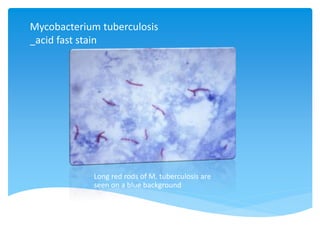
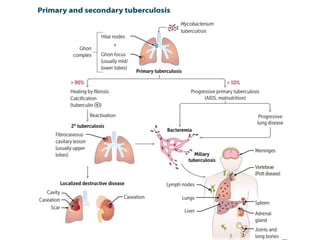
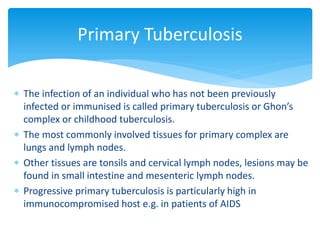
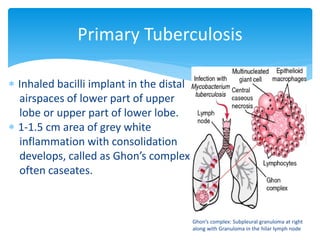
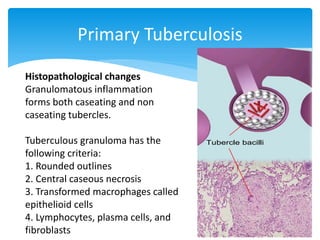
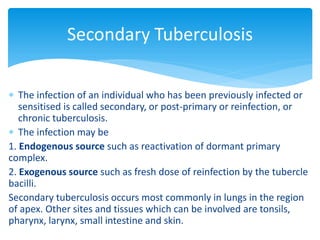
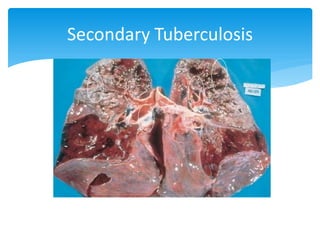
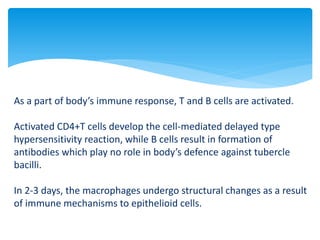
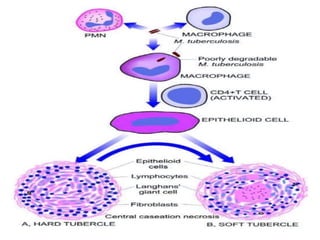
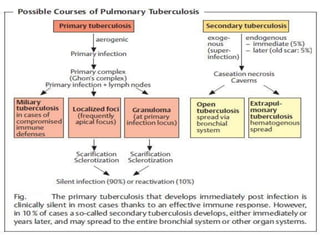
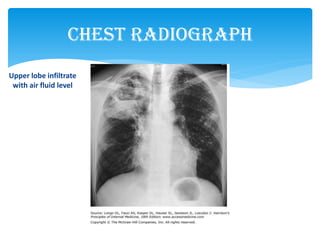
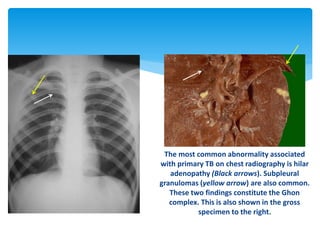
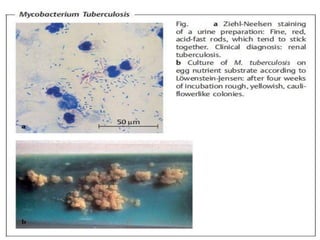
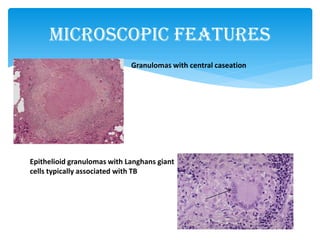
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is an aerobic, non-spore-forming, and acid-fast bacillus responsible for tuberculosis, which claims more lives globally than any other microbial agent. The disease manifests primarily through two stages: primary tuberculosis, where initial infection occurs, and secondary tuberculosis, which arises from reactivation in previously infected individuals. Clinical manifestations include asymptomatic cases, progressive primary TB resembling pneumonia, and disseminated miliary TB, with diagnosis relying on radiographic findings and acid-fast staining of sputum, while treatment typically involves a regimen of antitubercular drugs.


























![Reference:
[Levinson W.] Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology.
[Jaypee] Review of Microbiology and Immunology.
Color Atlas of Microbiology .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mycobacteriumtuberculosis-180401131034/85/Mycobacterium-Tuberculosis-42-320.jpg)