This document discusses the phylum Actinobacteria, focusing on the order Actinomycetales. Key points:
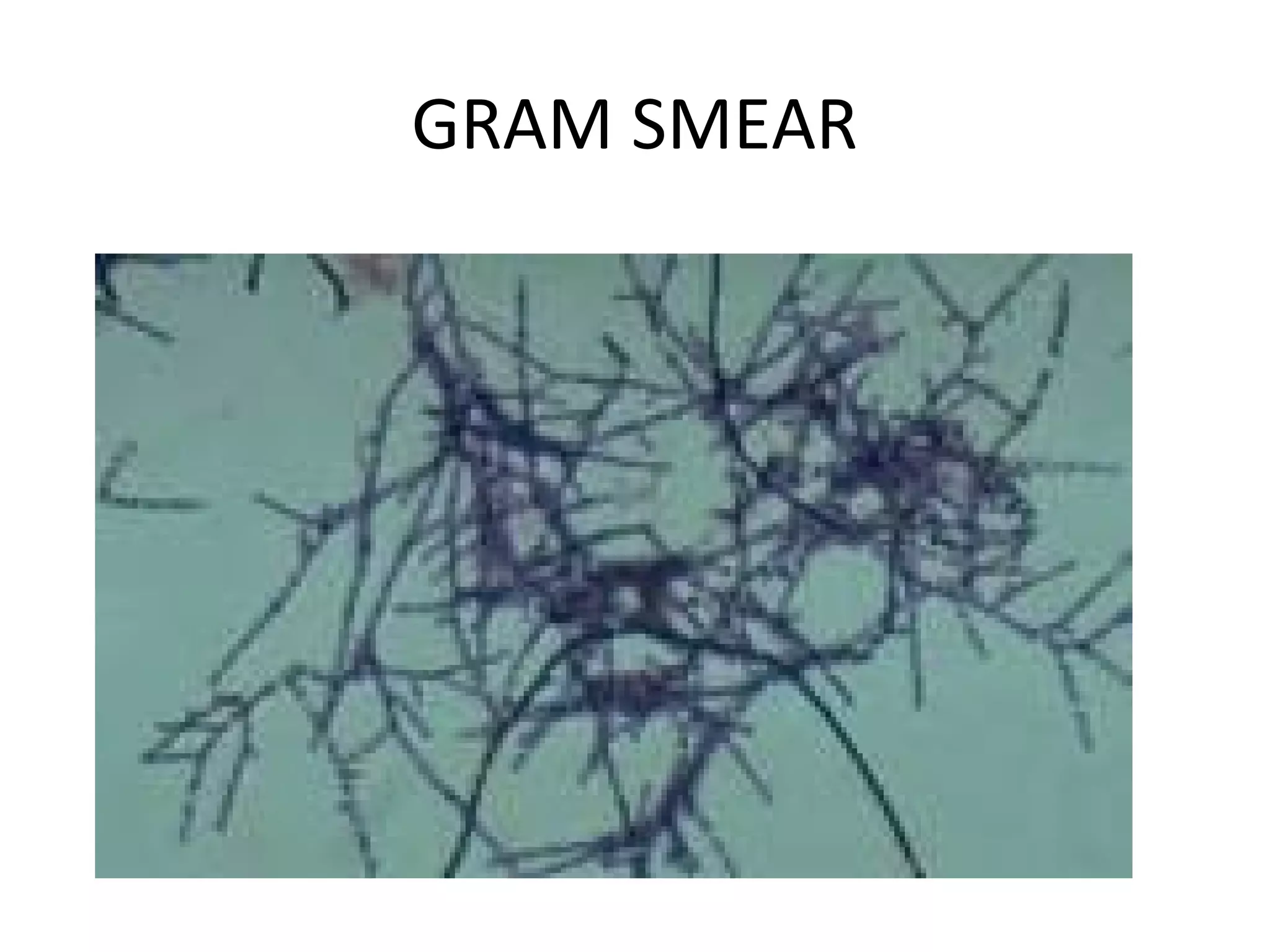
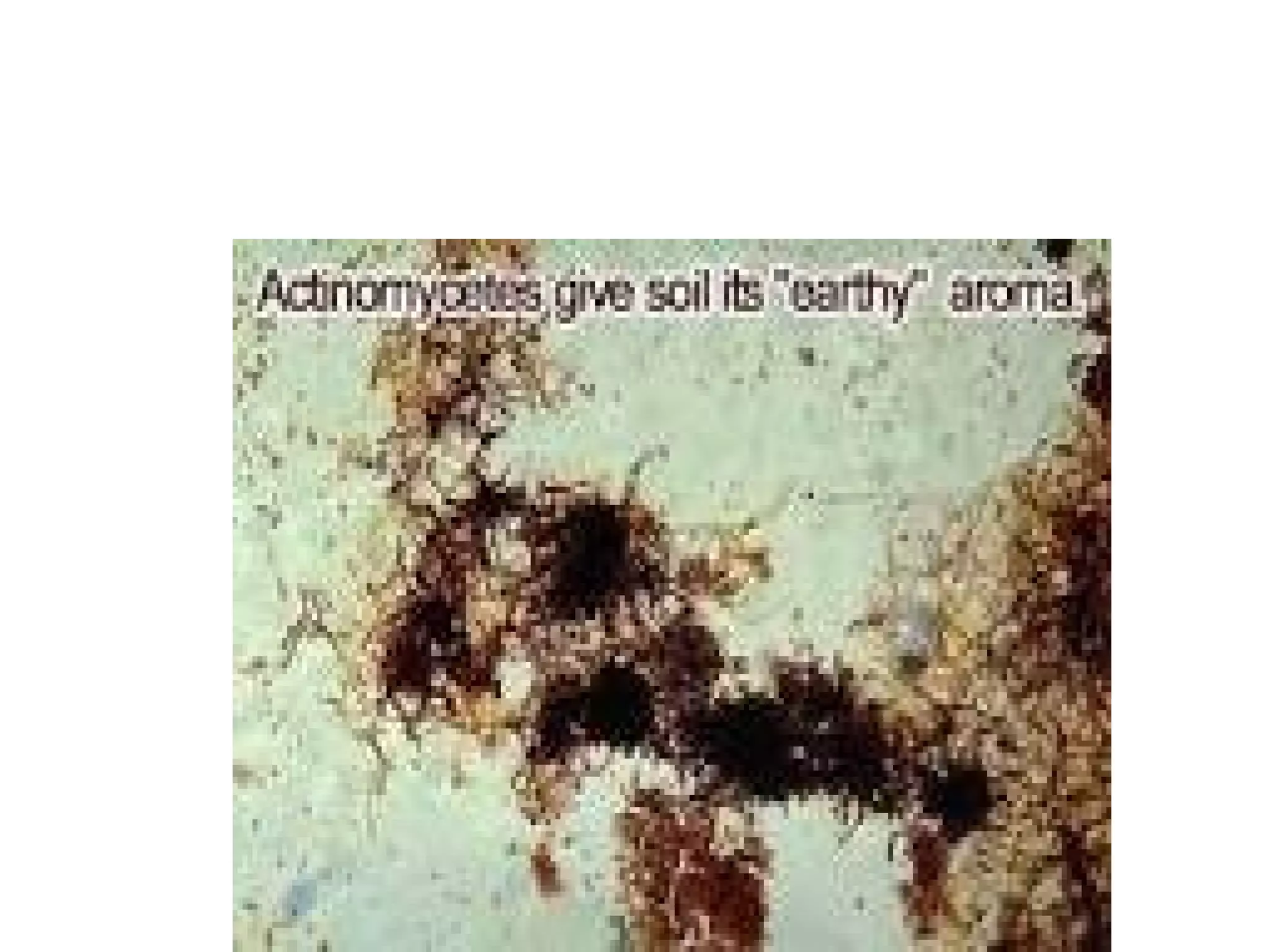
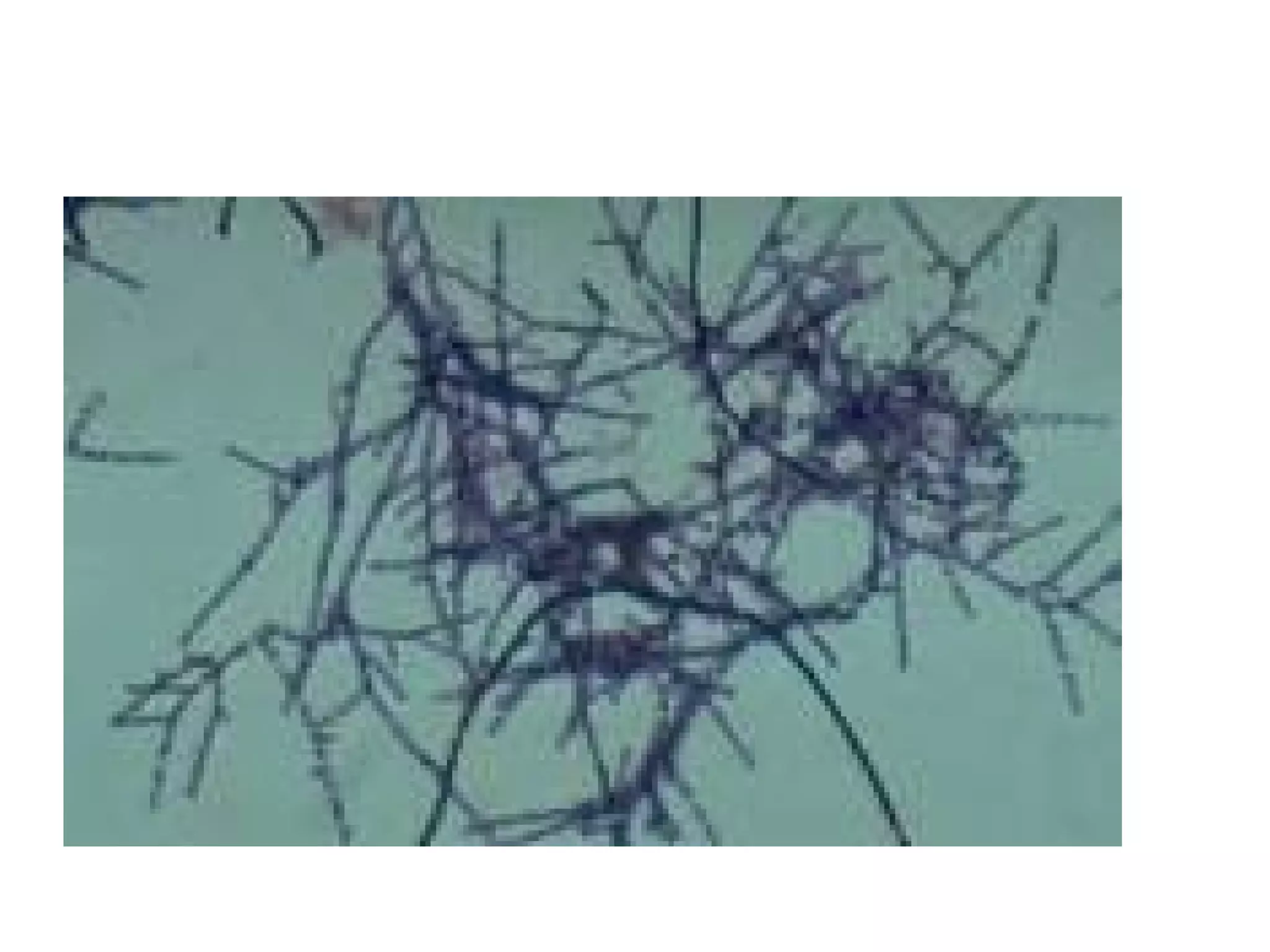
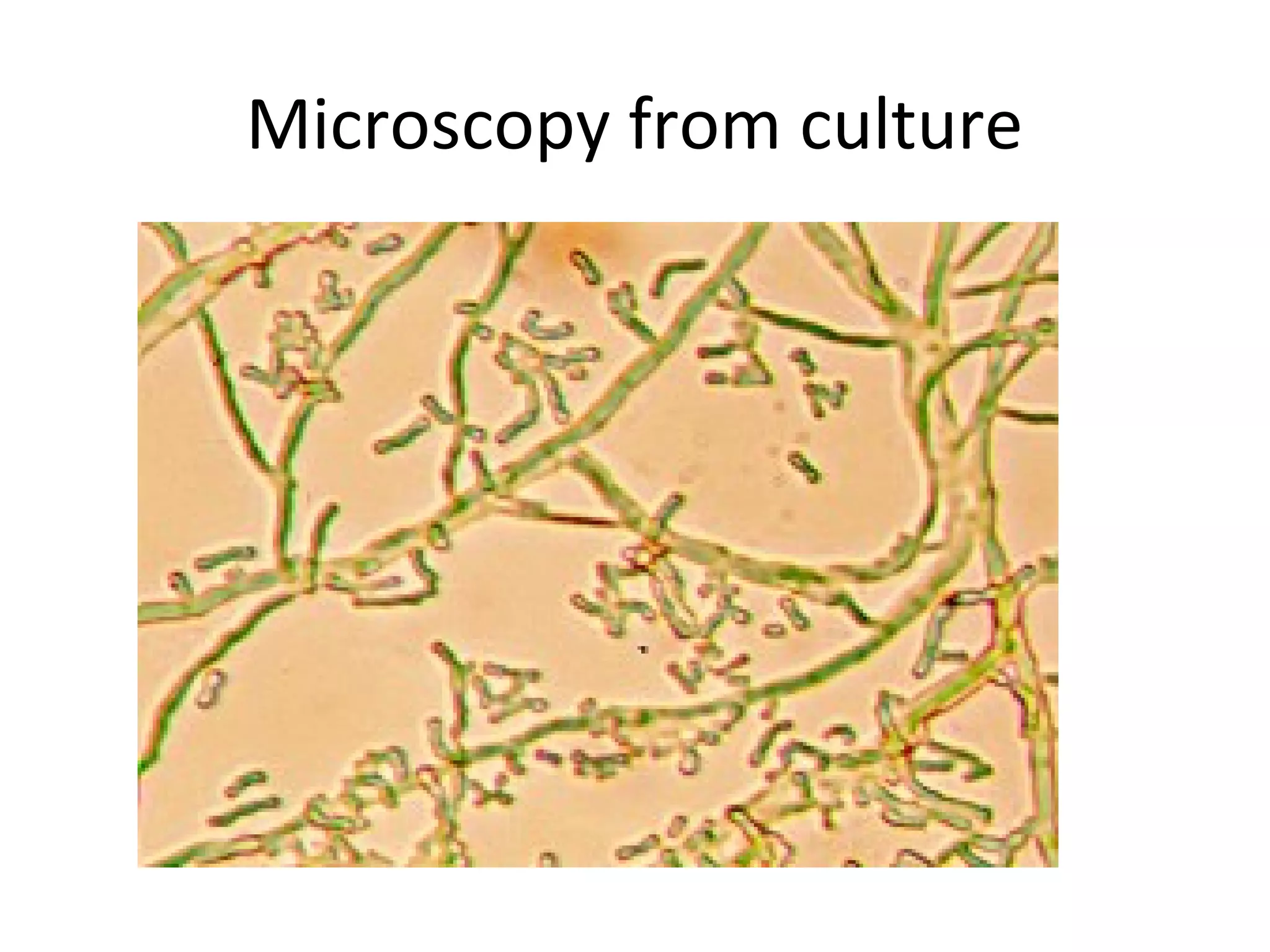
- Actinomycetales includes large, diverse Gram-positive bacilli that form chains or filaments. They are found worldwide, especially in soil and aquatic environments, and play roles in decomposition, antibiotic production, and occasionally pathogenesis.
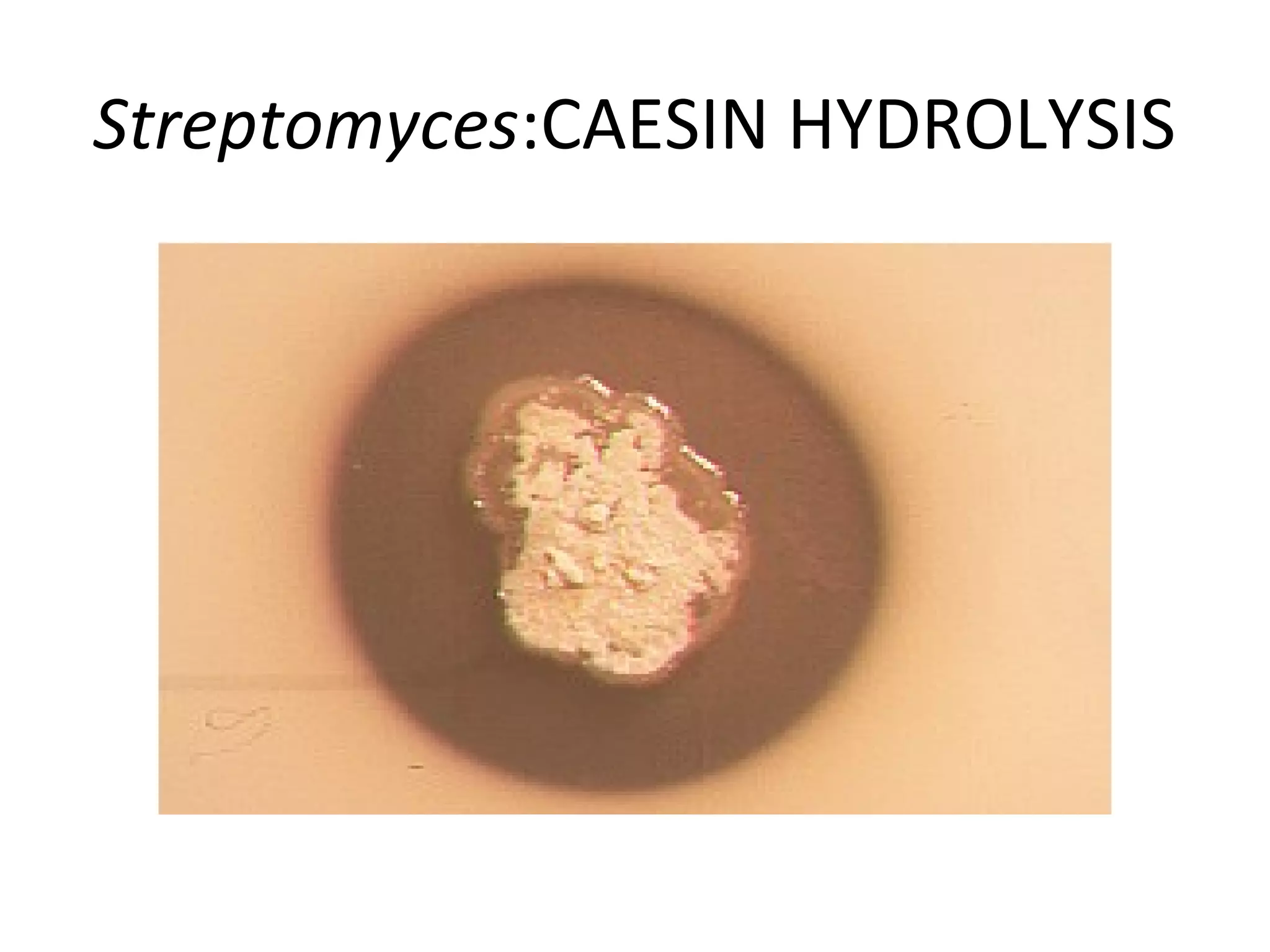
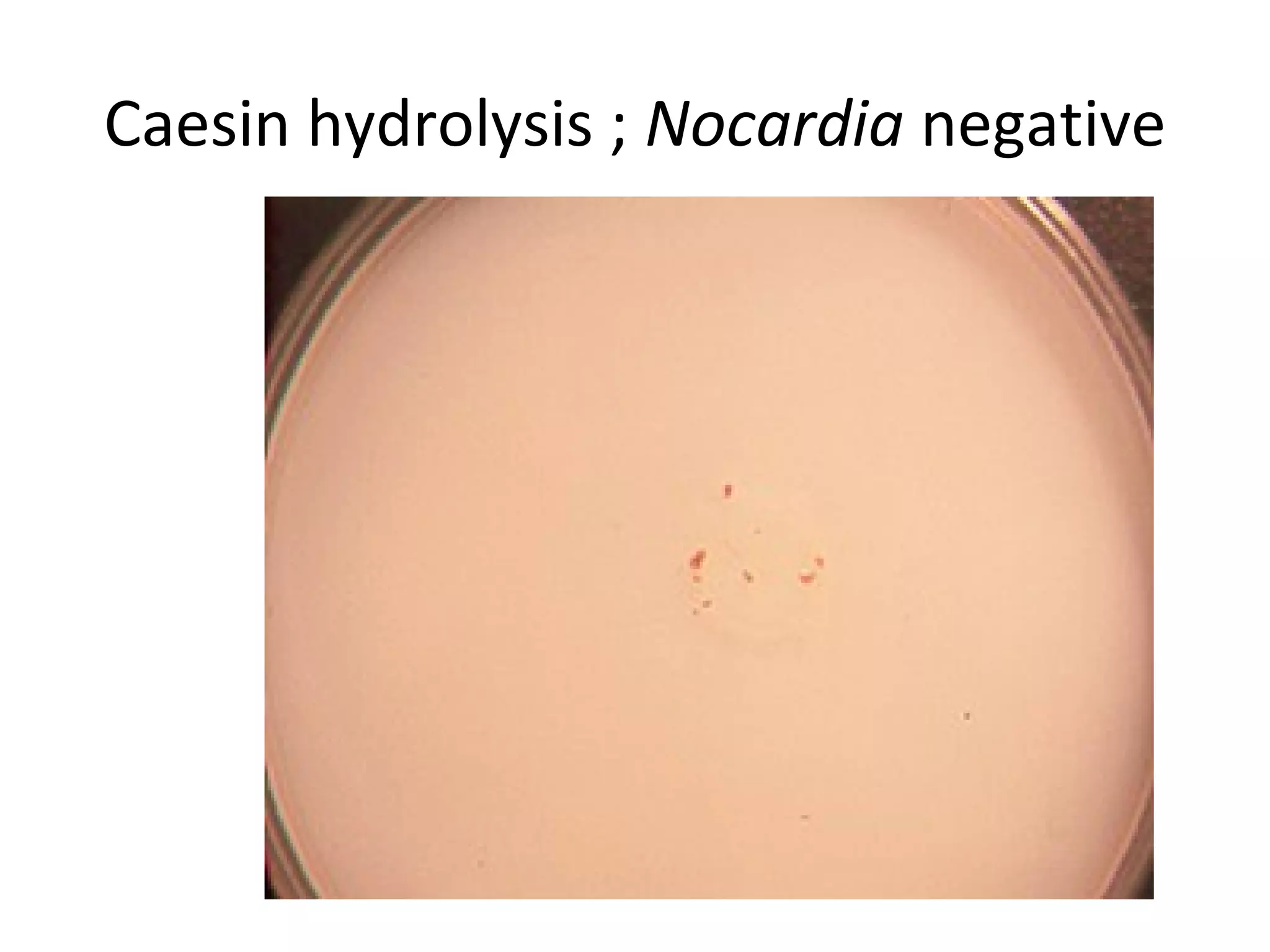
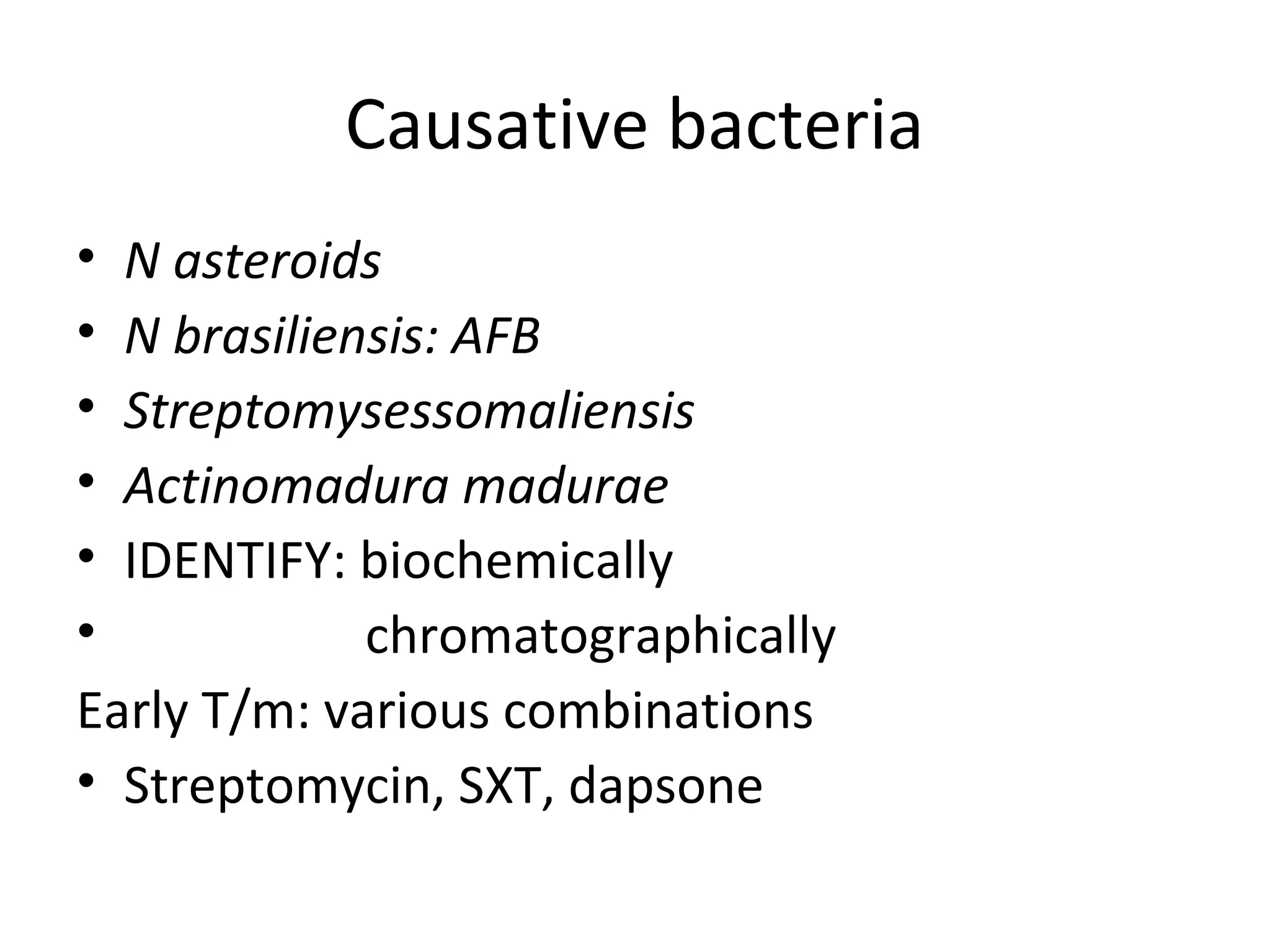
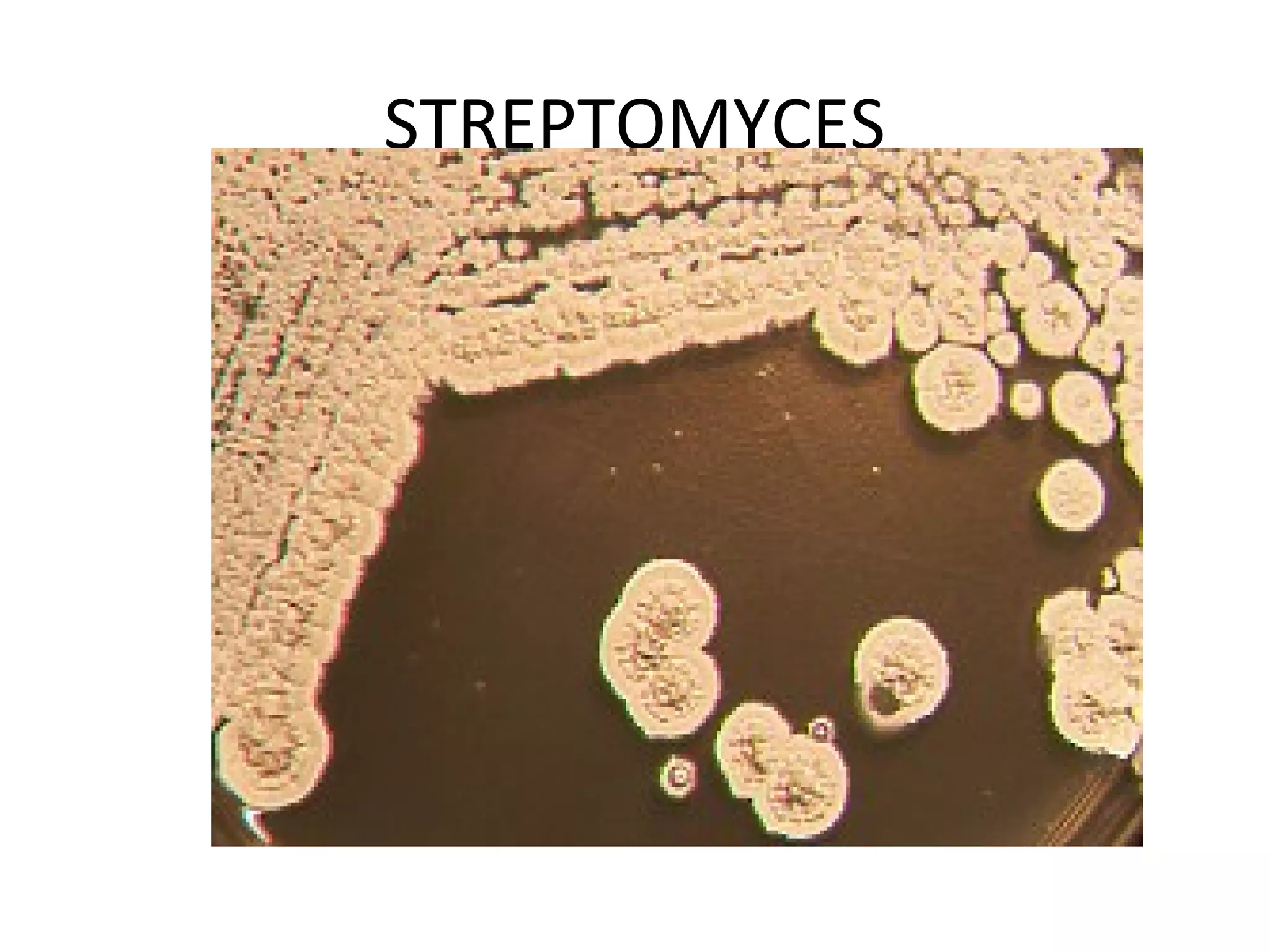
- Genera discussed include Streptomyces, Nocardia, Rhodococcus, Corynebacterium, and Mycobacterium. Nocardia can cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised individuals.
- Characteristics include aerobic growth, branching filaments, and high G+C DNA content. Colonies of