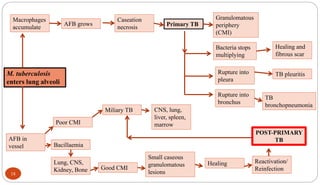
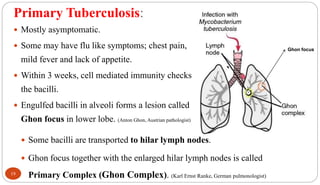
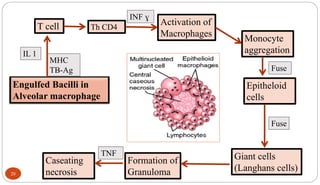
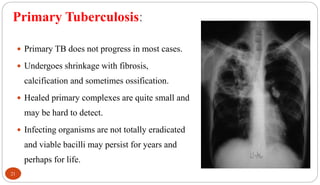
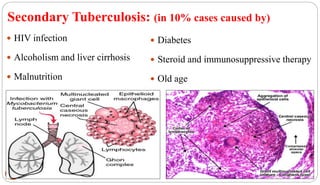
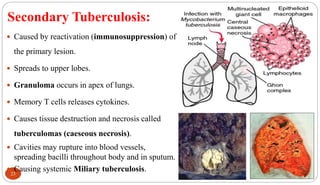
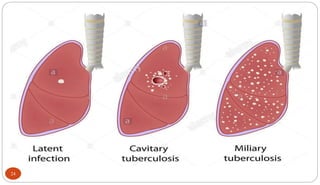
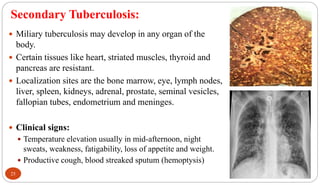
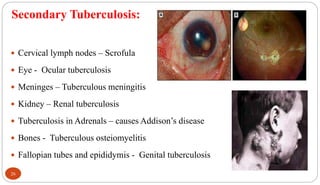
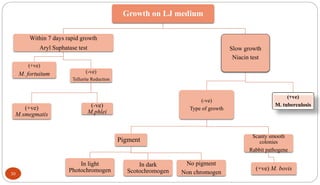
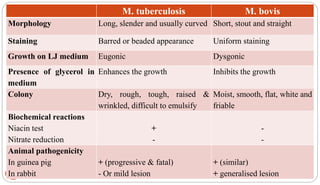
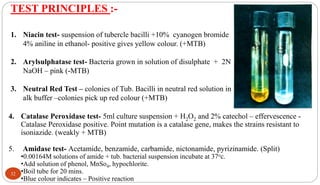
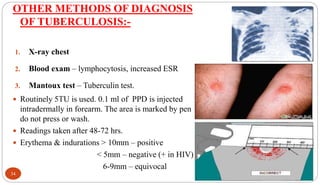
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that causes tuberculosis (TB). It is spread through the air when people who are sick with active pulmonary TB cough, sneeze or spit. Most infections are asymptomatic, but about 10% reactivate later in life, usually in the upper lobes of the lungs. Upon reactivation, TB bacilli can spread throughout the body and cause serious illness. Laboratory diagnosis of TB involves microscopic examination of samples for acid-fast bacilli or culturing samples on selective media like Lowenstein-Jensen medium.