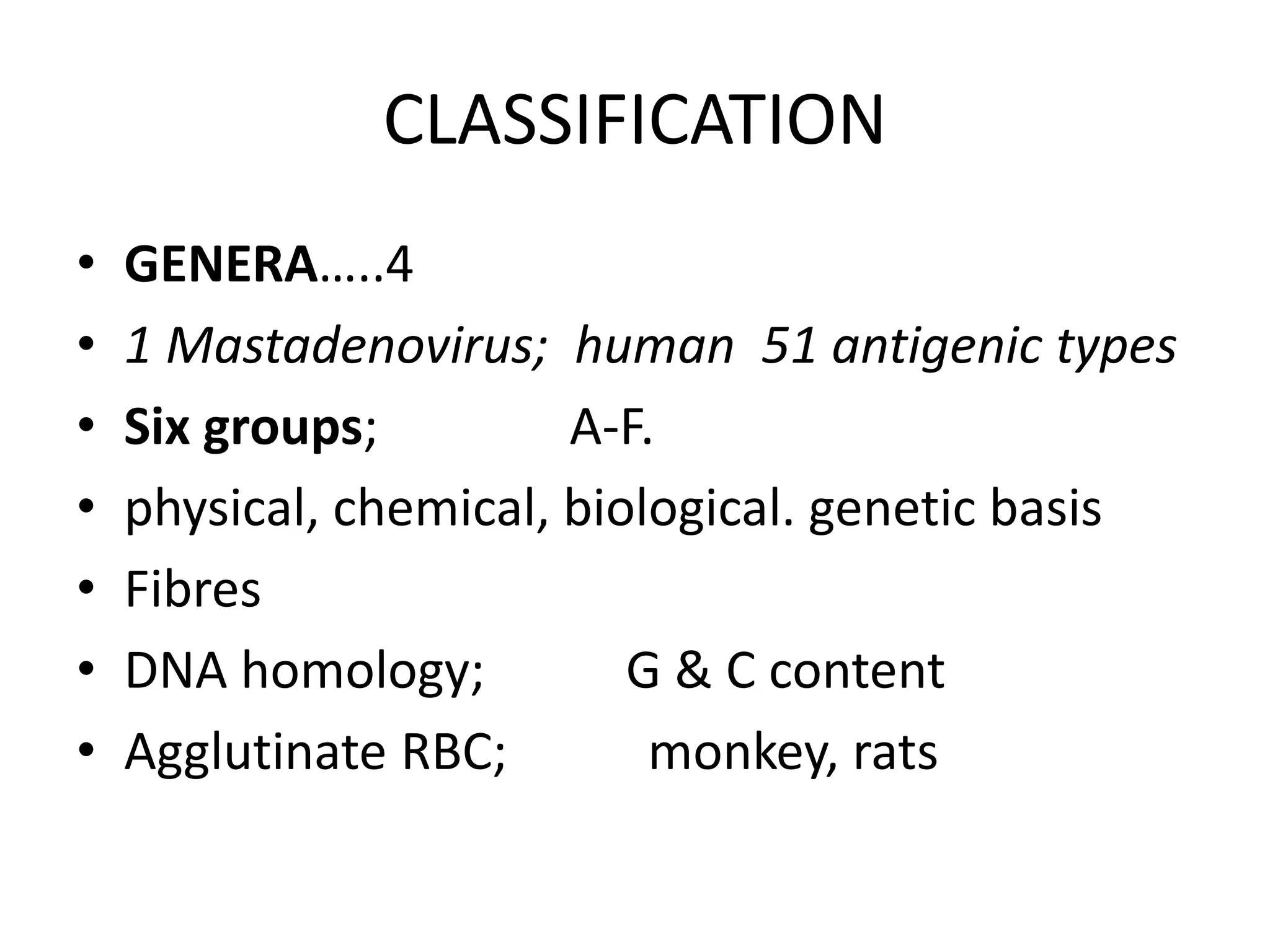
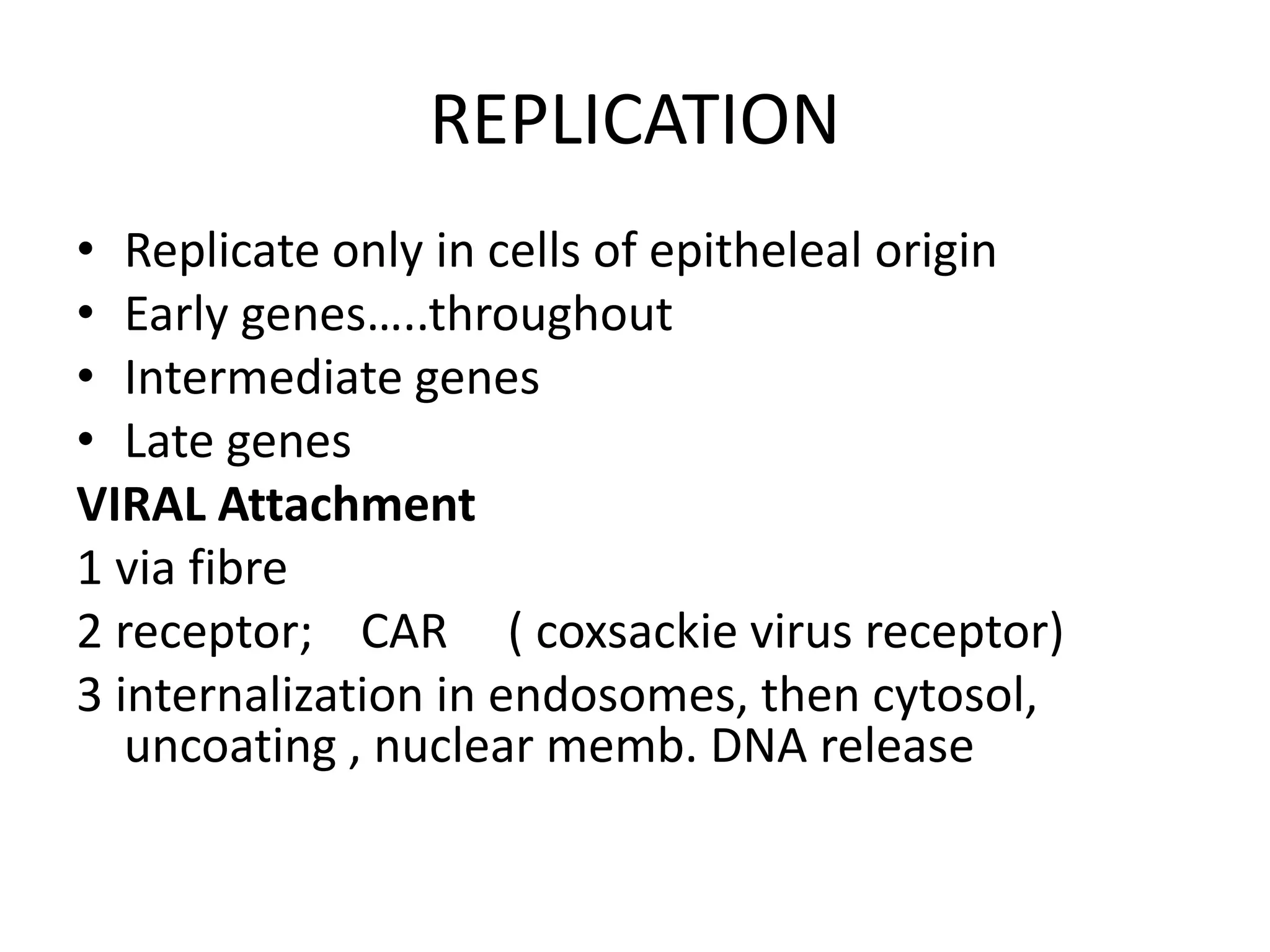
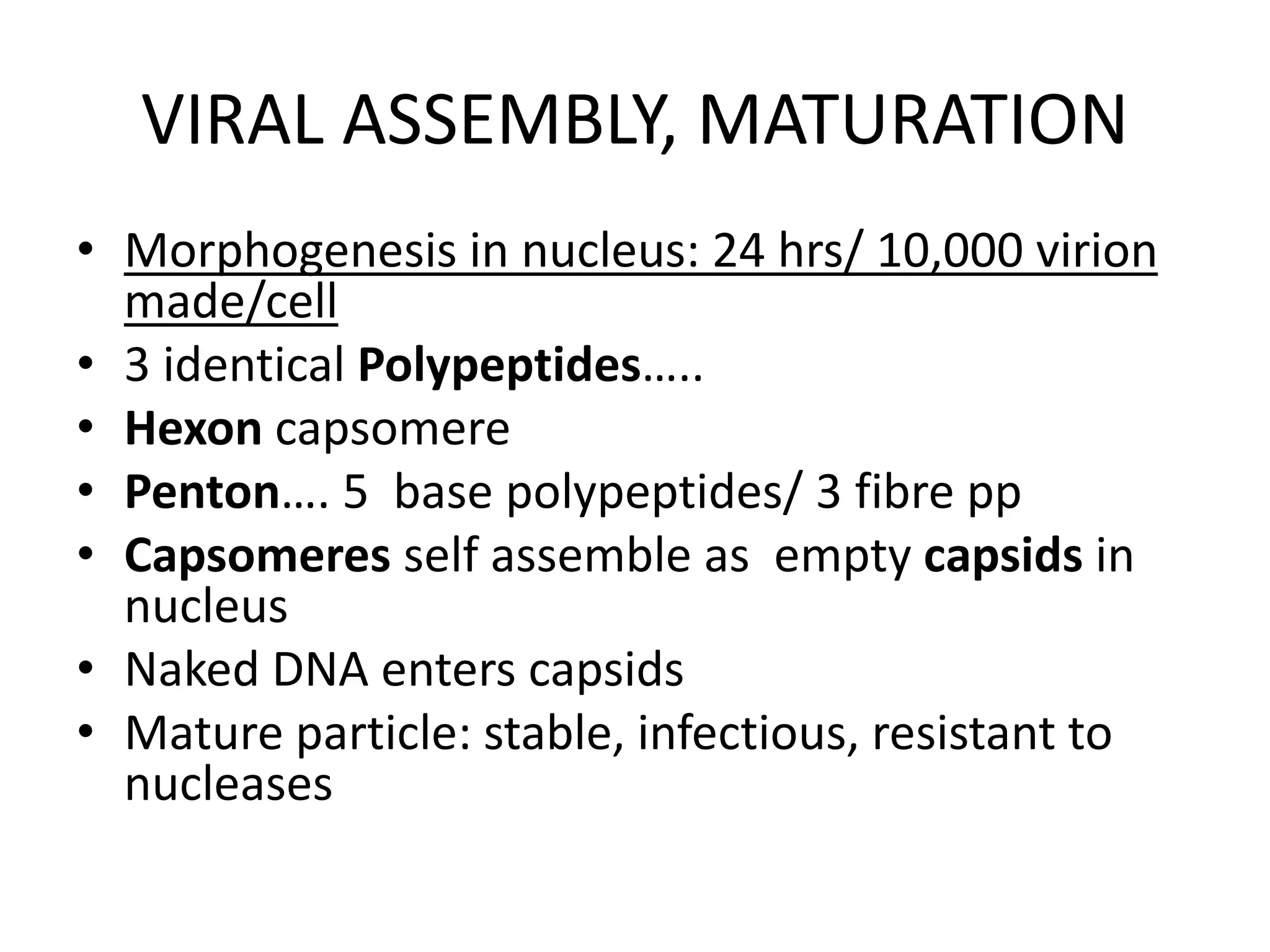
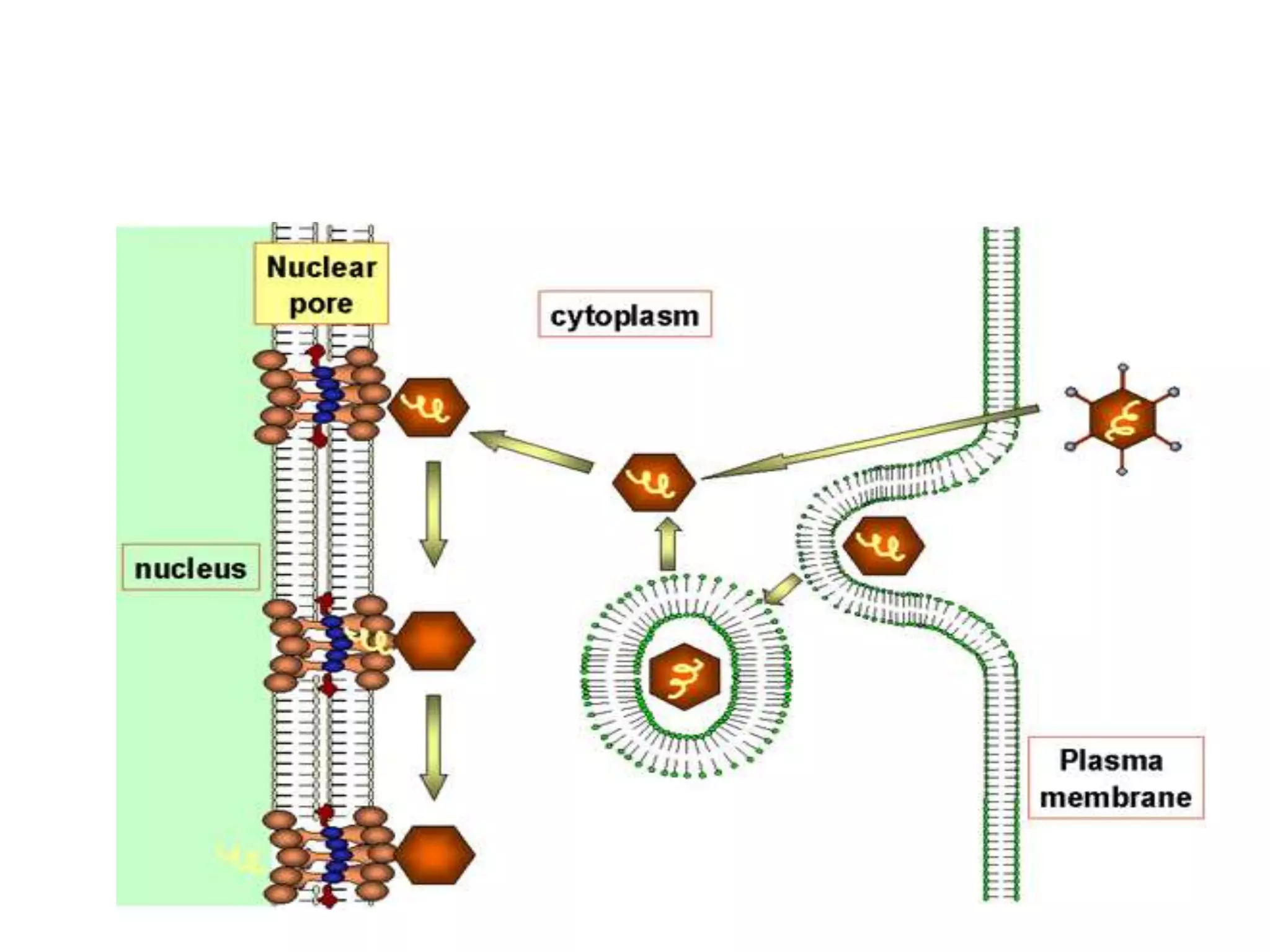
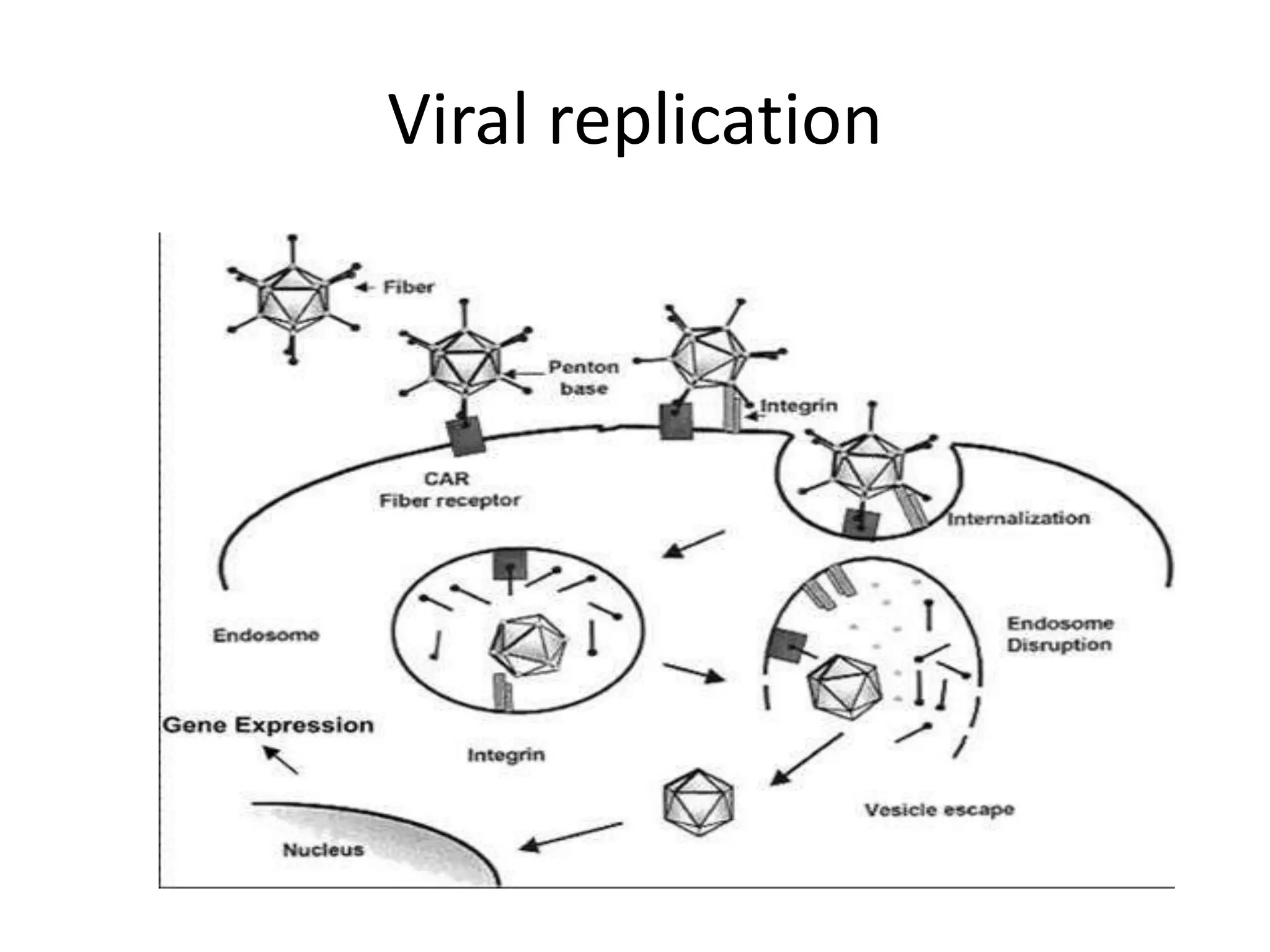
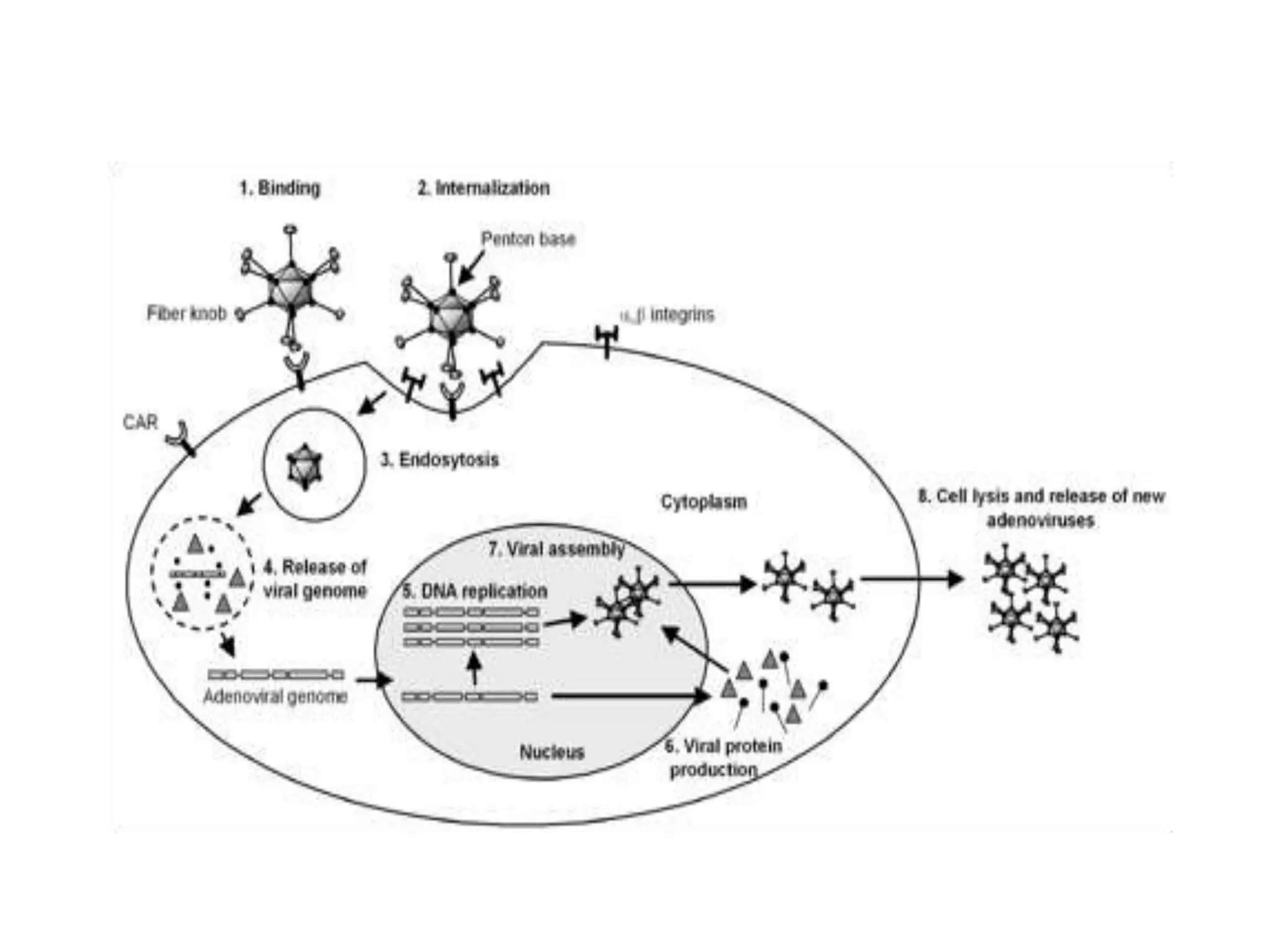
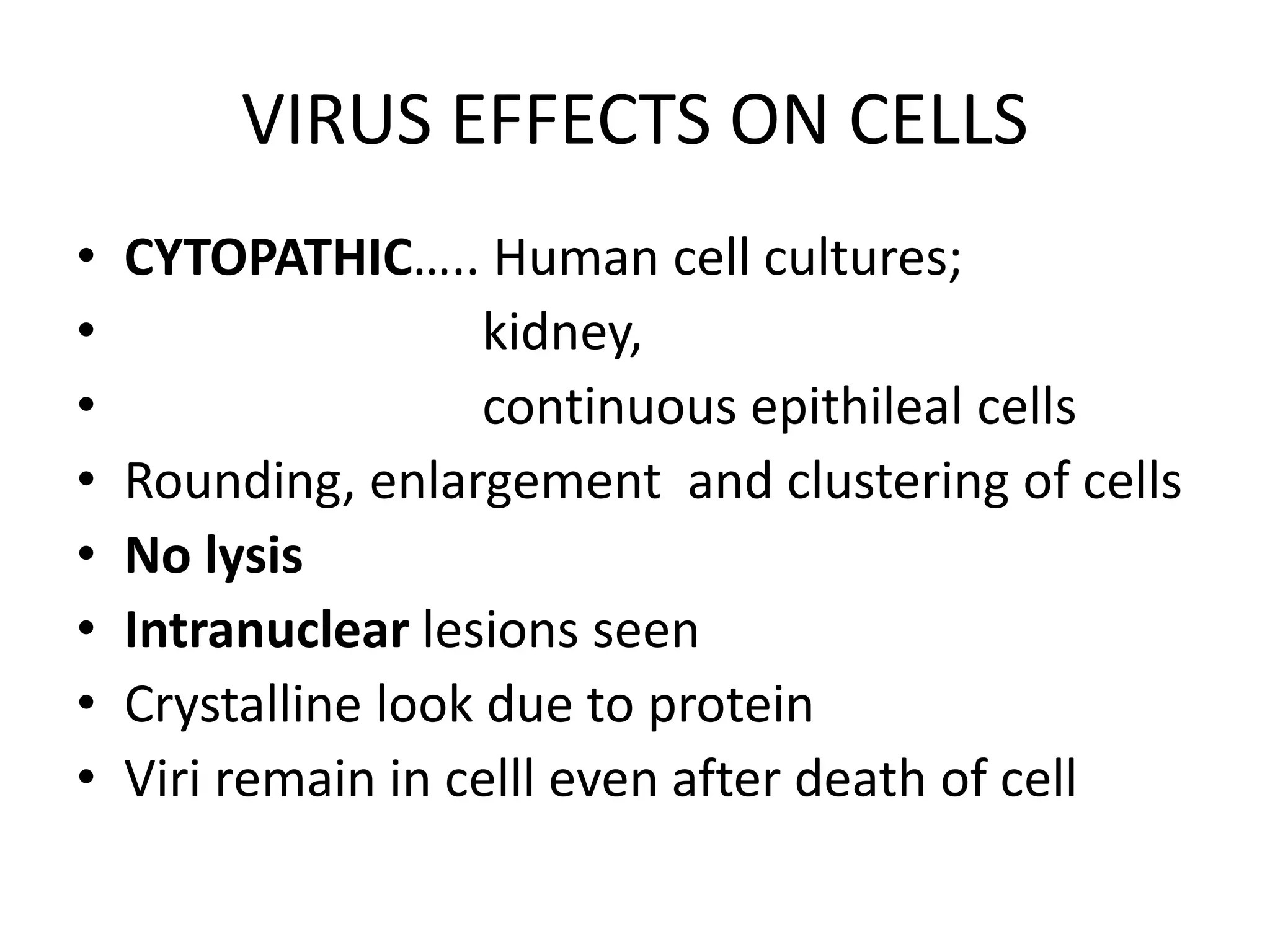
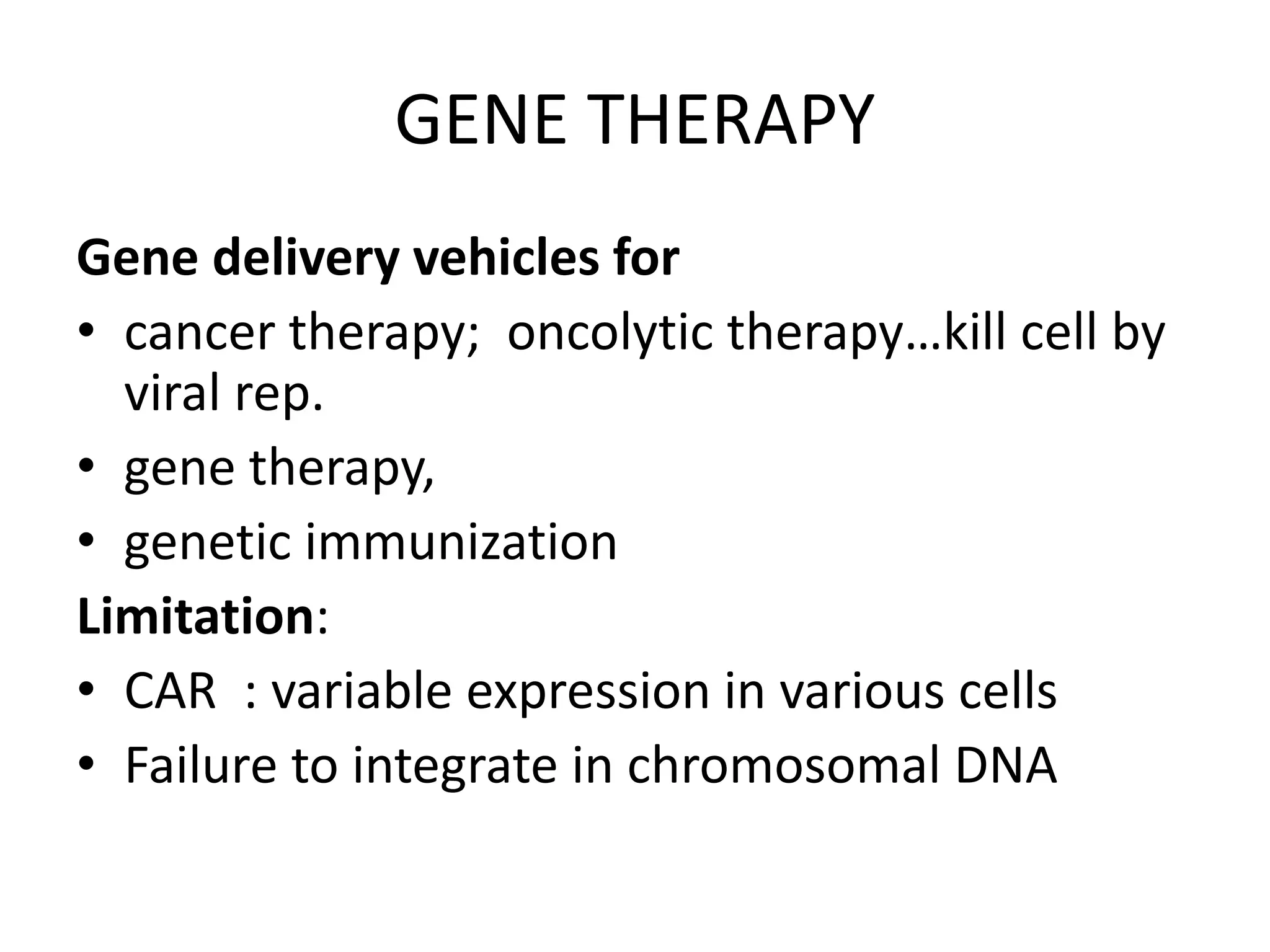
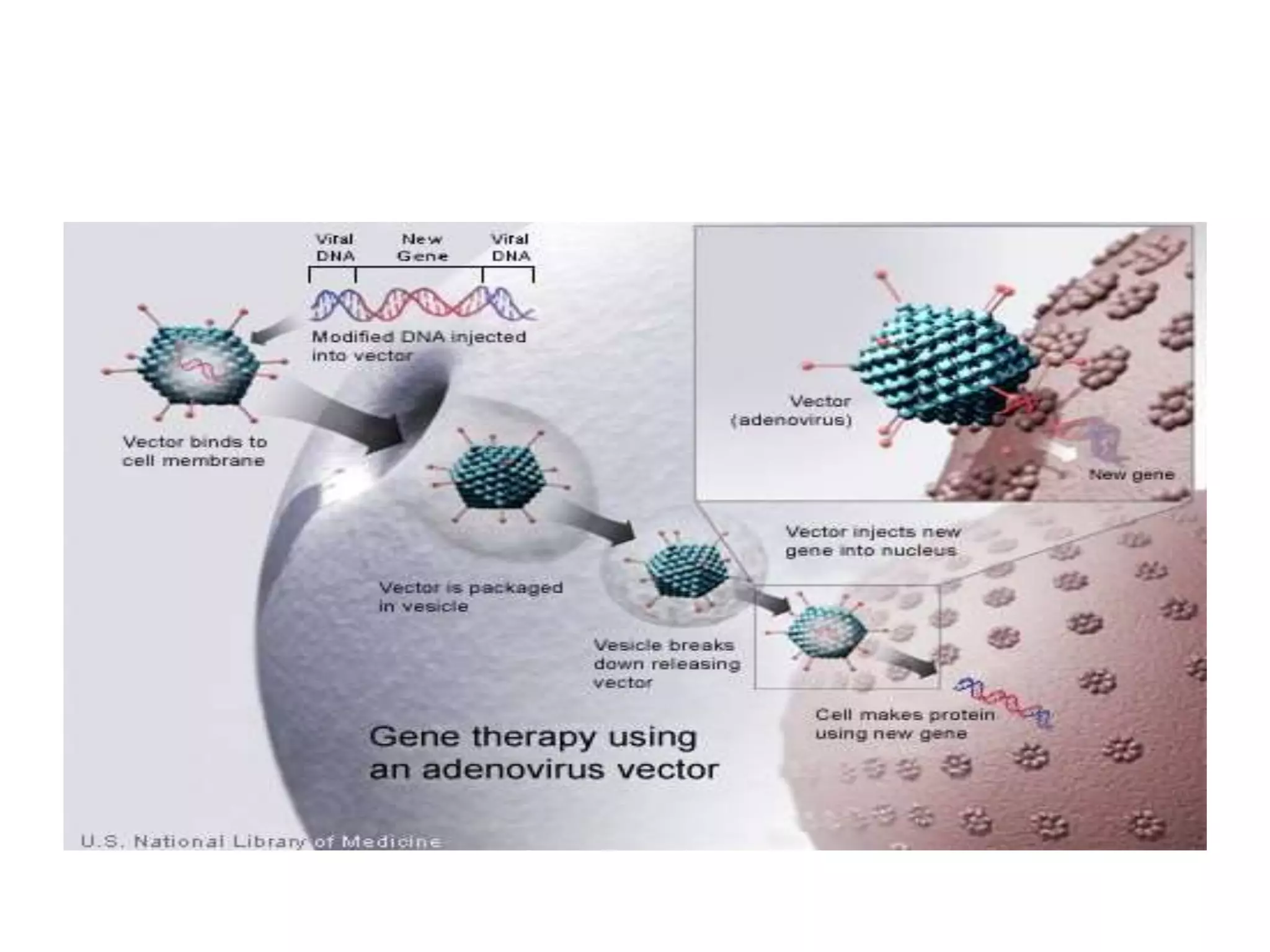
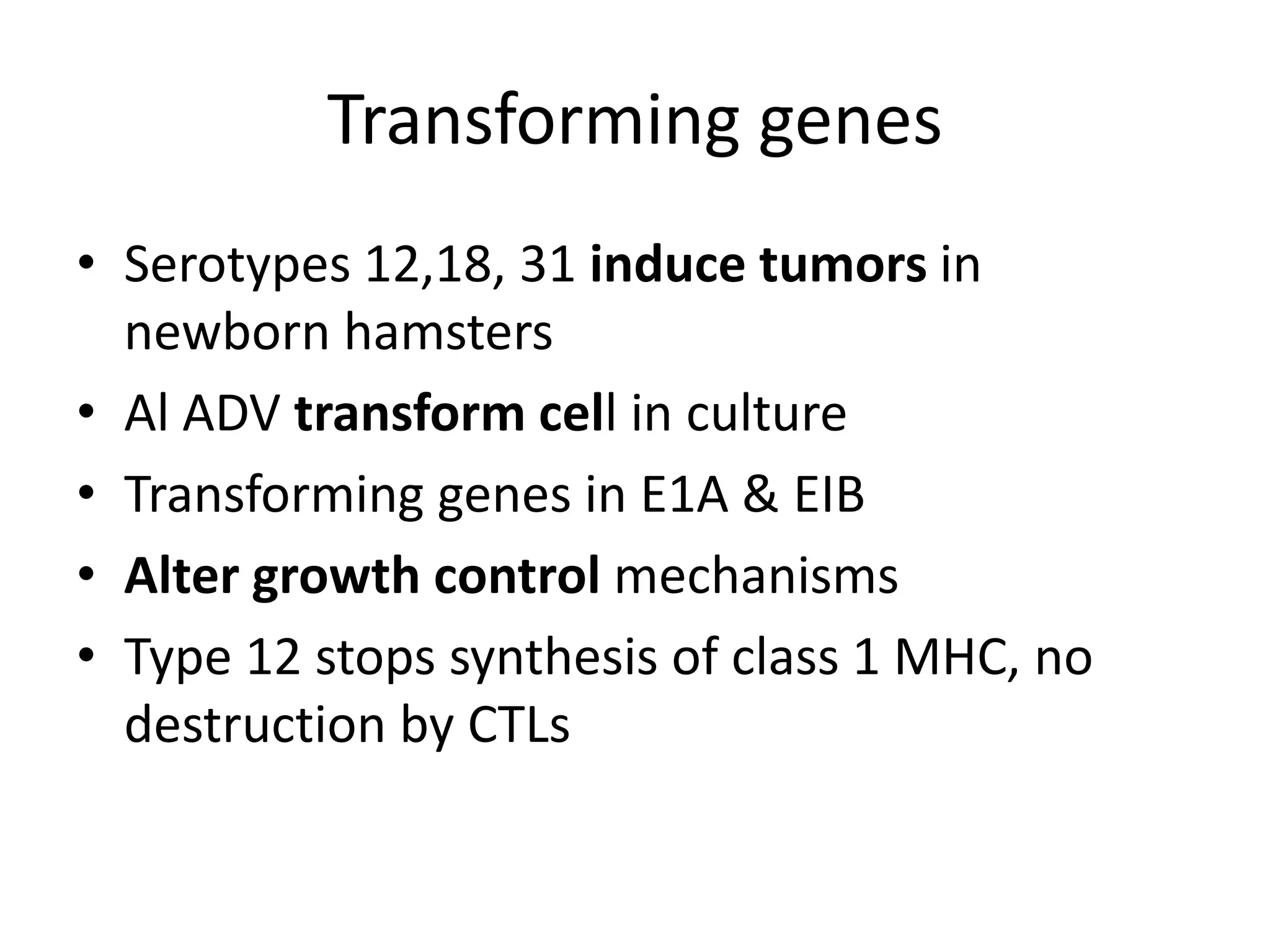
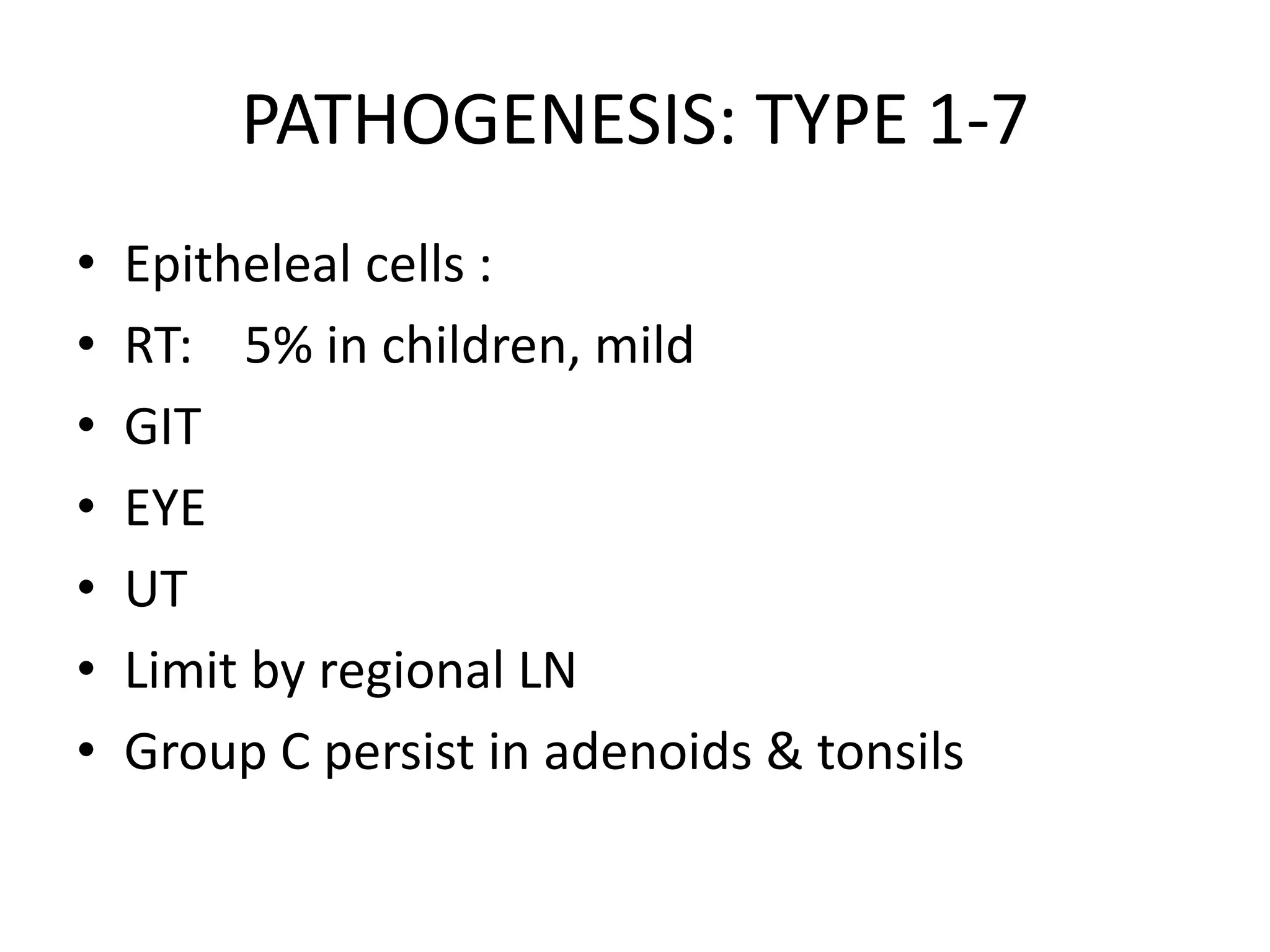
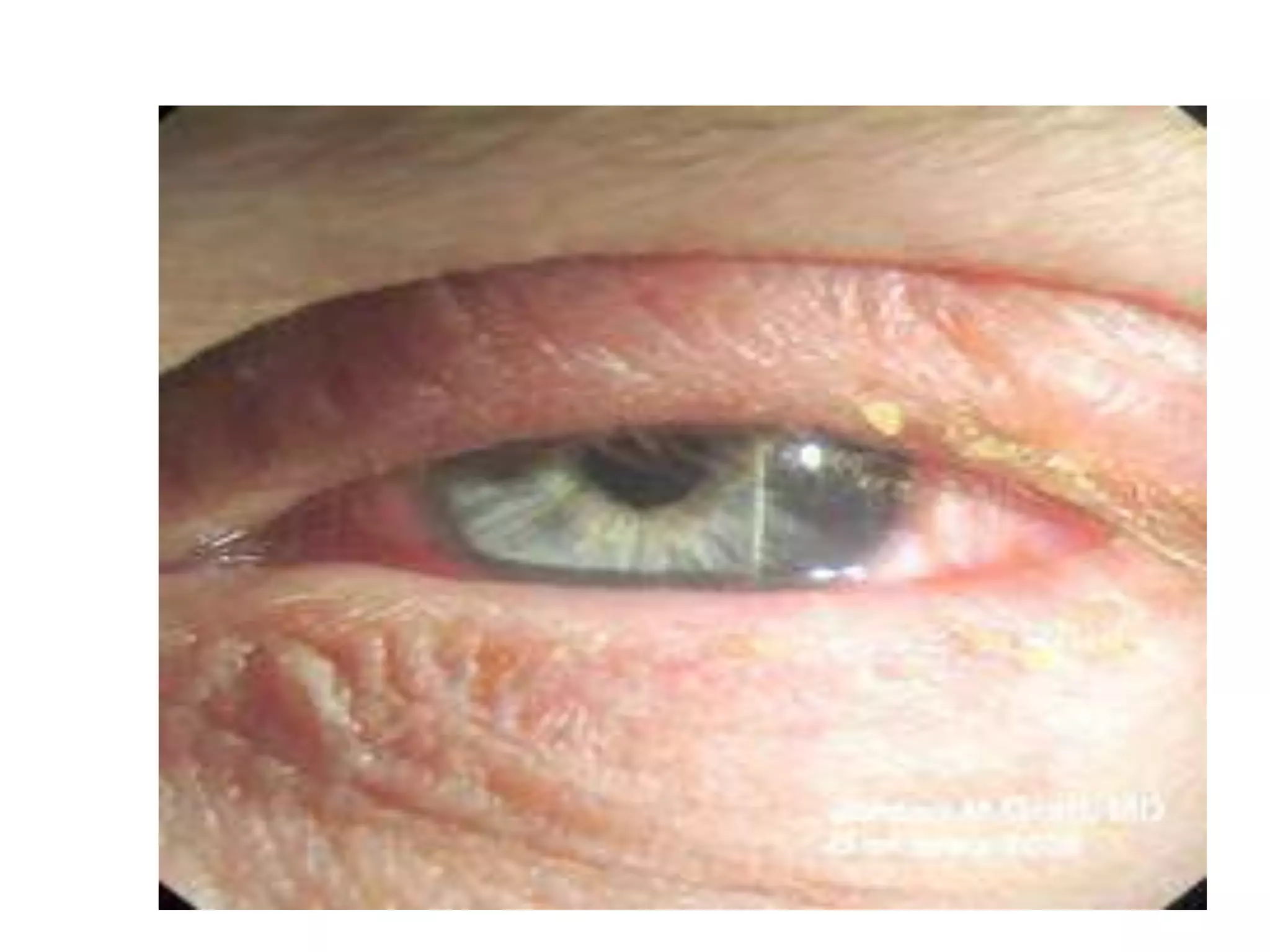
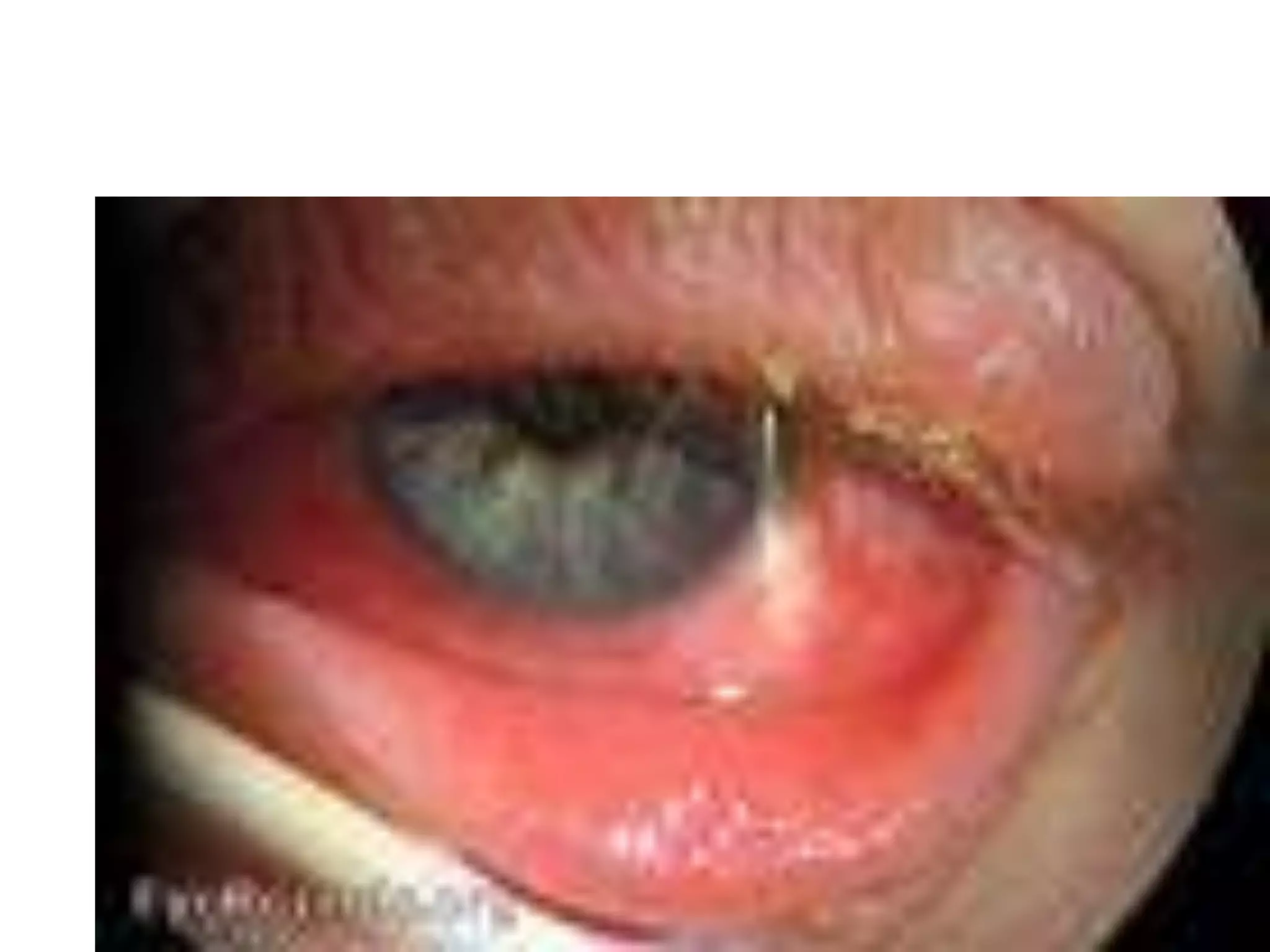
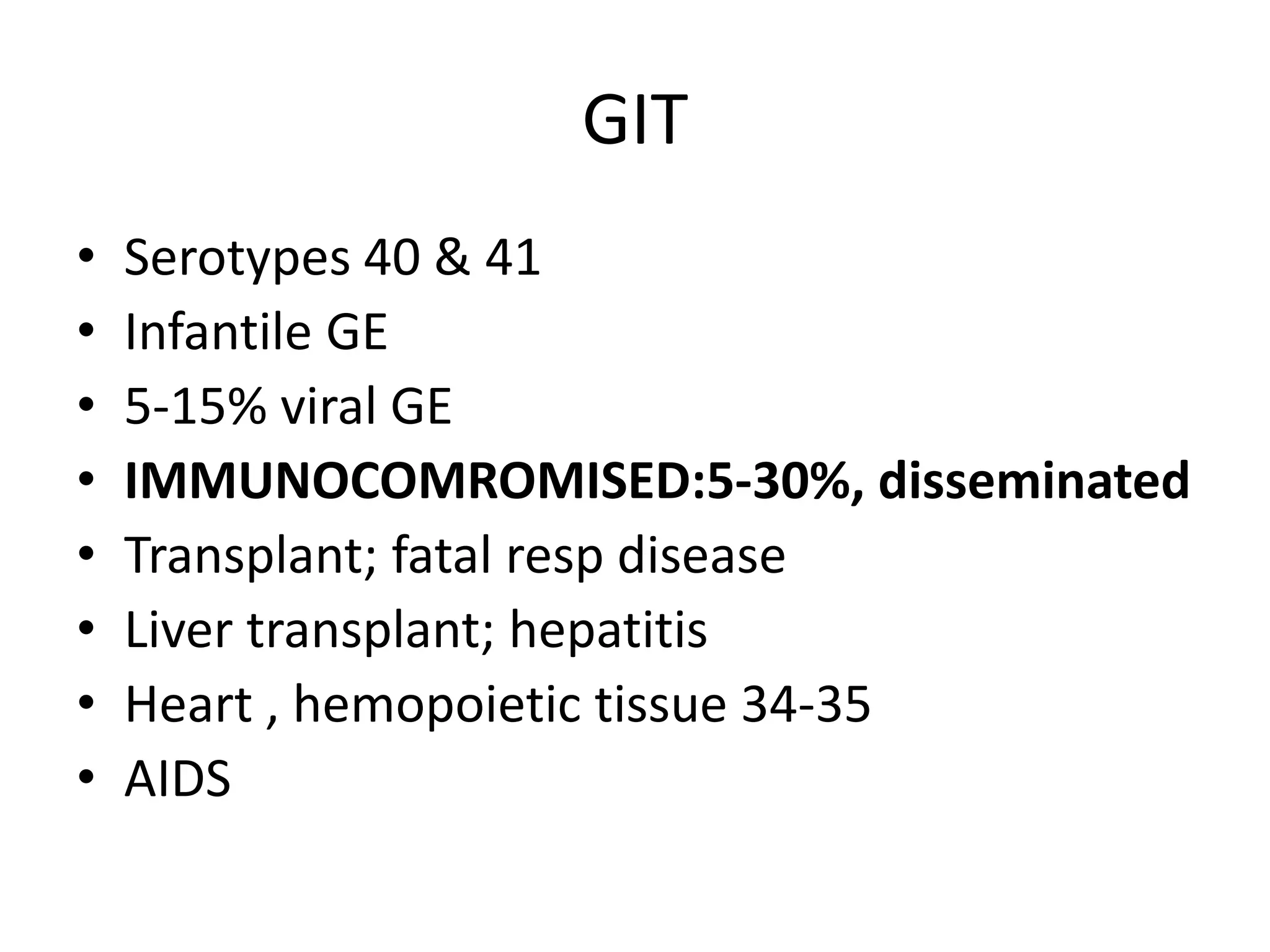
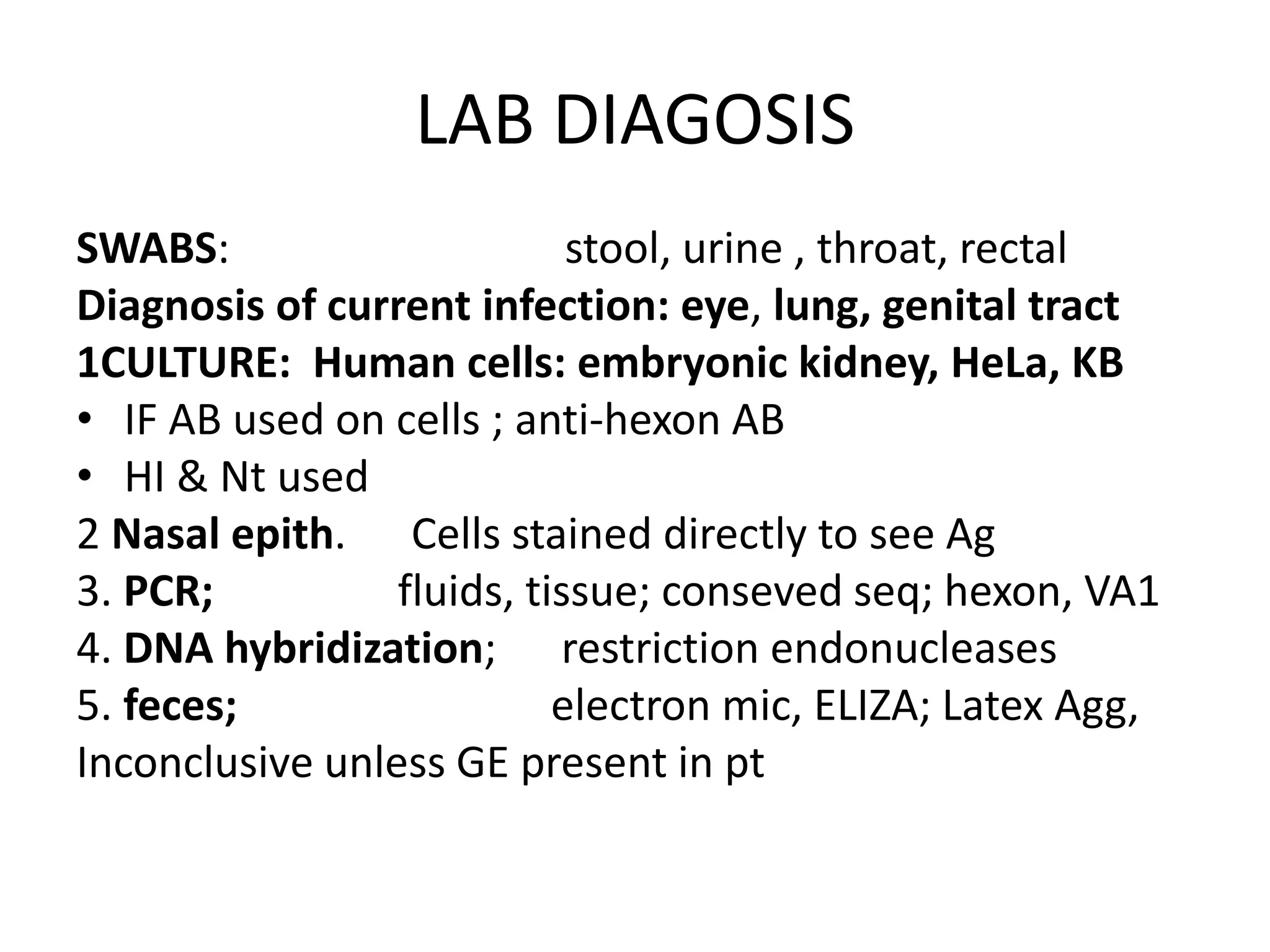
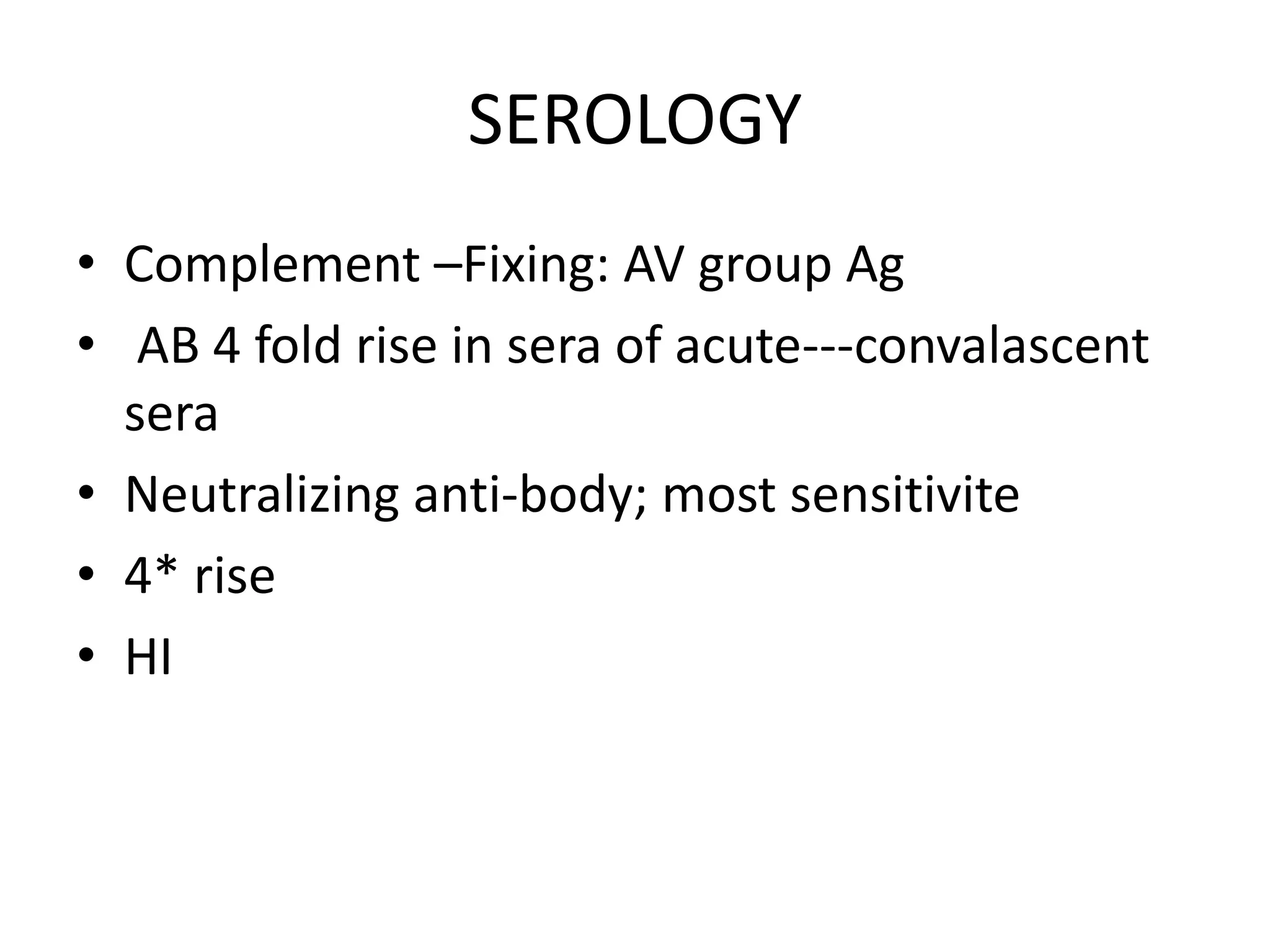
Adenoviruses are a group of viruses that can infect the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, and eyes. There are 51 known serotypes of human adenoviruses. They are non-enveloped viruses that contain double-stranded DNA. Adenoviruses can cause respiratory illness in children and military recruits, gastroenteritis in infants, and epidemic keratoconjunctivitis in adults. Prevention methods include hand washing, disinfection, chlorination, and a live oral vaccine for types 4 and 7. Laboratory diagnosis involves cell culture, PCR, and serology to detect antibodies.

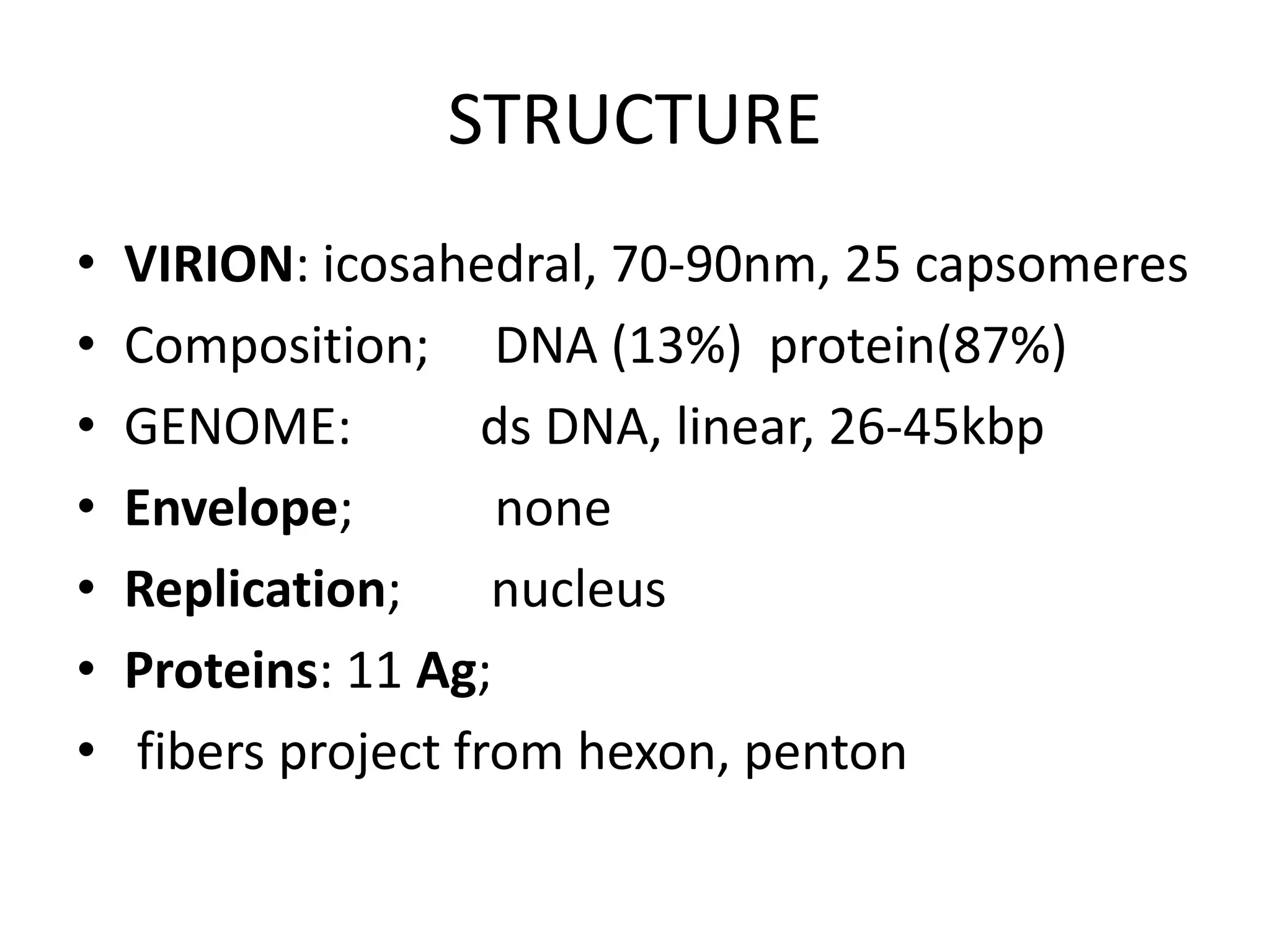
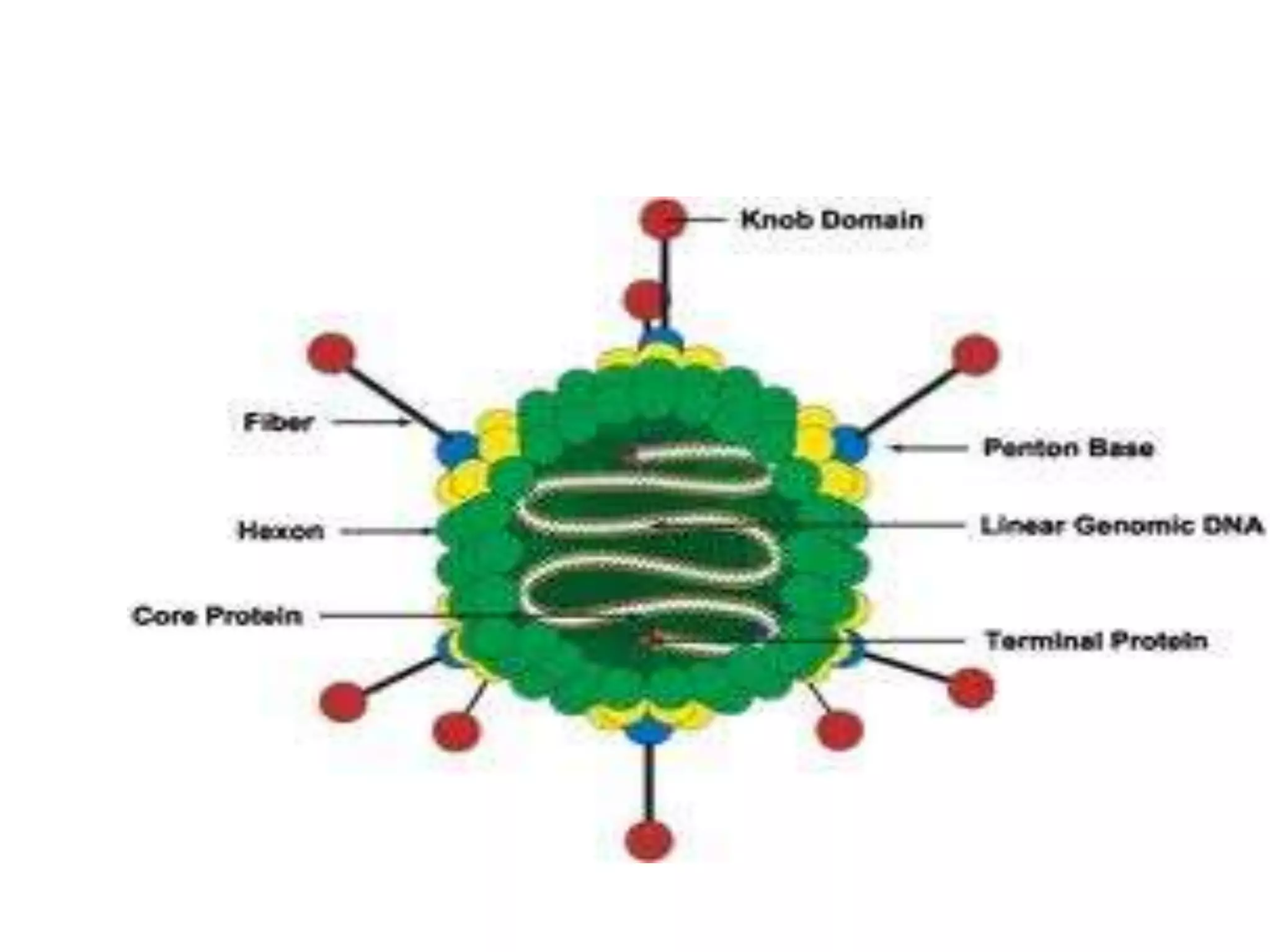
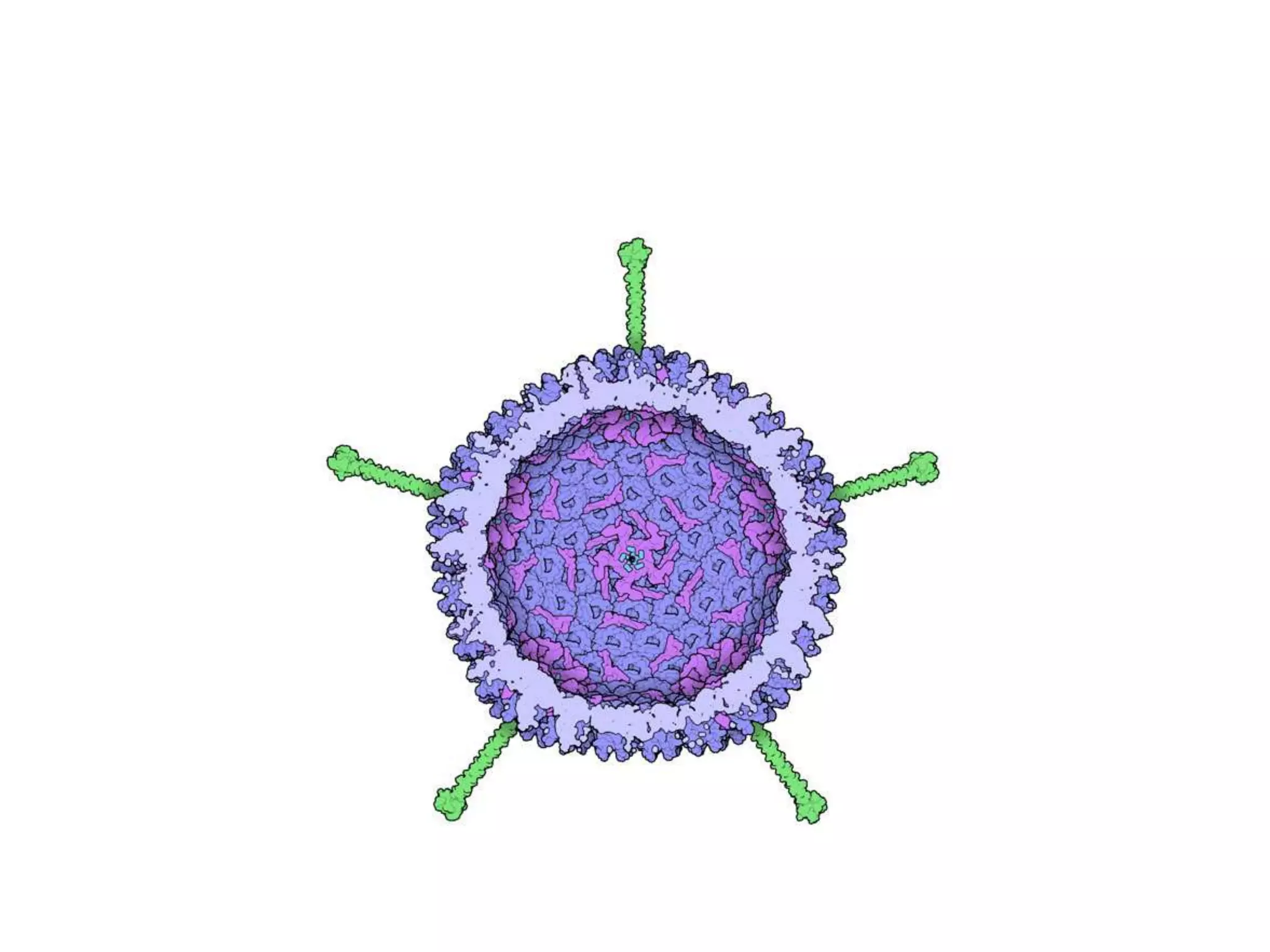
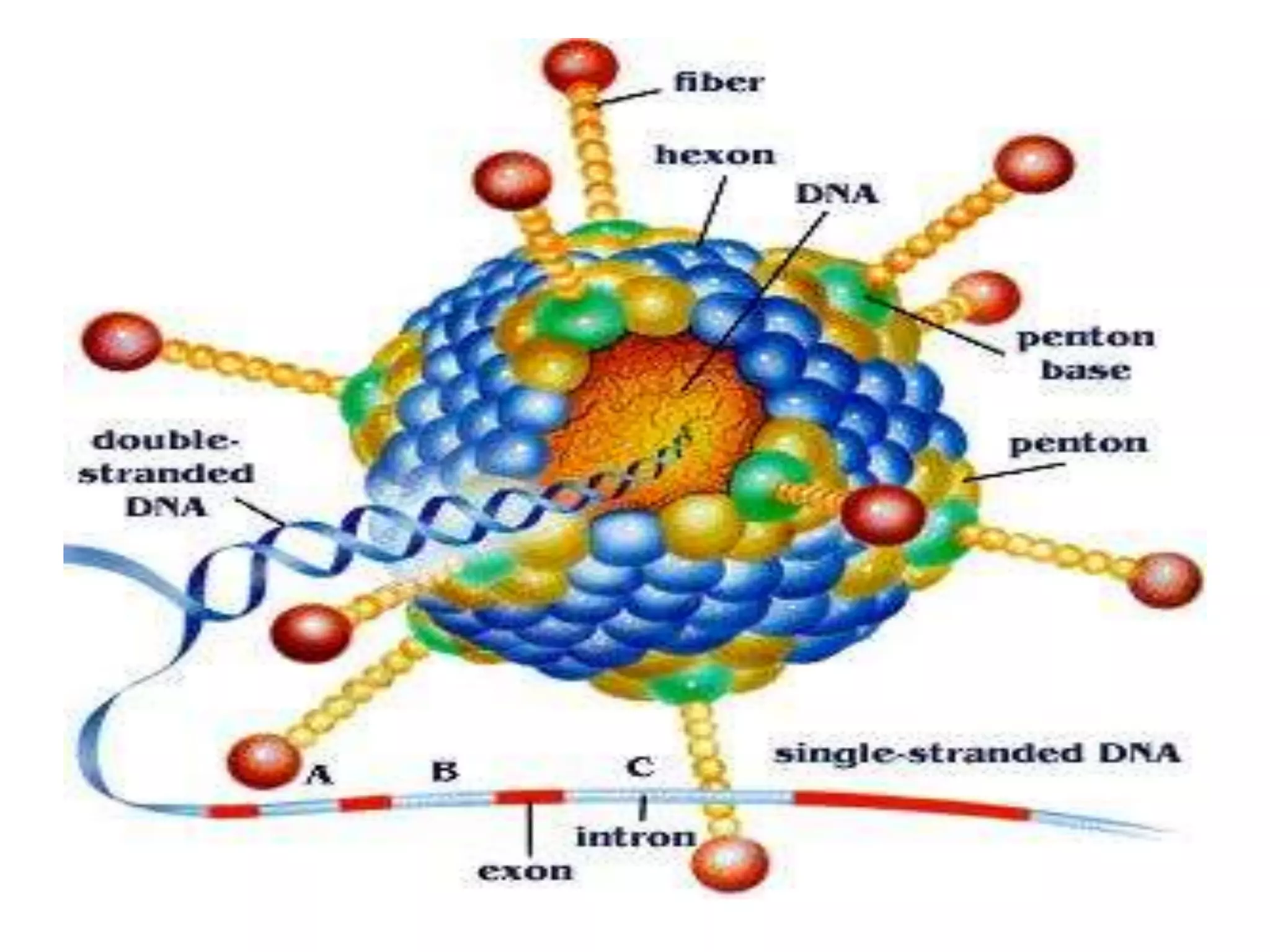







![[Micro] adenoviruses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rqzzph7ktam2nsjysnxg-signature-2127a2ca5368c7fdfd023e8d90dde3fc0b9fe7d91346a4189562c9f63dc0d19d-poli-150819190753-lva1-app6891/75/Micro-adenoviruses-30-2048.jpg)
![[Micro] adenoviruses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rqzzph7ktam2nsjysnxg-signature-2127a2ca5368c7fdfd023e8d90dde3fc0b9fe7d91346a4189562c9f63dc0d19d-poli-150819190753-lva1-app6891/75/Micro-adenoviruses-31-2048.jpg)
![[Micro] adenoviruses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rqzzph7ktam2nsjysnxg-signature-2127a2ca5368c7fdfd023e8d90dde3fc0b9fe7d91346a4189562c9f63dc0d19d-poli-150819190753-lva1-app6891/75/Micro-adenoviruses-32-2048.jpg)