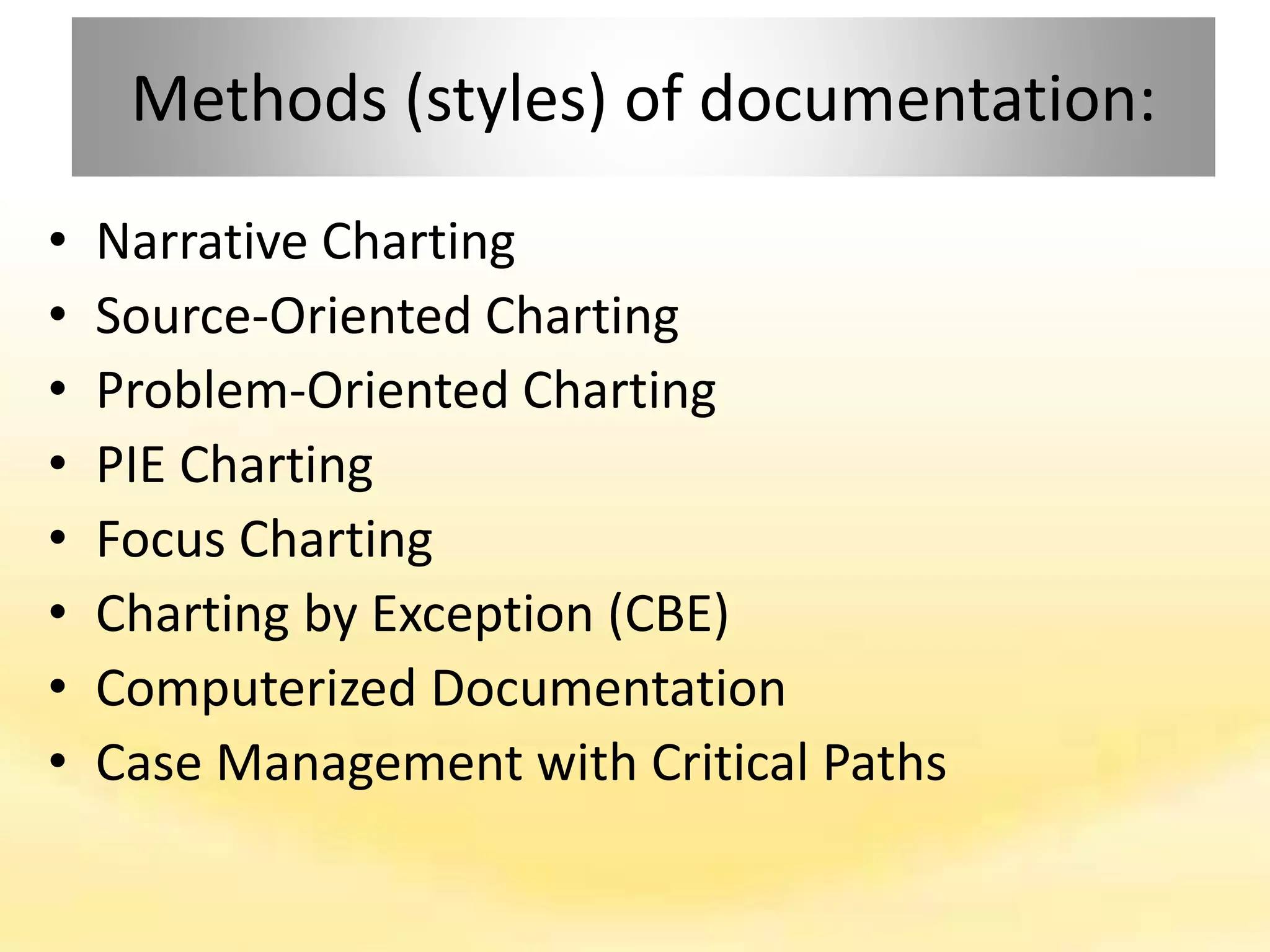
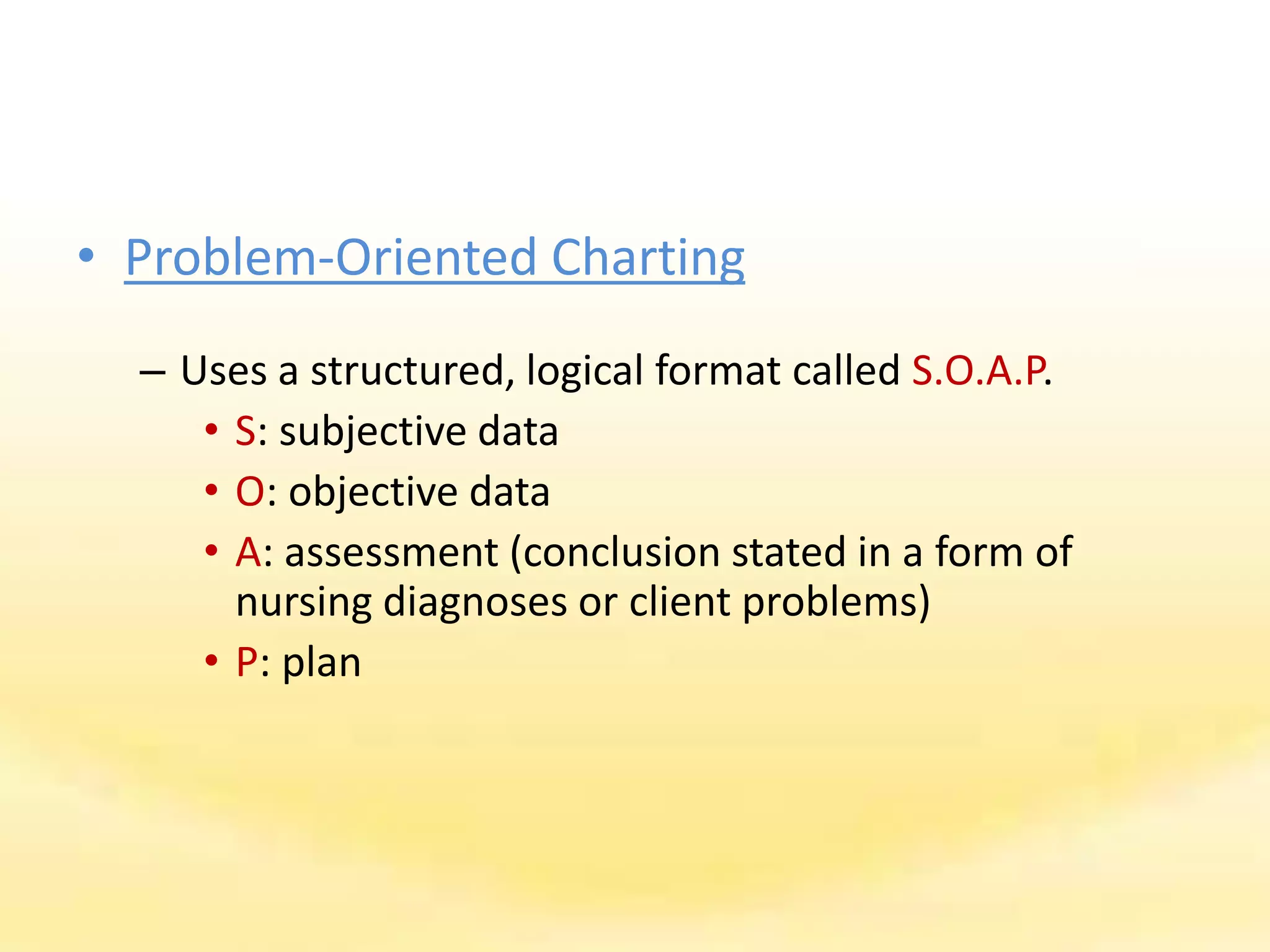
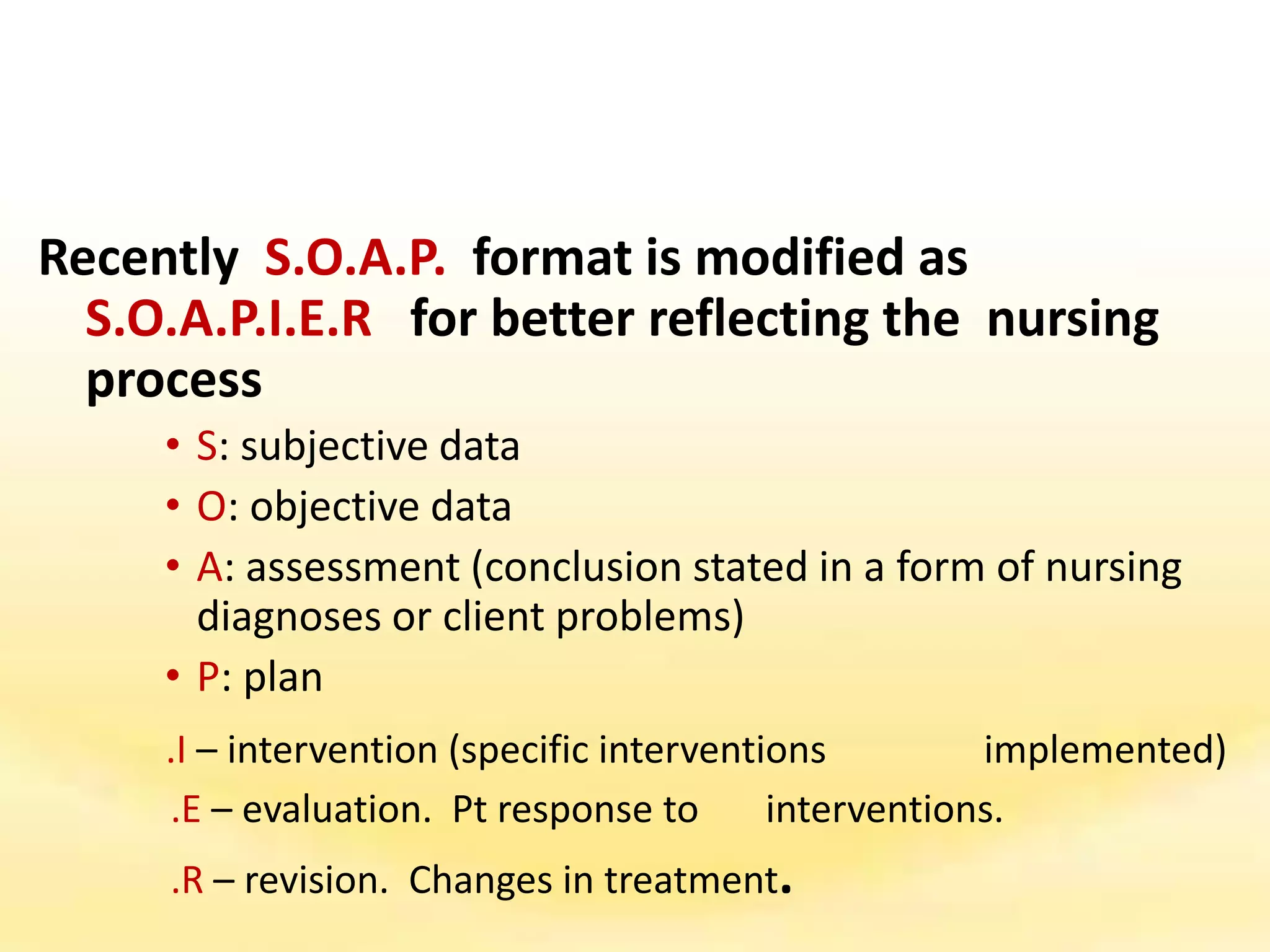
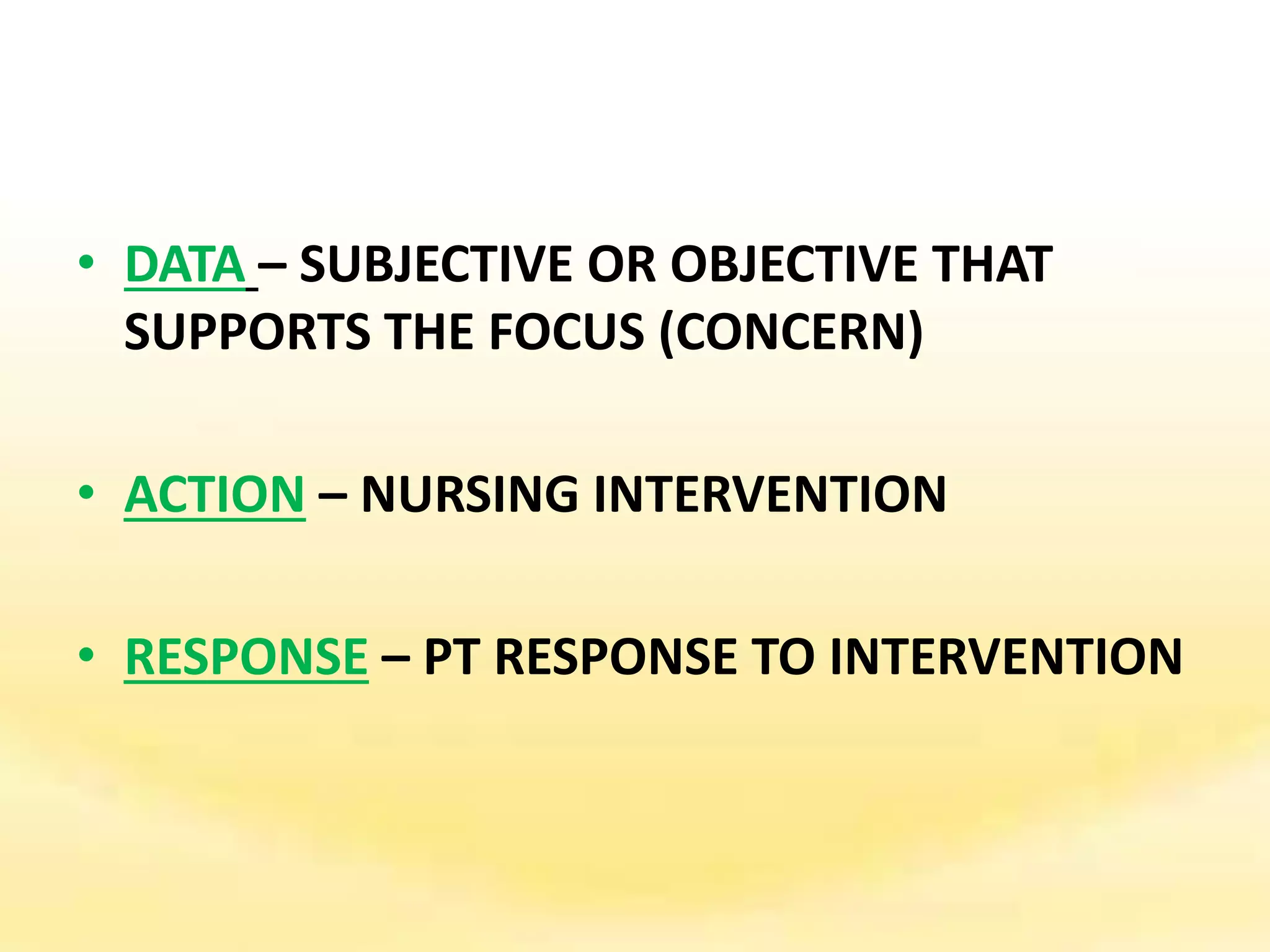
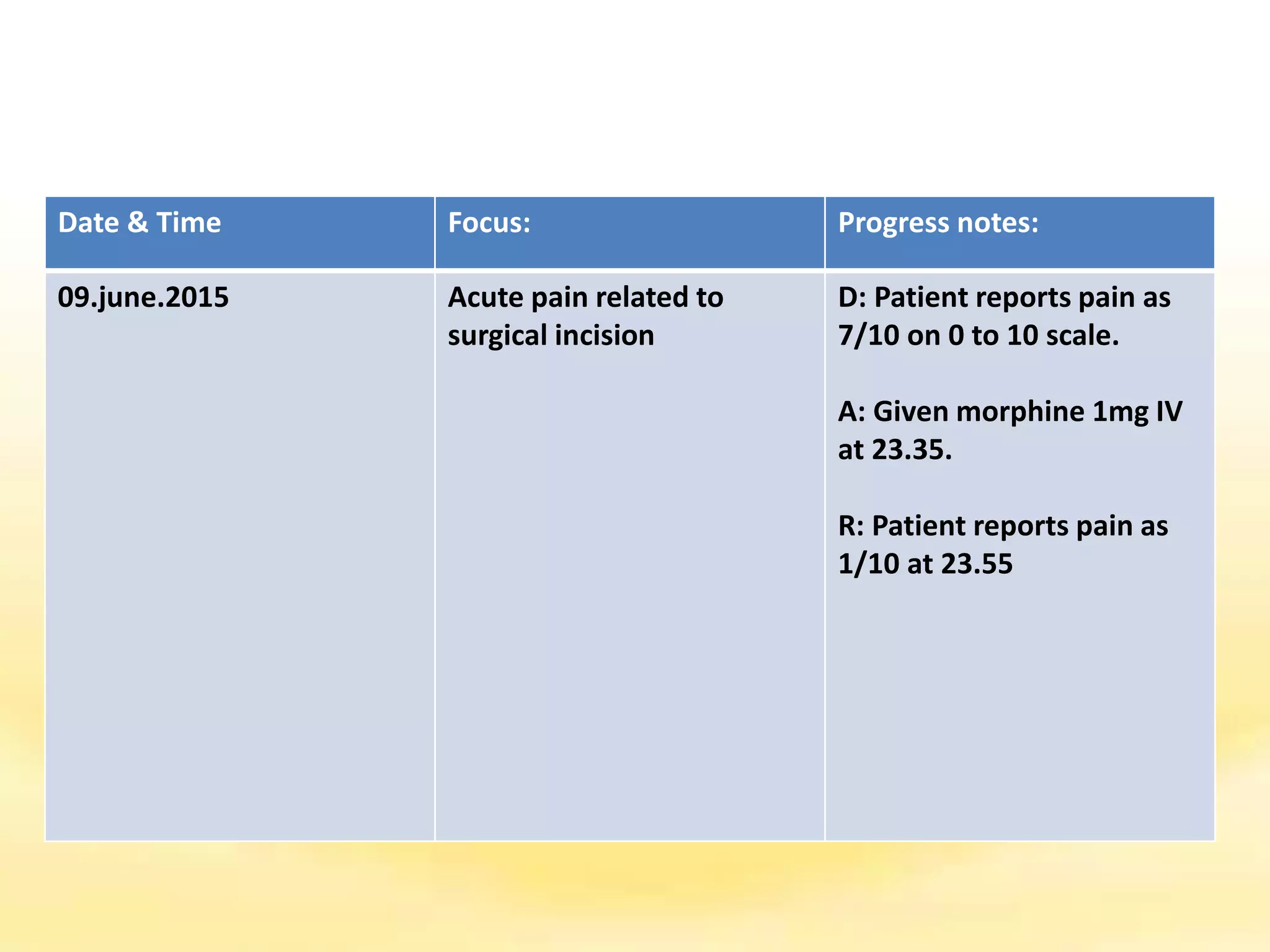
There are several documentation systems used in healthcare to record patient data, either electronically or on paper. Some common systems include narrative charting, source-oriented charting, problem-oriented charting using the SOAP format, PIE charting, focus charting, charting by exception, computerized documentation, and case management using critical paths. Problem-oriented charting using the SOAP format is a structured approach that documents subjective data, objective data, assessment, and plan.