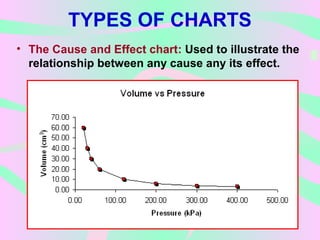
This document discusses non-projected audiovisual aids. It defines audiovisual aids as tools that stimulate learning through sight and sound. Non-projected aids include charts, diagrams, posters, flashcards, graphs, maps, cartoons, newspapers, comic strips, puppets, display boards, and models. Various types of each are described, such as bar graphs, pie charts, political maps, and solid models. Examples and uses of different non-projected audiovisual aids are provided.